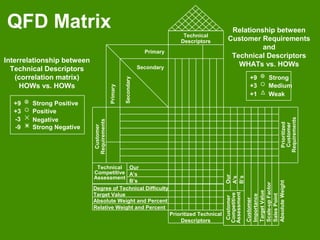
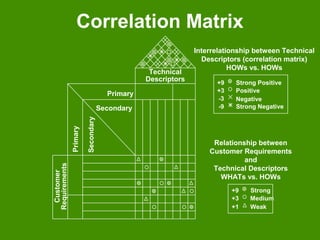
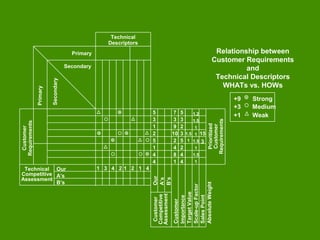
This document provides an overview of Quality Function Deployment (QFD). It describes key aspects of QFD including the benefits, the voice of the customer, building a house of quality, prioritizing customer requirements and technical descriptors, and the QFD process. QFD is a structured approach to defining customer needs and translating them into design requirements and product characteristics to help maximize customer satisfaction.