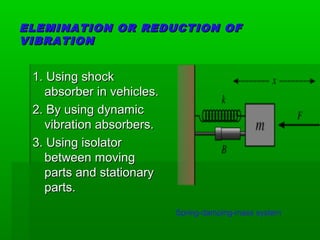
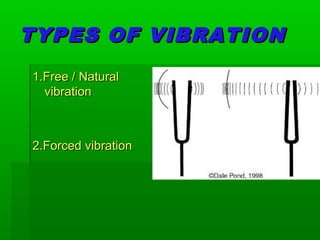
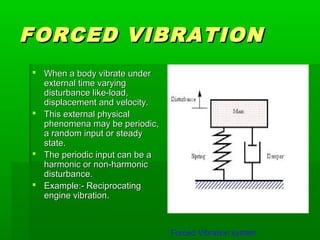
Vibration refers to the oscillatory motion of an object about an equilibrium position. It can be caused by unbalanced forces in machines, earthquakes, or external forces that make a system vibrate. Improper balancing, lack of lubrication, or external loads can lead to harmful vibrations that produce stresses, noise, and damage to machine parts over time. Vibration can be reduced through methods like using shock absorbers, dynamic vibration absorbers, or isolators between moving and stationary parts. There are two main types of vibration: free vibration, which occurs without external forces as a system vibrates at its natural frequency, and forced vibration, where external time-varying forces cause periodic or non-periodic vibration.