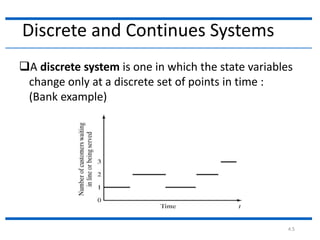
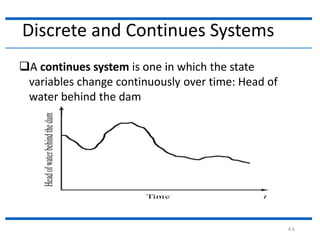
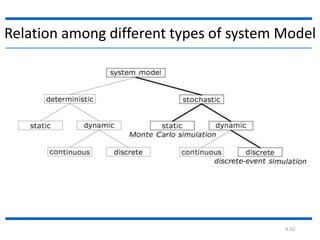
This document discusses different types of systems and system simulations. It defines a system as a group of interacting objects working toward a common purpose. A system is affected by its environment. A system can be discrete, meaning its state variables change at discrete points in time, or continuous, meaning its state variables change continuously over time. The document also describes different types of system models, including mathematical, physical, static vs. dynamic, deterministic vs. stochastic, and discrete vs. continuous models. The purpose is to understand how to choose the appropriate type of simulation based on the system being modeled.