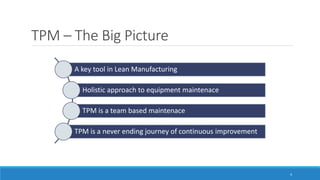
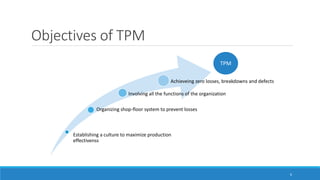
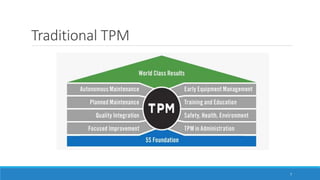
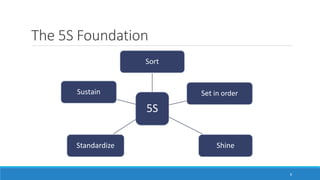
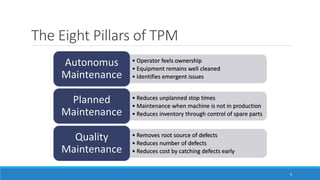
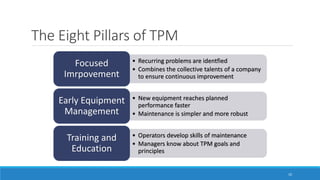
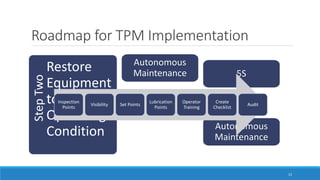
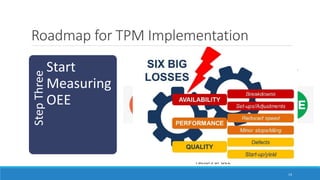
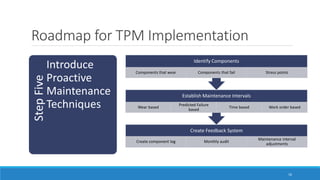
This document outlines Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) as a key strategy in lean manufacturing, emphasizing employee involvement and proactive maintenance to improve production efficiency and reduce equipment-related issues. It details the five pillars of TPM, the benefits of its implementation, and provides a roadmap for incorporating TPM within an organization. Successful TPM implementation can lead to significant increases in equipment uptime, reduced defects, and overall cost savings.