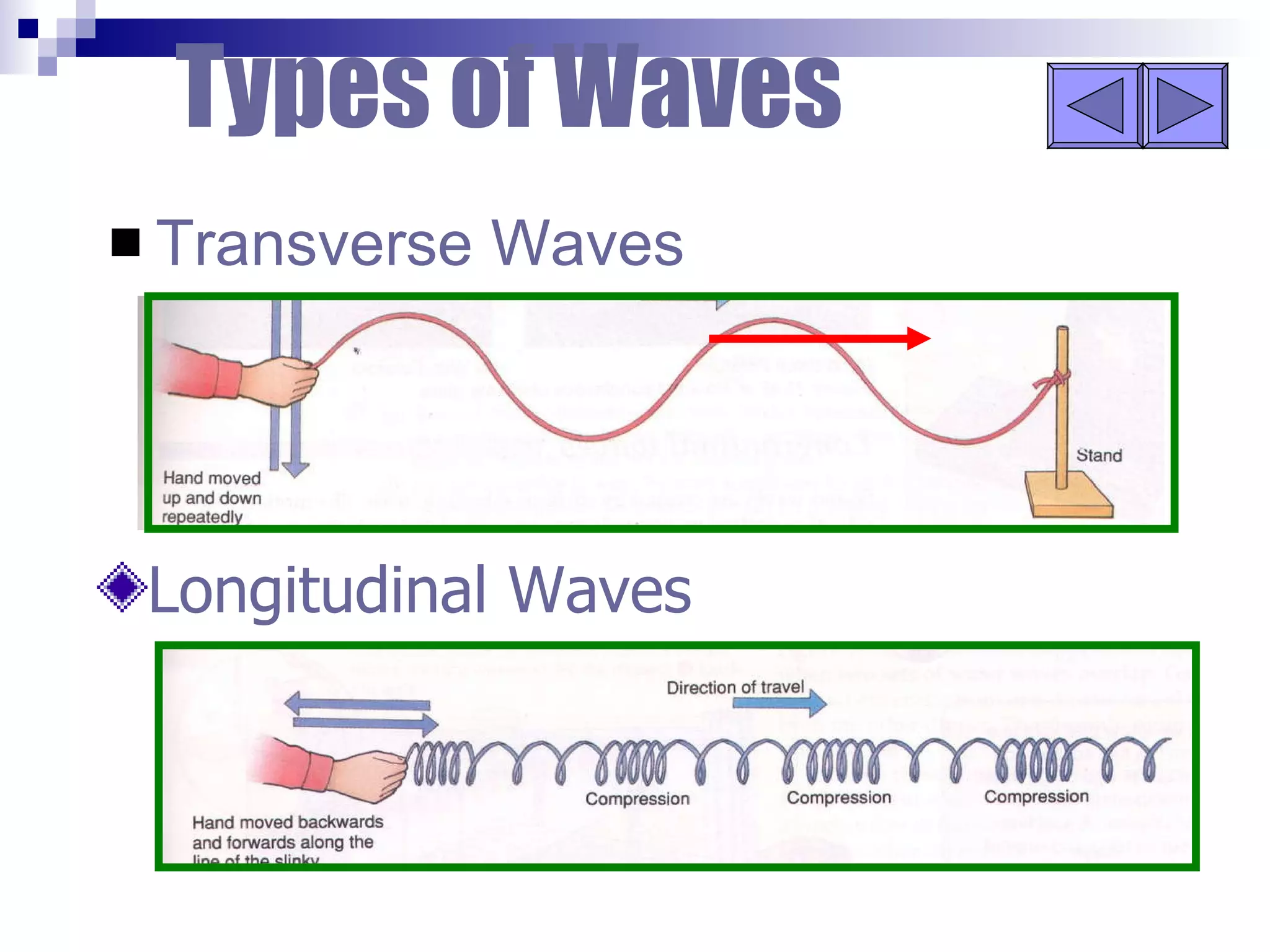
