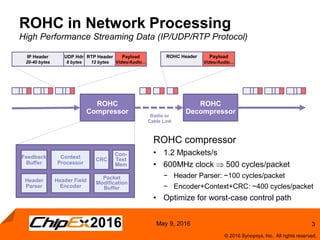
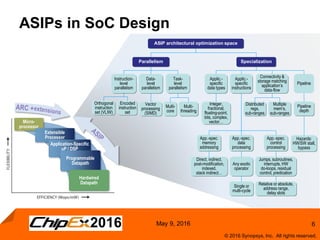
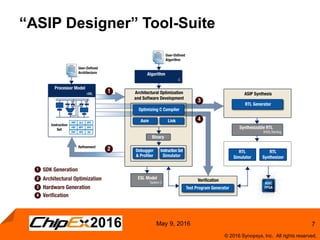
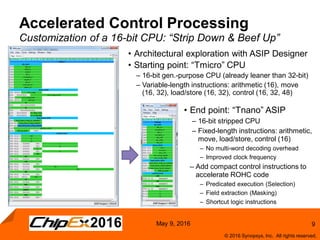
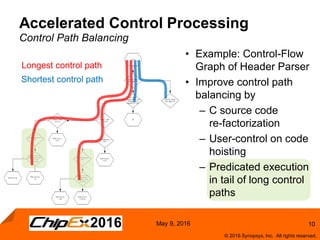
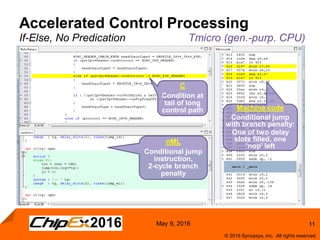
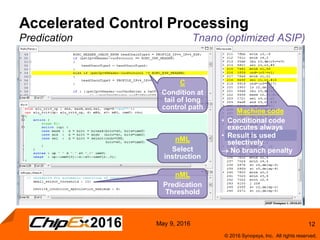
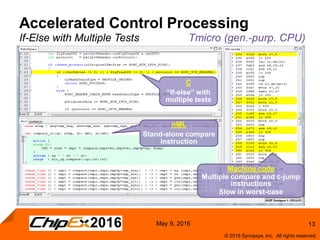
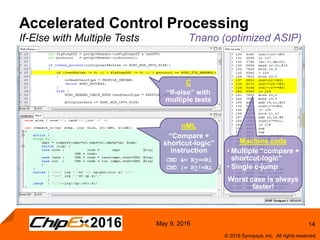
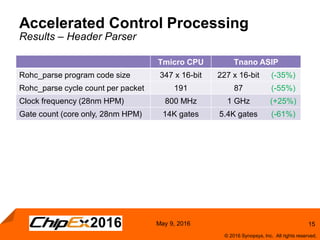
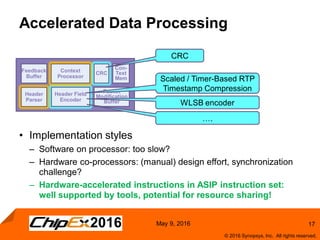
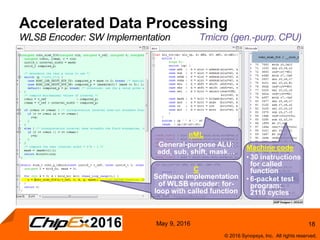
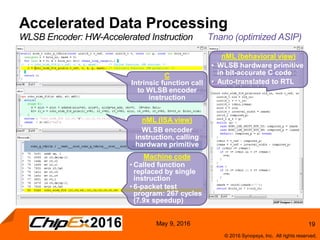
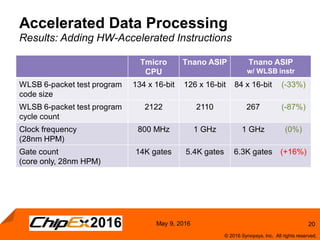
This document discusses using an application-specific processor (ASIP) to accelerate Robust Header Compression (ROHC). It describes how the ASIP methodology was used to design a customized processor that significantly improved performance over a general purpose CPU. The ASIP achieved up to 87% faster cycle counts and up to 7.9x speedup for specific data processing compared to software implementations. In conclusion, the ASIP approach enabled both control and data processing to be accelerated like fixed hardware, but with the flexibility of a programmable processor.