The document discusses the Data Encryption Standard (DES), including:
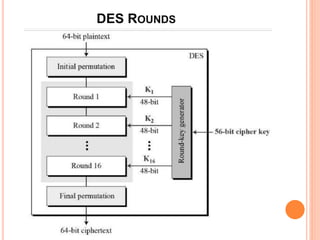
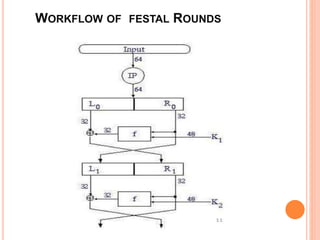
- DES is a block cipher that encrypts data in 64-bit blocks using a 56-bit key and 16 rounds of encryption.
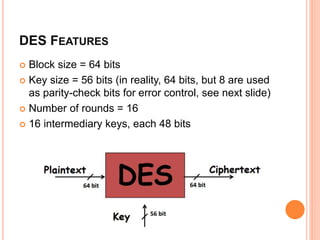
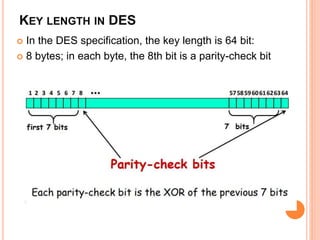
- DES has a block size of 64 bits, a key size of 56 bits (though the key specification is 64 bits with 8 bits used for error checking), and uses 16 intermediate 48-bit keys over its 16 rounds.
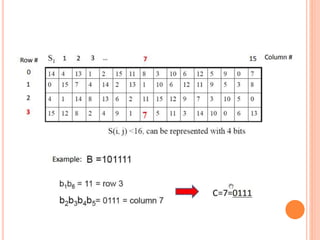
- The DES encryption process uses substitution boxes (S-boxes) to encrypt each block, and has 4 known weak keys that should be avoided during key generation.