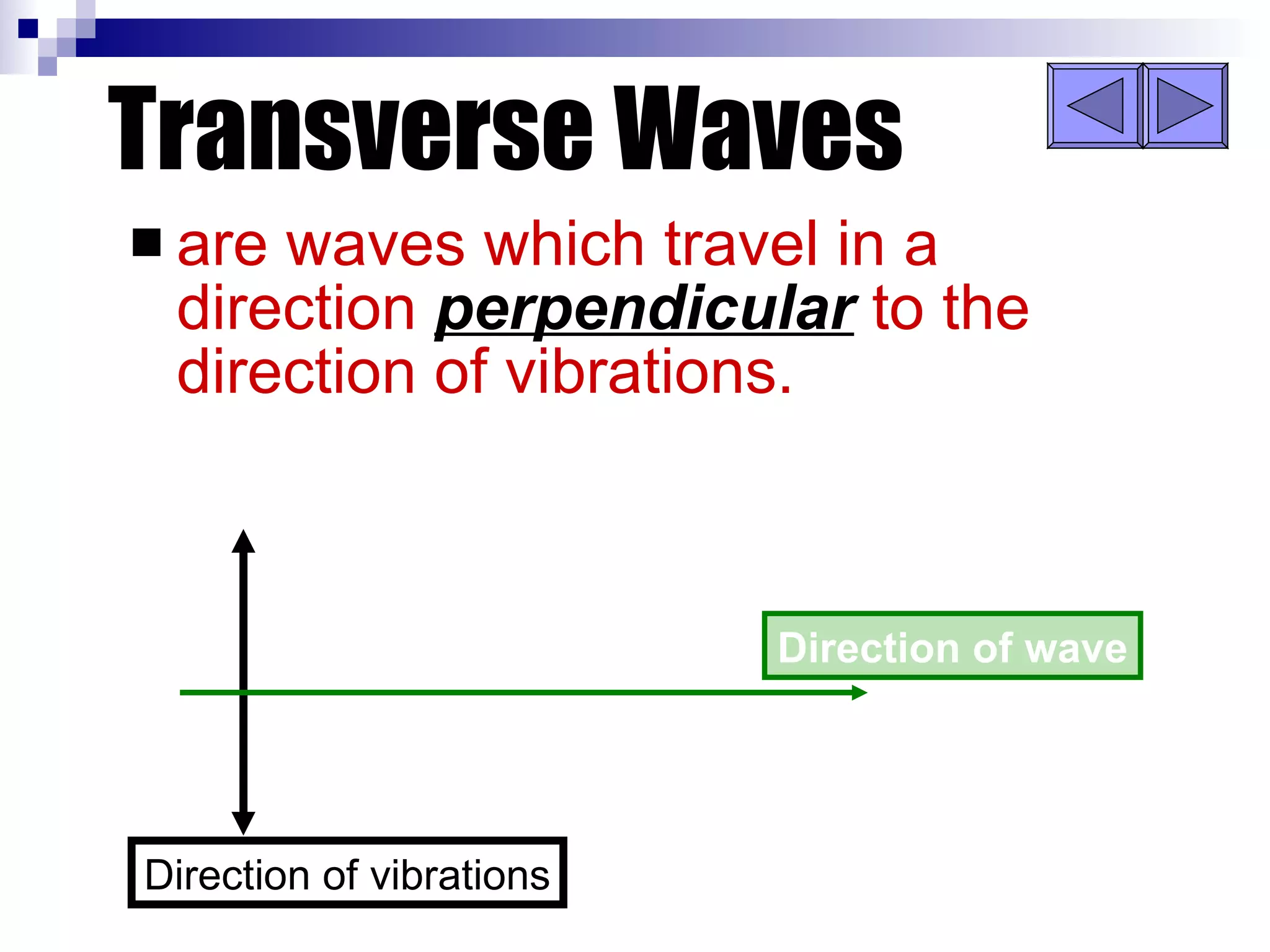
