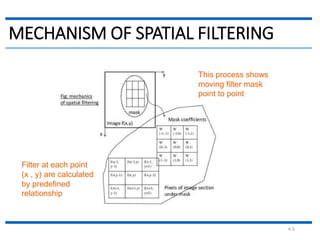
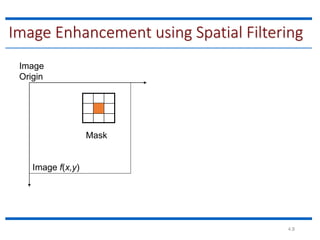
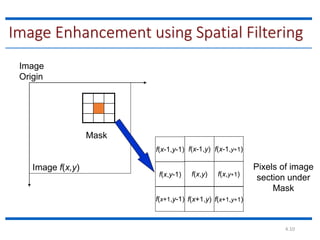
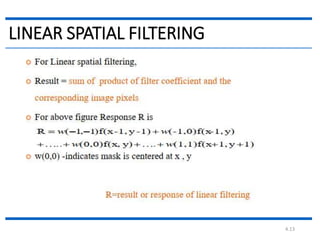
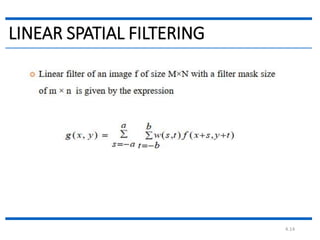
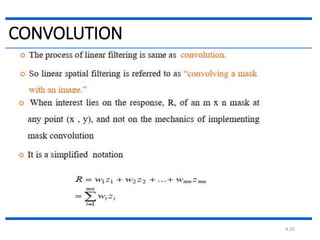
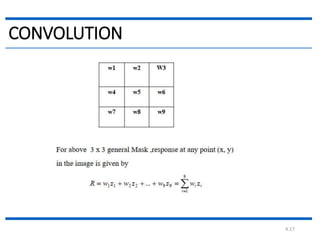
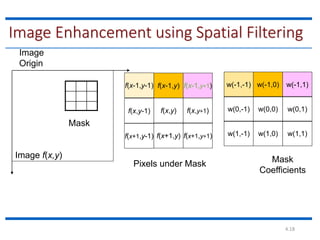
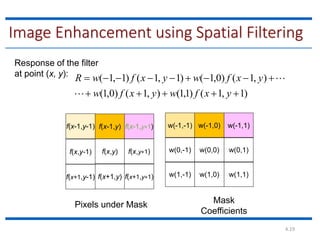
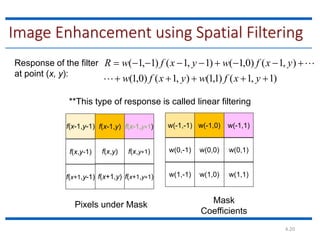
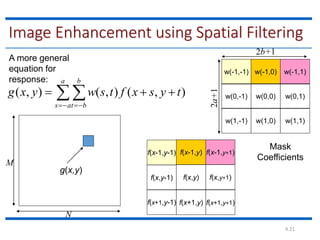
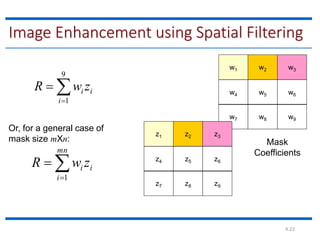
This document discusses spatial filtering for image enhancement. It begins by introducing filters and explaining that filtering can modify or enhance images by highlighting certain features or removing others. It then explains that spatial filtering involves applying a filter mask to an image point by point. The mechanism of spatial filtering is described as calculating filter responses at each point (x,y) using a predefined relationship between pixels under the mask and mask coefficients. Linear spatial filtering is discussed where each pixel is replaced by a constant value. Convolution is introduced as the process of applying filters to an image. The approaches and types of spatial filtering are outlined. In summary, spatial filtering uses a mask that is applied point by point to an image to calculate new pixel values using neighboring pixel values and