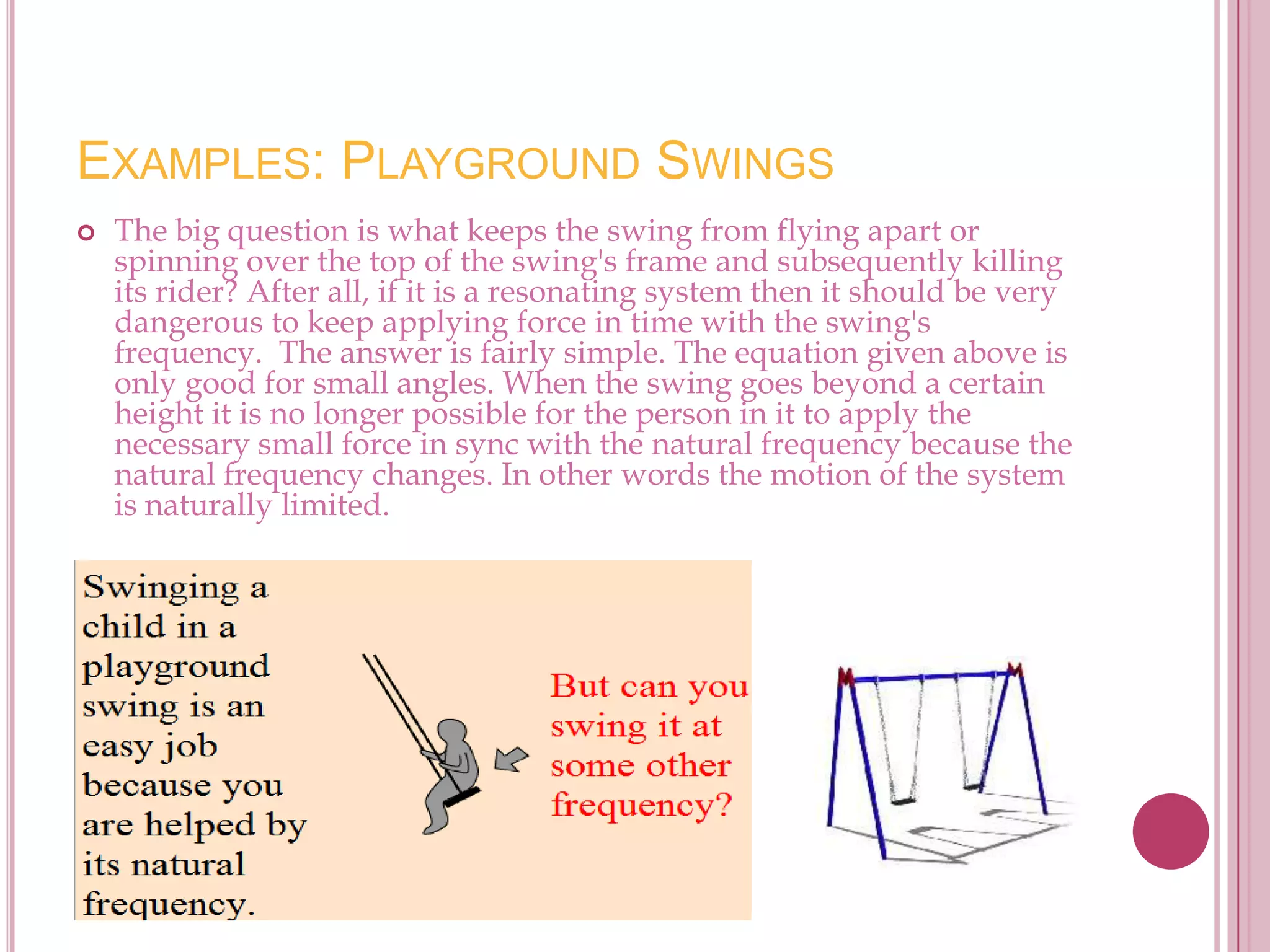
Resonance occurs when an object is driven at its natural frequency, causing oscillations to build up rapidly. There are three conditions for resonance: 1) an object with a natural frequency, 2) a forcing function at the same frequency, and 3) a lack of damping. When these conditions are met, the oscillations reinforce each other and grow larger. Examples of resonance include playground swings, washing machines, opera singers shattering wine glasses, and bridges collapsing from marching soldiers.