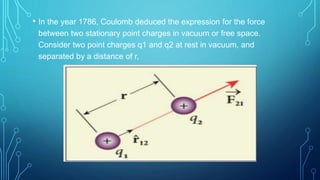
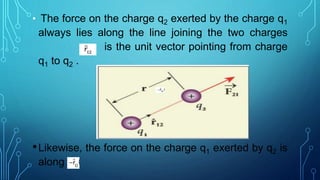
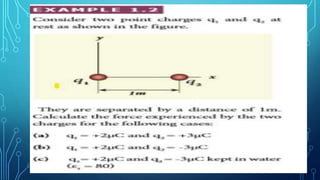
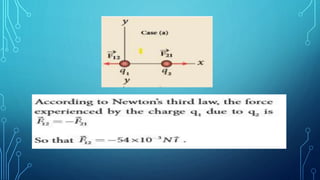
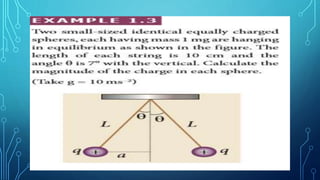
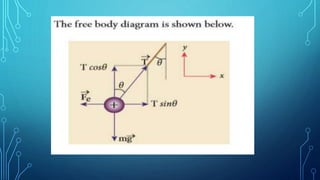
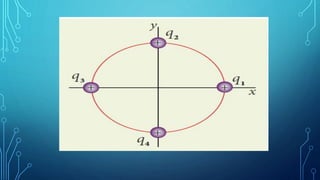
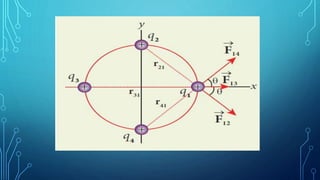
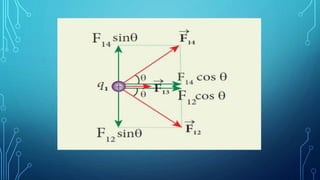
Coulomb's law describes the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges. It states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The law also specifies that the force is along the line joining the two charges. The superposition principle allows calculating the total electrostatic force on a charge from the vector sum of the individual forces exerted by each of the other charges.