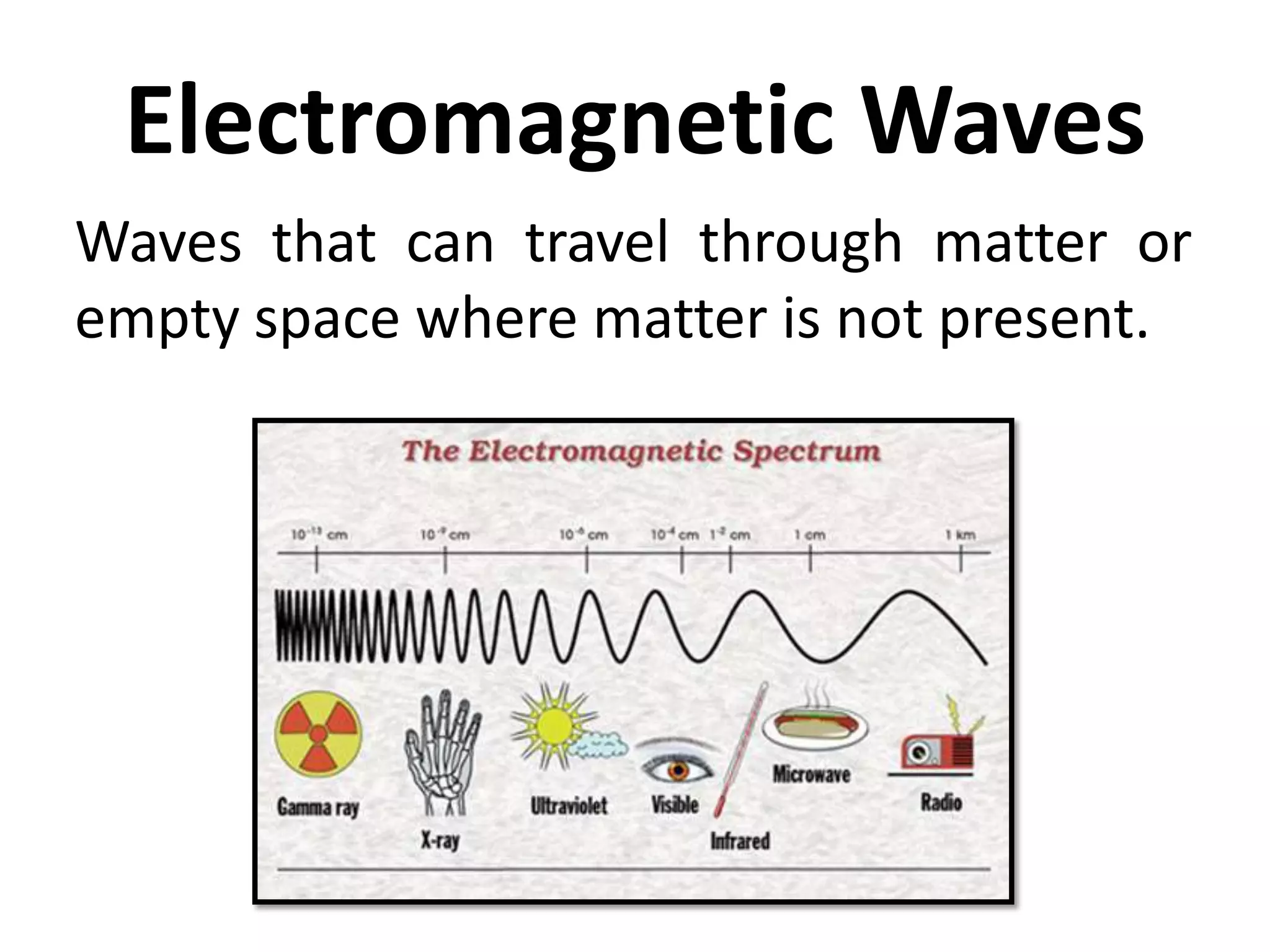
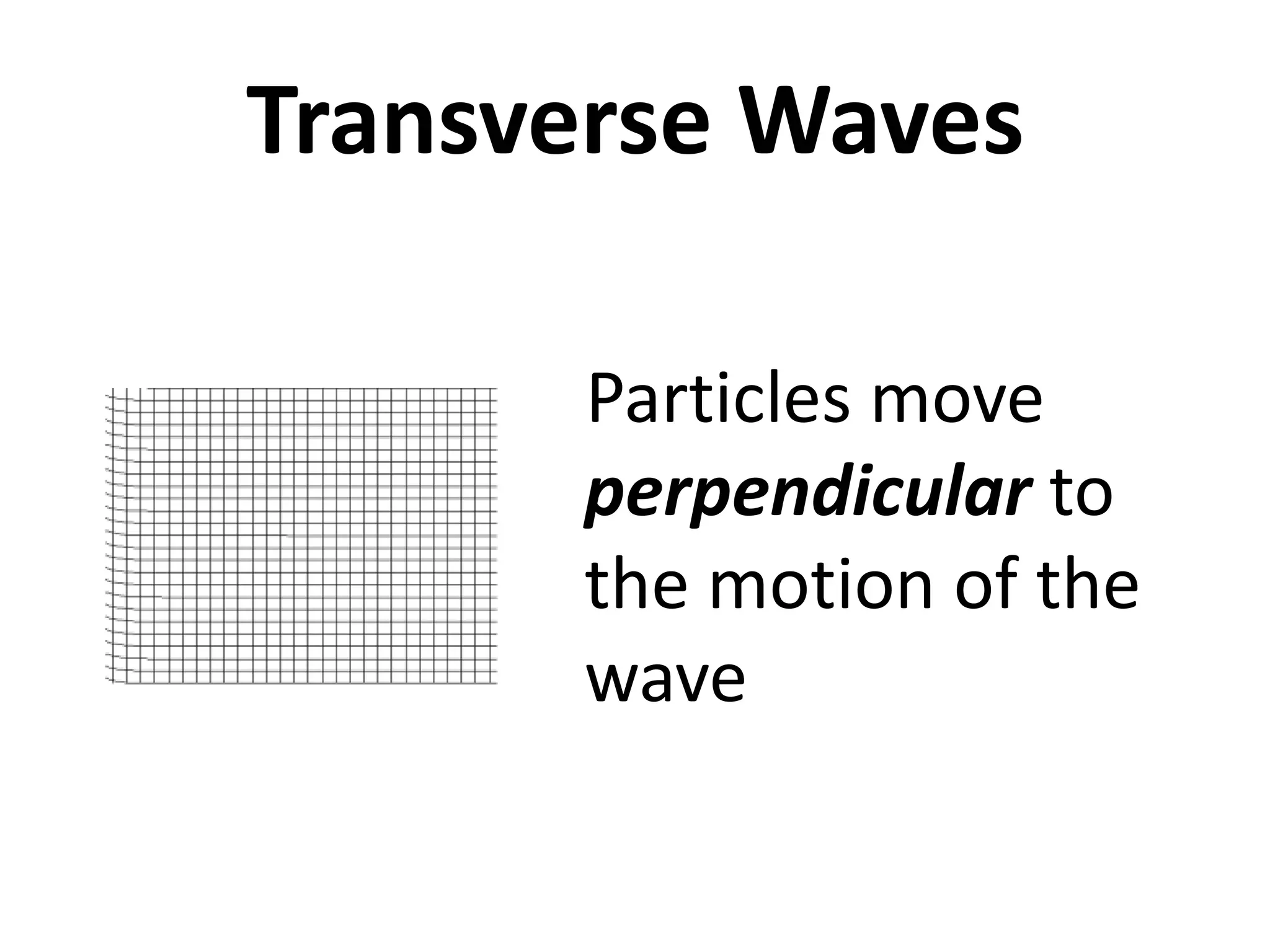
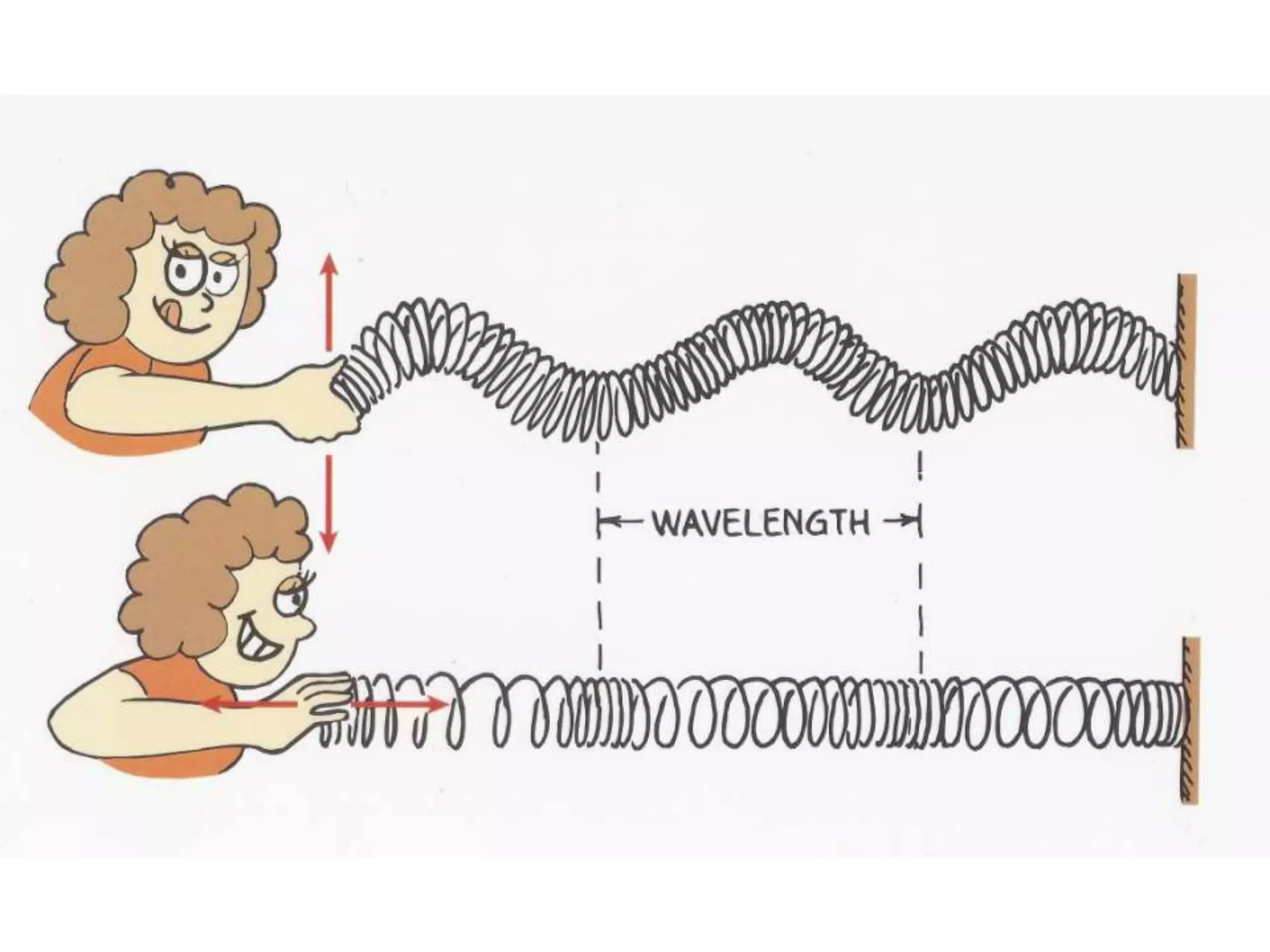