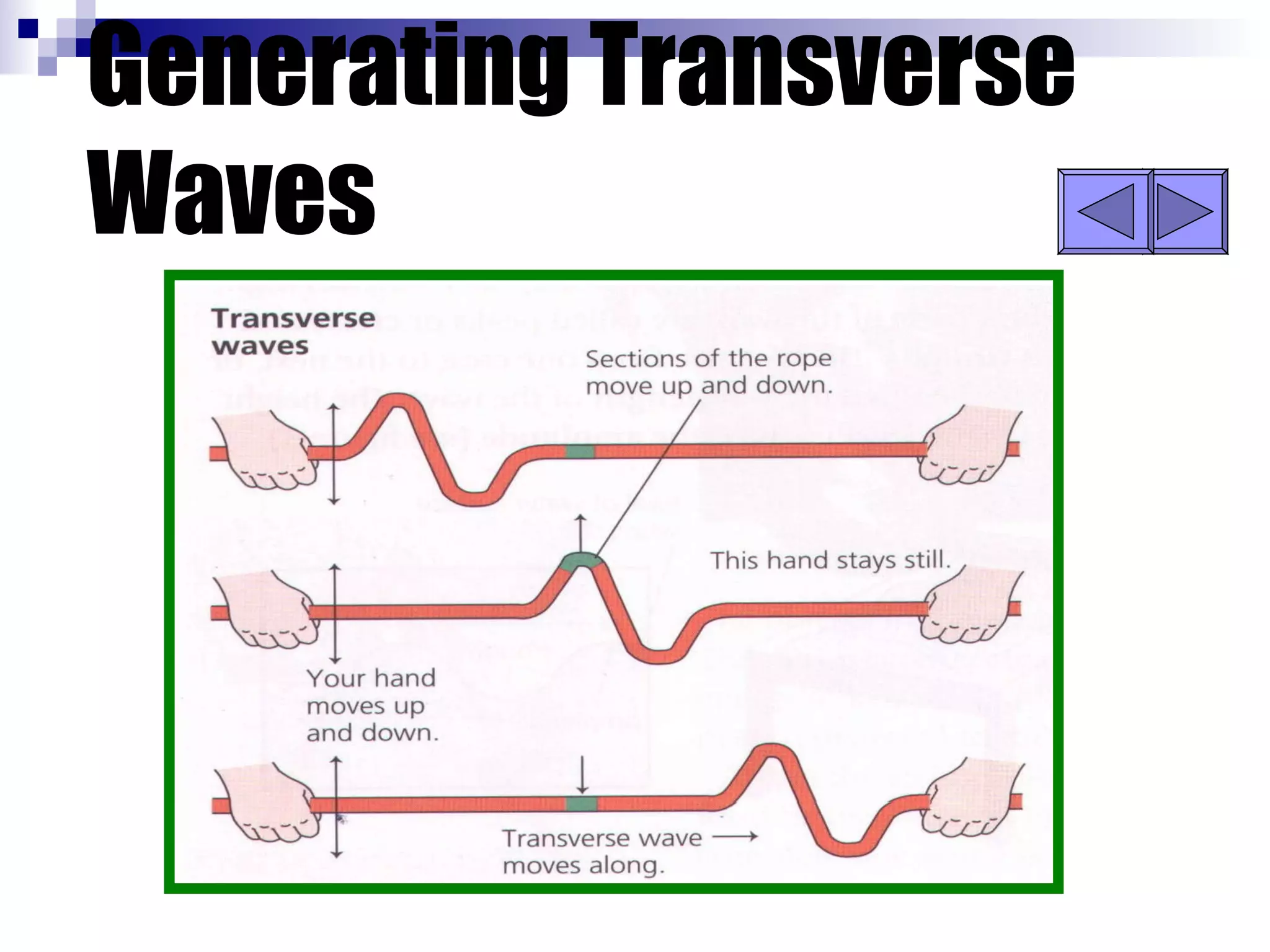
