Embed presentation
Downloaded 20 times



![4.10
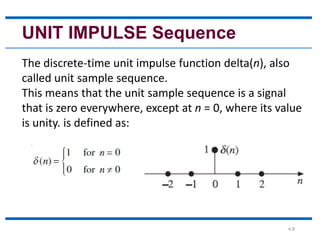
Real Exponential Sequence
The discrete-time real exponential sequence 𝑎𝑛is
defined as:
• a > 1, the sequence grows exponentially as
shown in Figure (a).
• 0 < a < 1, the sequence decays exponentially
as shown in Figure (b).
• a < 0, the sequence takes alternating signs as
shown in Figure [(c) and (d)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-210718050208/85/1-elementary-signals-10-320.jpg)

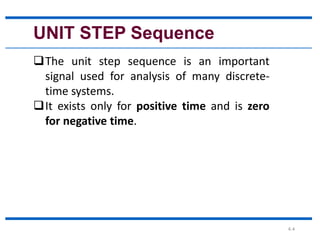
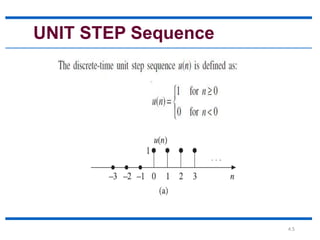
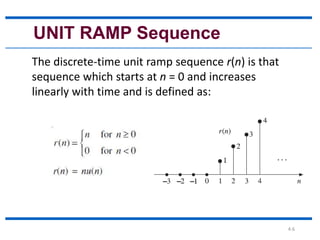
This document discusses elementary signals that are basic building blocks for more complex signals in signal and systems analysis. It identifies six types of elementary signals: unit step, unit ramp, unit parabolic, unit impulse, sinusoidal, and real exponential sequences. Each signal type is defined, with the unit step existing only for positive time, the unit ramp increasing linearly over time, the unit parabolic following a quadratic function, and the unit impulse being equal to one only at time zero. The document also notes that sinusoidal sequences can be periodic or not depending on frequency, and that real exponential sequences grow, decay, or alternate based on their constant value.









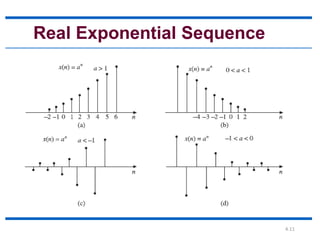
![4.10
Real Exponential Sequence
The discrete-time real exponential sequence 𝑎𝑛is
defined as:
• a > 1, the sequence grows exponentially as
shown in Figure (a).
• 0 < a < 1, the sequence decays exponentially
as shown in Figure (b).
• a < 0, the sequence takes alternating signs as
shown in Figure [(c) and (d)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-210718050208/85/1-elementary-signals-10-320.jpg)