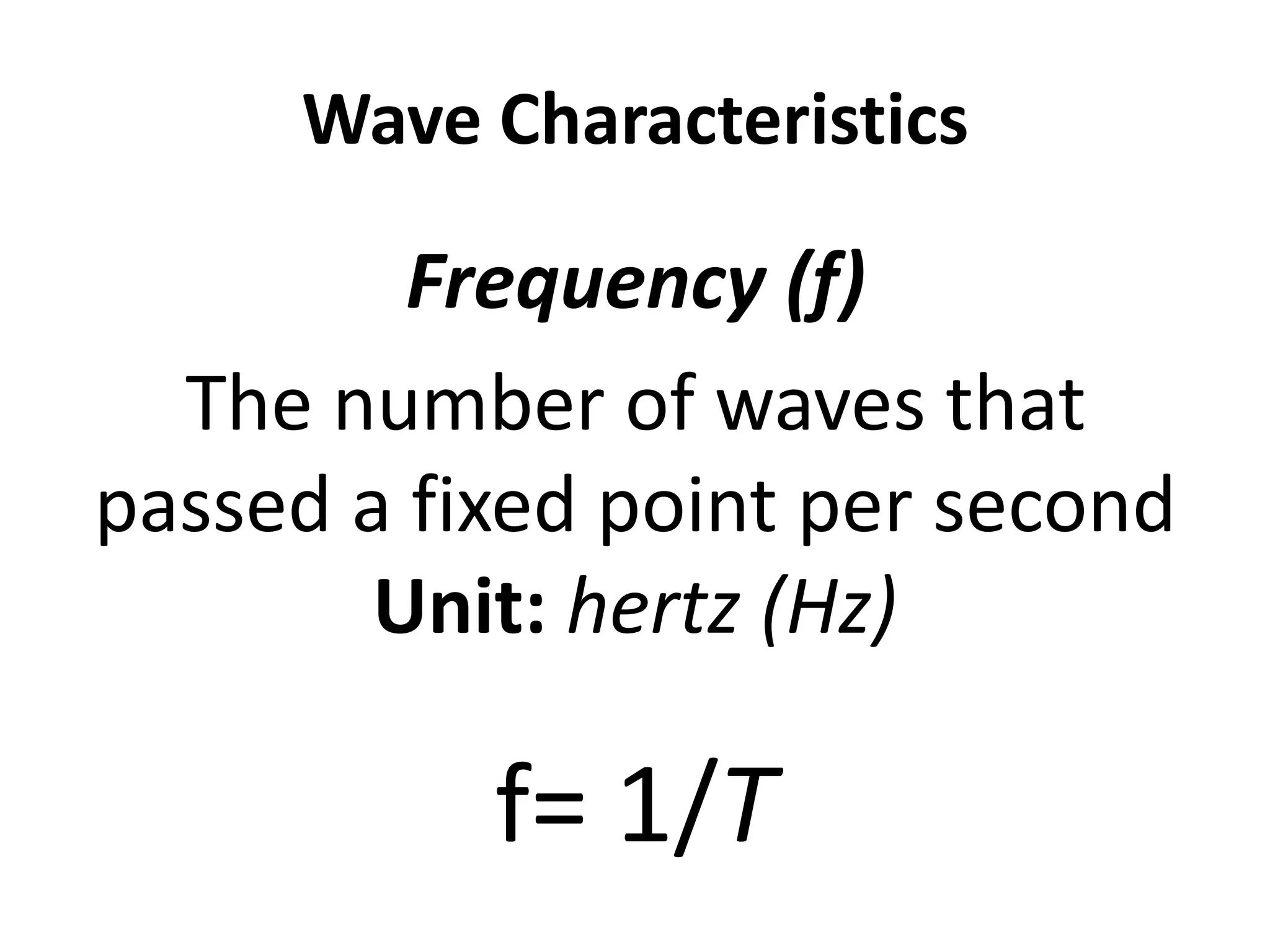
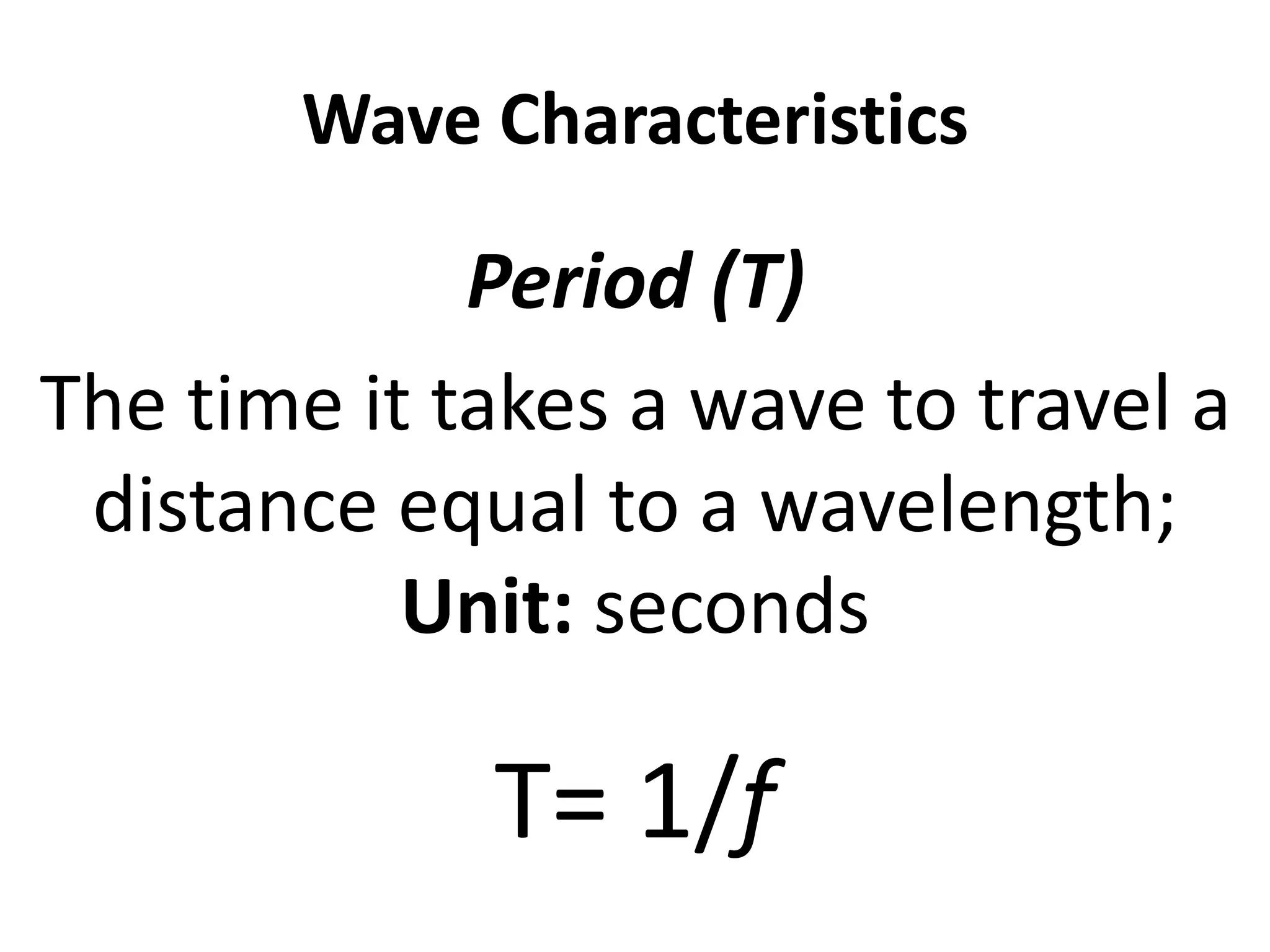
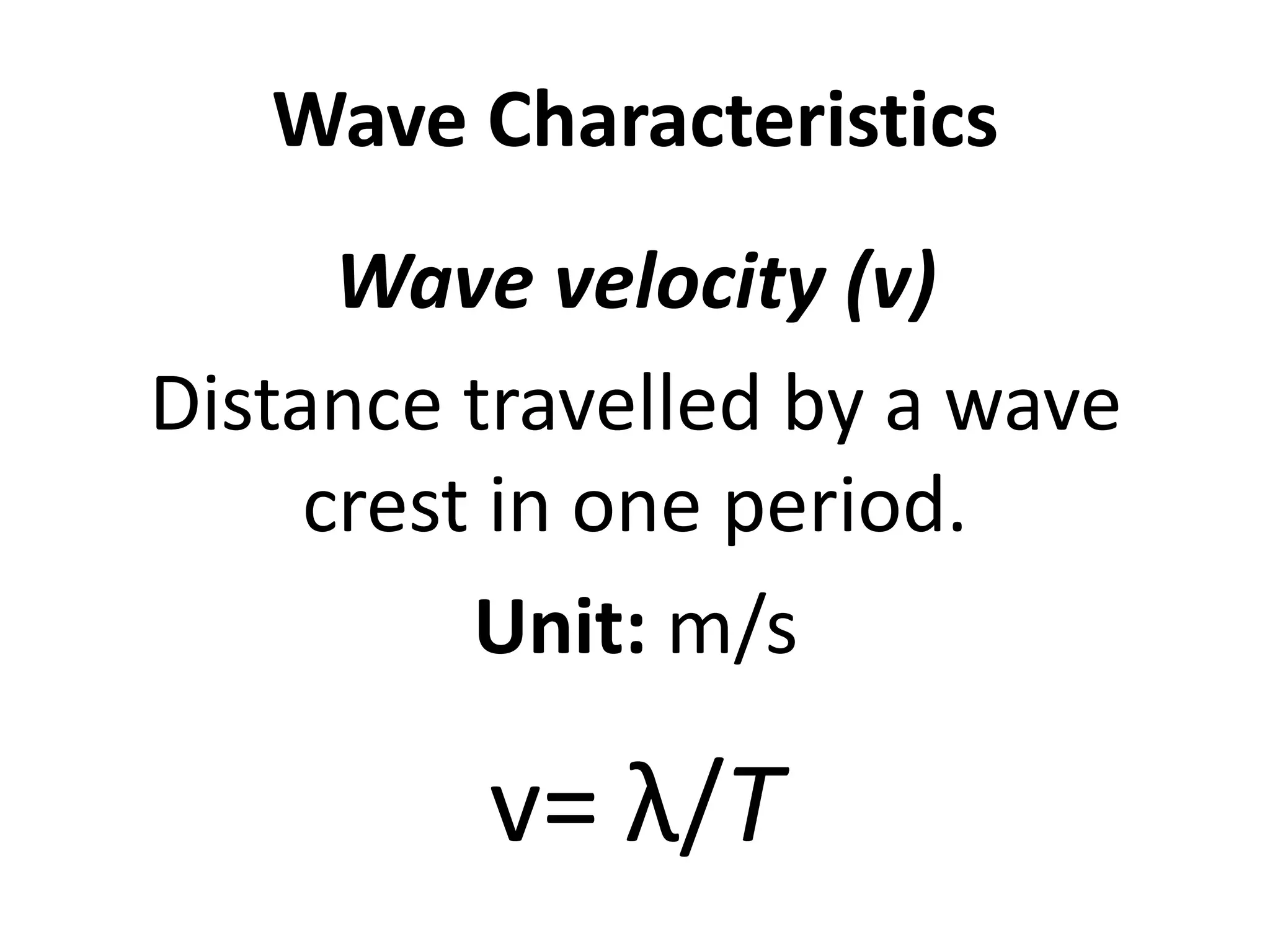
