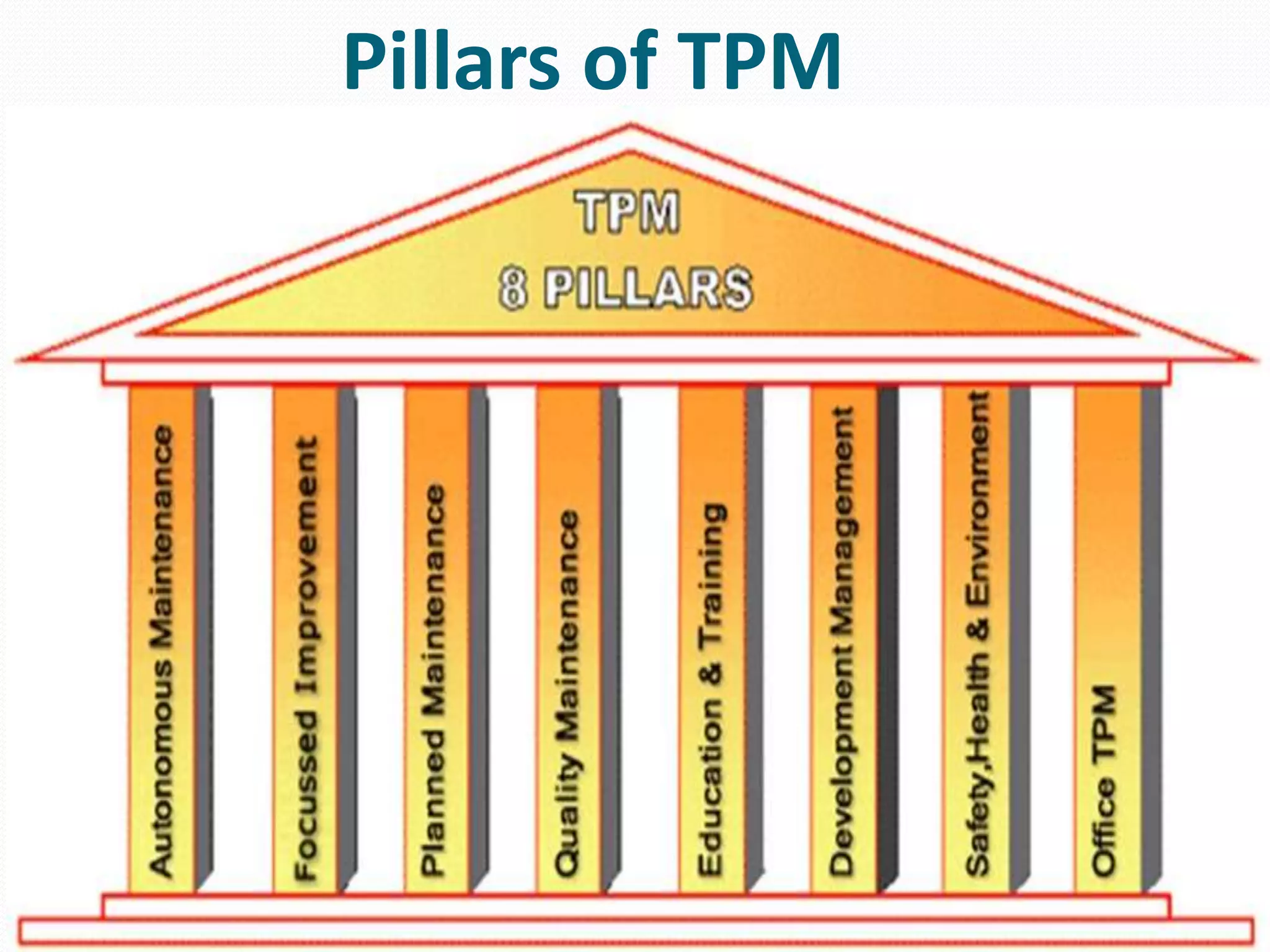
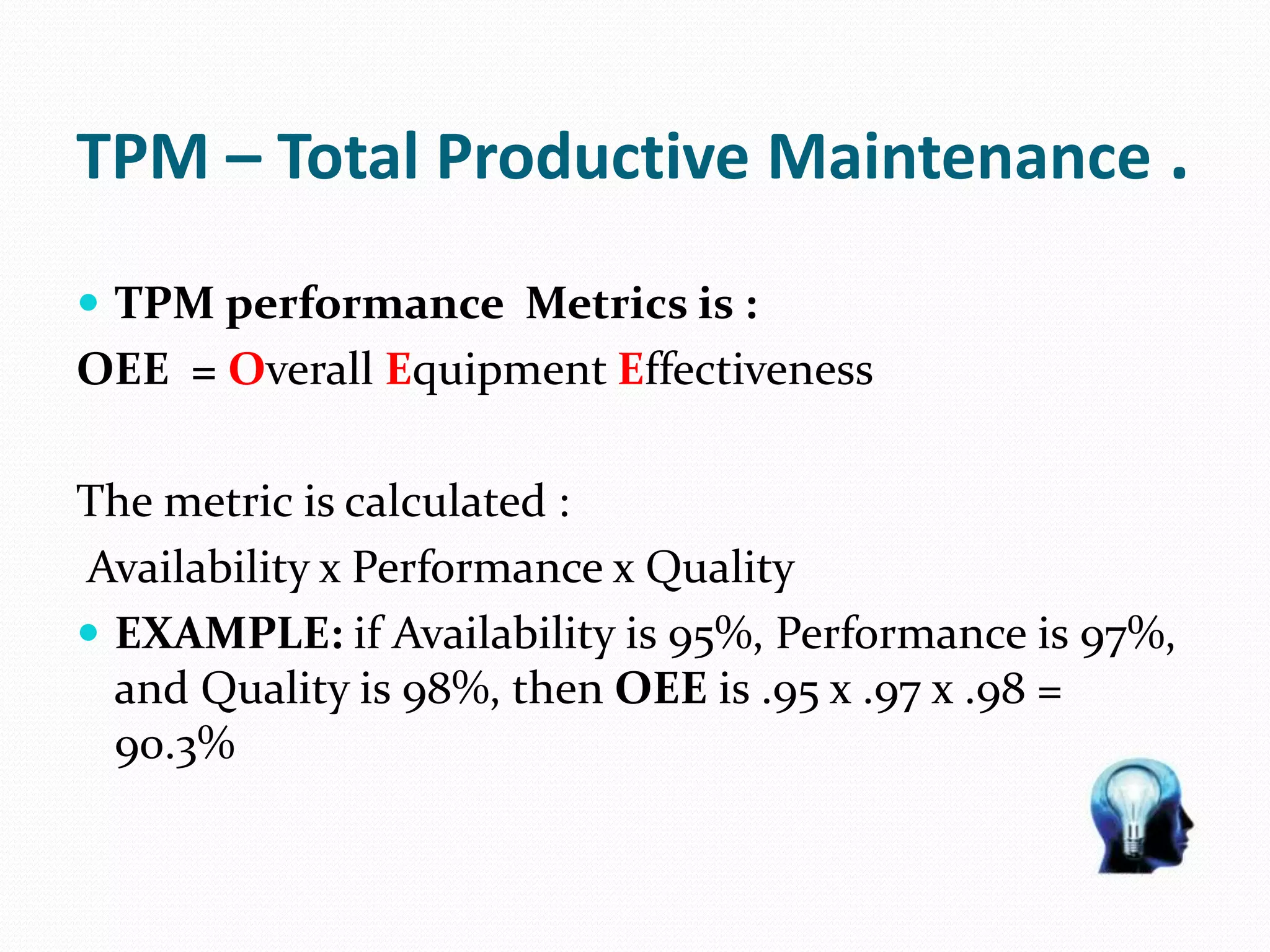
TPM stands for Total Productive Maintenance and aims to improve productivity through more reliable and less wasteful processes. It focuses on preventative maintenance to keep equipment in good working condition through techniques like autonomous maintenance, where operators are trained to monitor equipment and address early issues. TPM has goals of zero defects, failures, and accidents and uses metrics like Overall Equipment Effectiveness to measure performance. It identifies sources of waste and advocates for 5S principles of organization to establish an efficient workplace. Regular use of TPM results in better equipment condition, fewer breakdowns, reduced spare parts needs, and improved production rates.