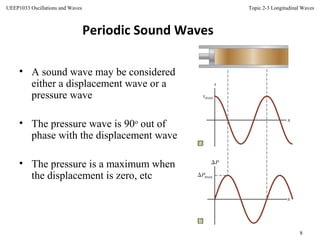
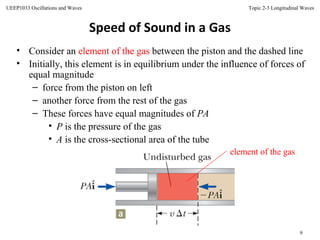
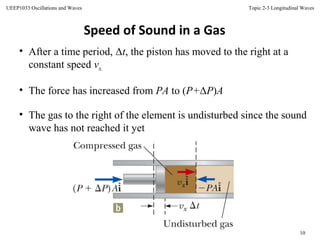
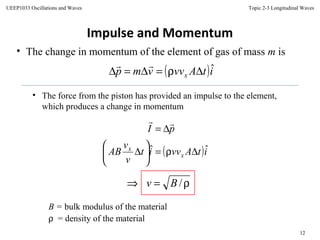
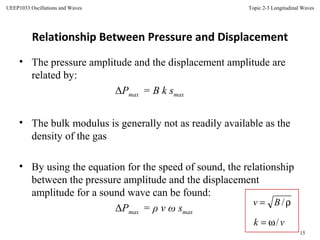
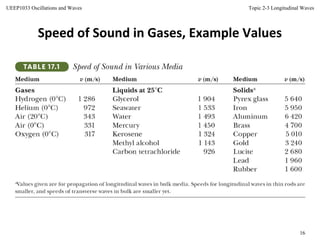
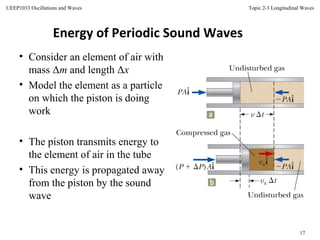
This document discusses longitudinal waves, in which particle motion is parallel to the direction of wave propagation. Longitudinal waves include sound waves, which can propagate through gases, liquids, and solids. The document describes how a periodic longitudinal wave can be produced by a piston moving with simple harmonic motion, causing variations in pressure and density. It defines key characteristics of longitudinal waves like displacement, pressure variation, wavelength, frequency, speed and relates these to properties of the medium like bulk modulus and density. The speed of sound, power, intensity, and the inverse square law for intensity from a point source are also covered.











![Topic 2-3 Longitudinal Waves
19
UEEP1033 Oscillations and Waves
)(sin
)]sin()][sin([
)]cos([)]sin([
ˆ)],([ˆ]),([Power
22
max
2
maxmax
maxmax
tkxAsv
tkxstkxAsv
tkxs
t
tkxAsv
itxs
t
iAtxP
ω−ωρ=
ω−ωω−ωρ=
ω−
∂
∂
ω−ωρ=
∂
∂
⋅∆=
• Find the time average power is over one period of the oscillation
2
1
2
2sin
2
1
sin
1
)0(sin
1
0
0
2
0
2
=
ω
ω
+=ω=ω− ∫∫
T
TT tt
T
dtt
T
dtt
T
• For any given value of x, which we choose to be x = 0, the average
value of over one period T is:)(sin2
tkx ω−](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic5longitudinalwave-140705124755-phpapp01/85/Topic-5-longitudinal-wave-19-320.jpg)