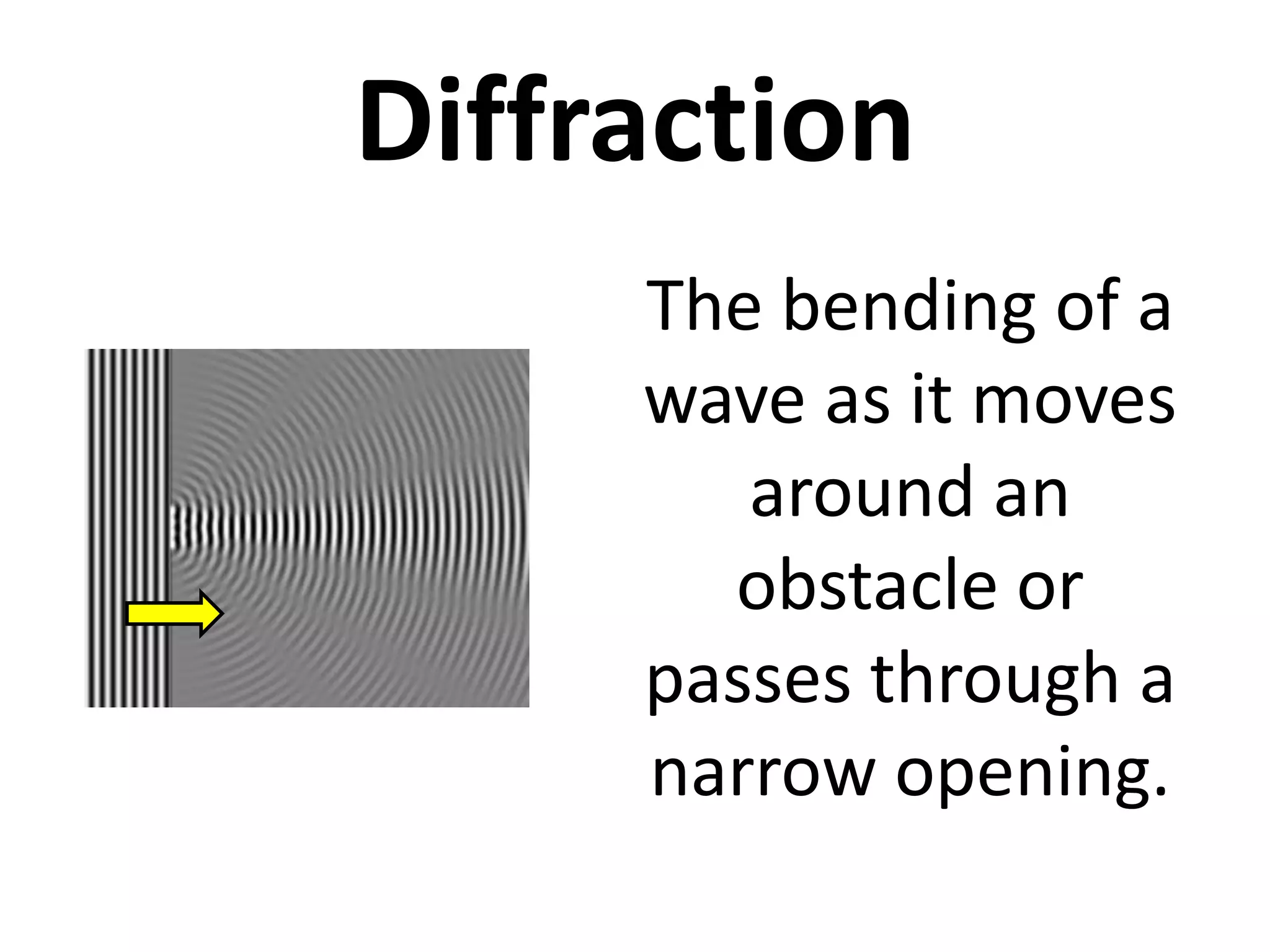
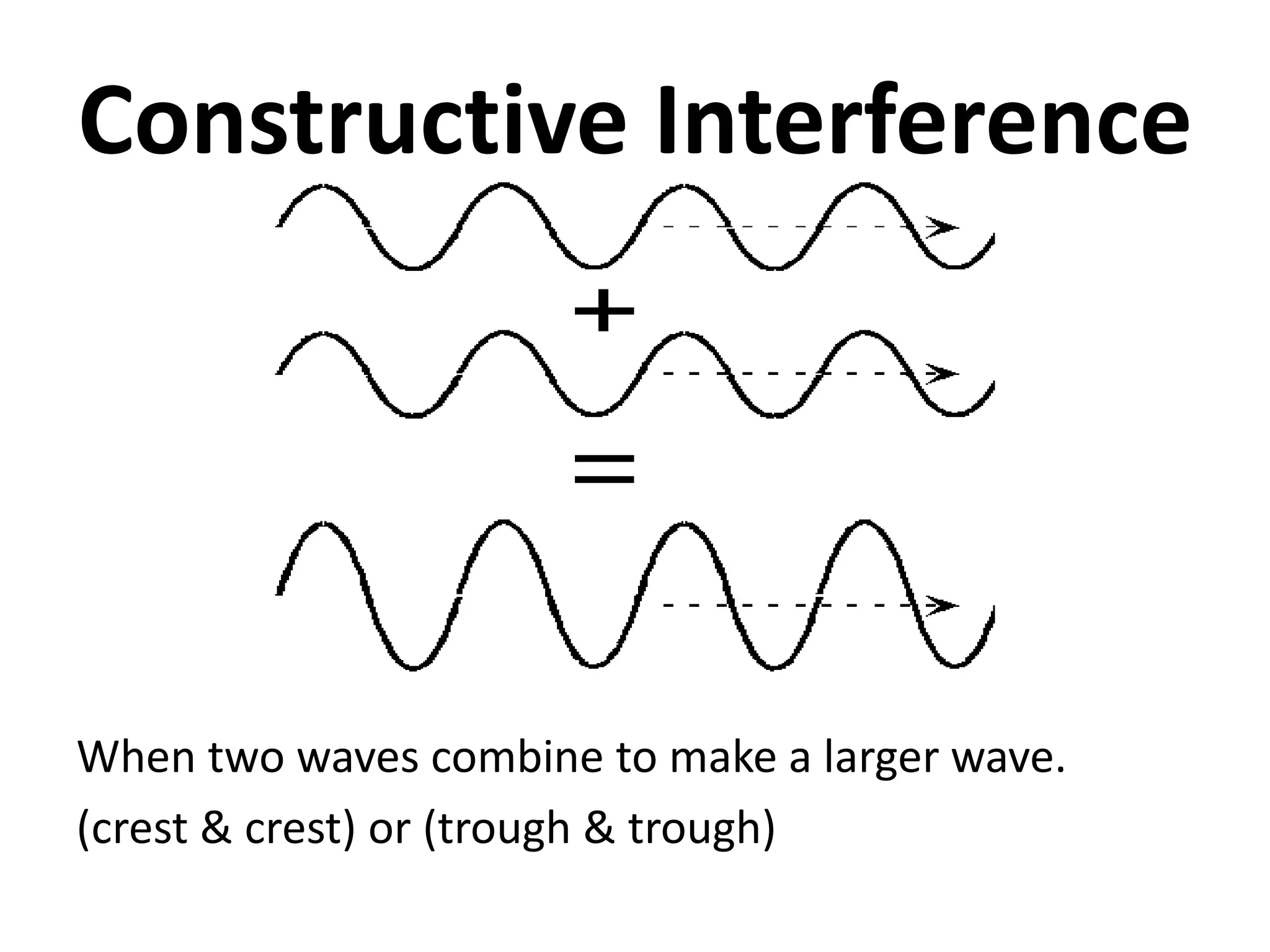
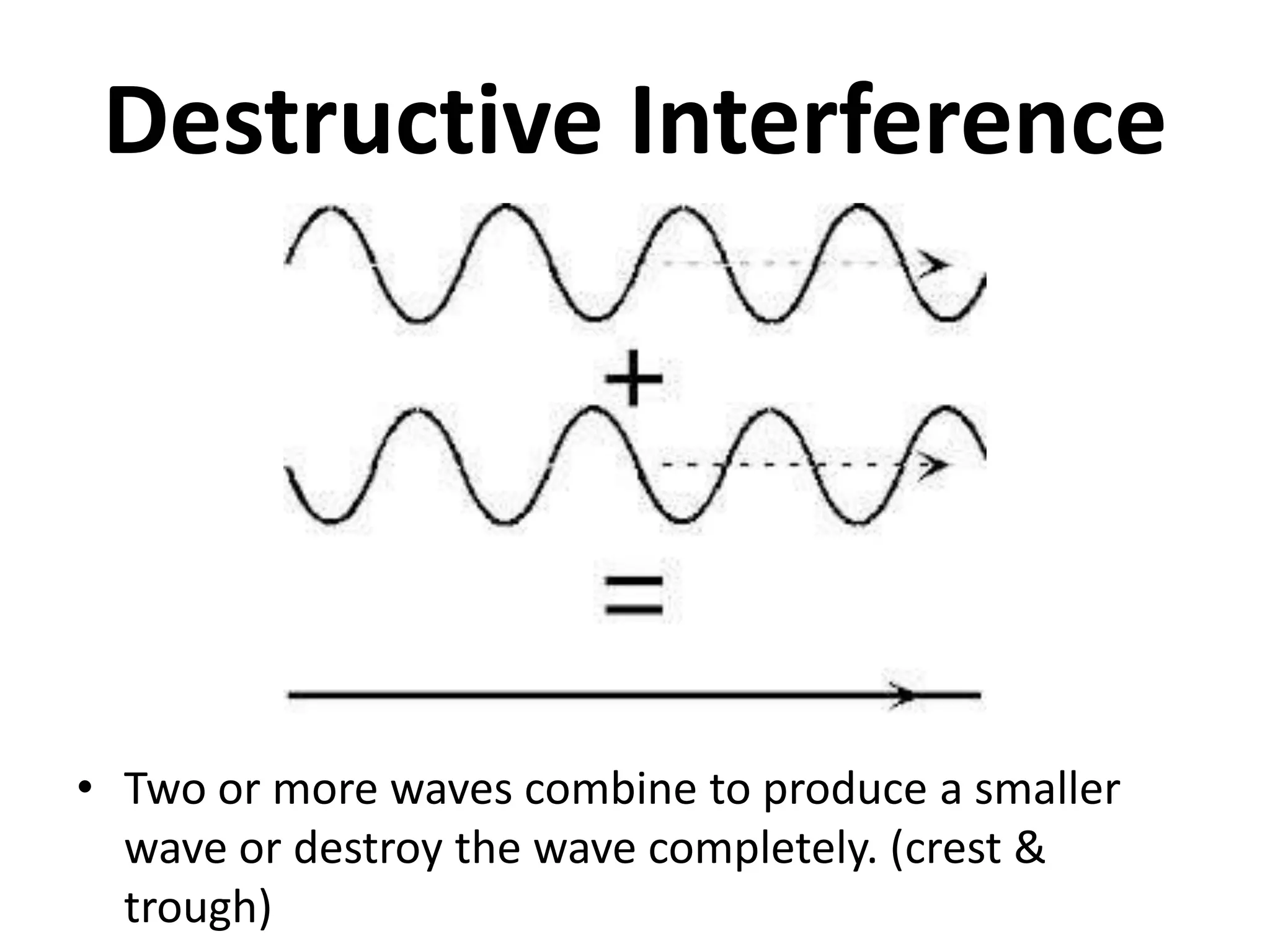
This document defines waves and classifies them according to their medium and particle motion. Waves transfer energy through a medium without transferring matter. They are classified as electromagnetic waves, which can travel through empty space, and mechanical waves, which require a medium. Mechanical waves are further divided into transverse waves, where particles move perpendicular to the wave, and longitudinal waves, where particles move parallel. The document also discusses wave characteristics like frequency, period, velocity, and behaviors such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, polarization, and resonance.