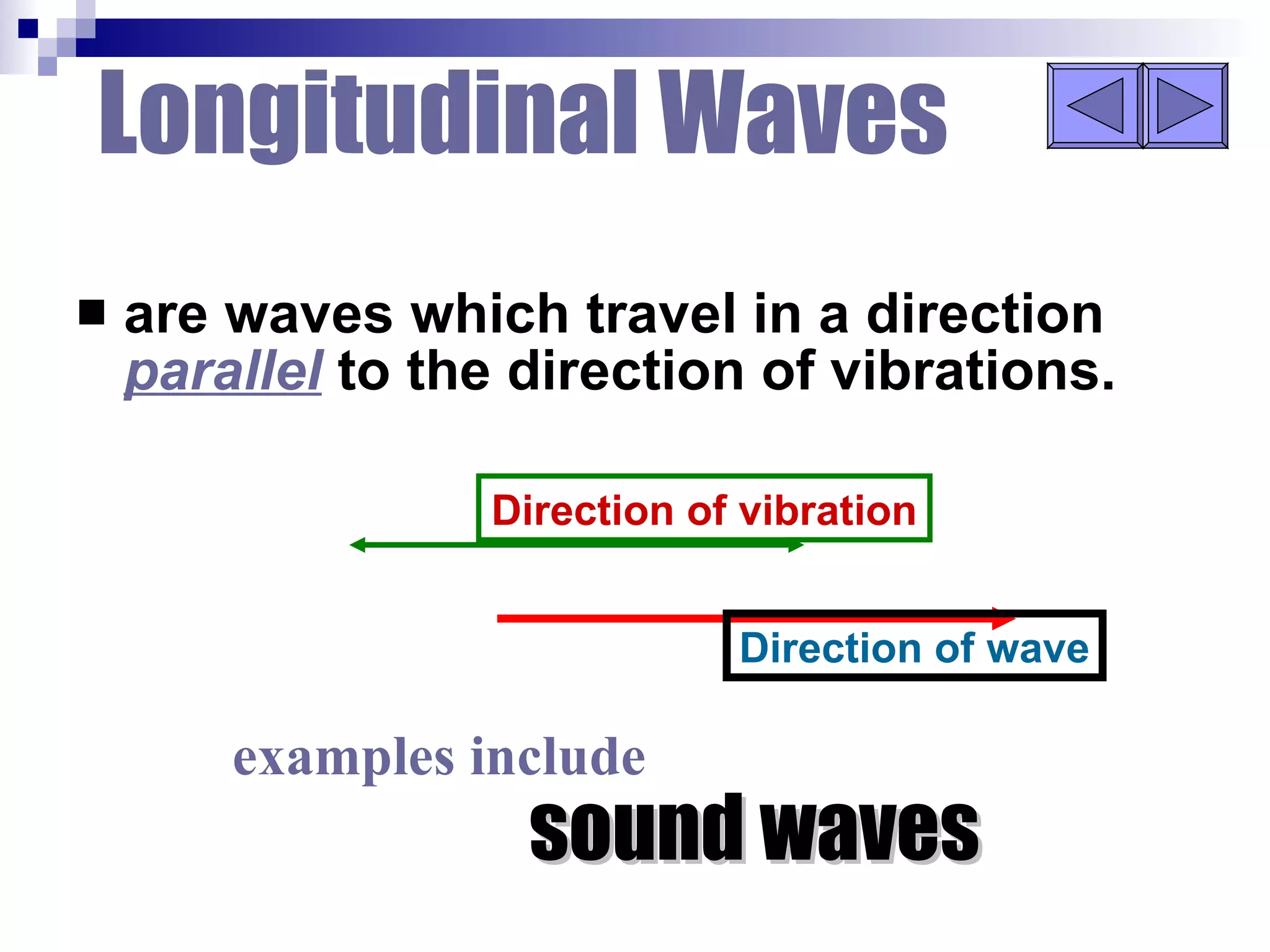
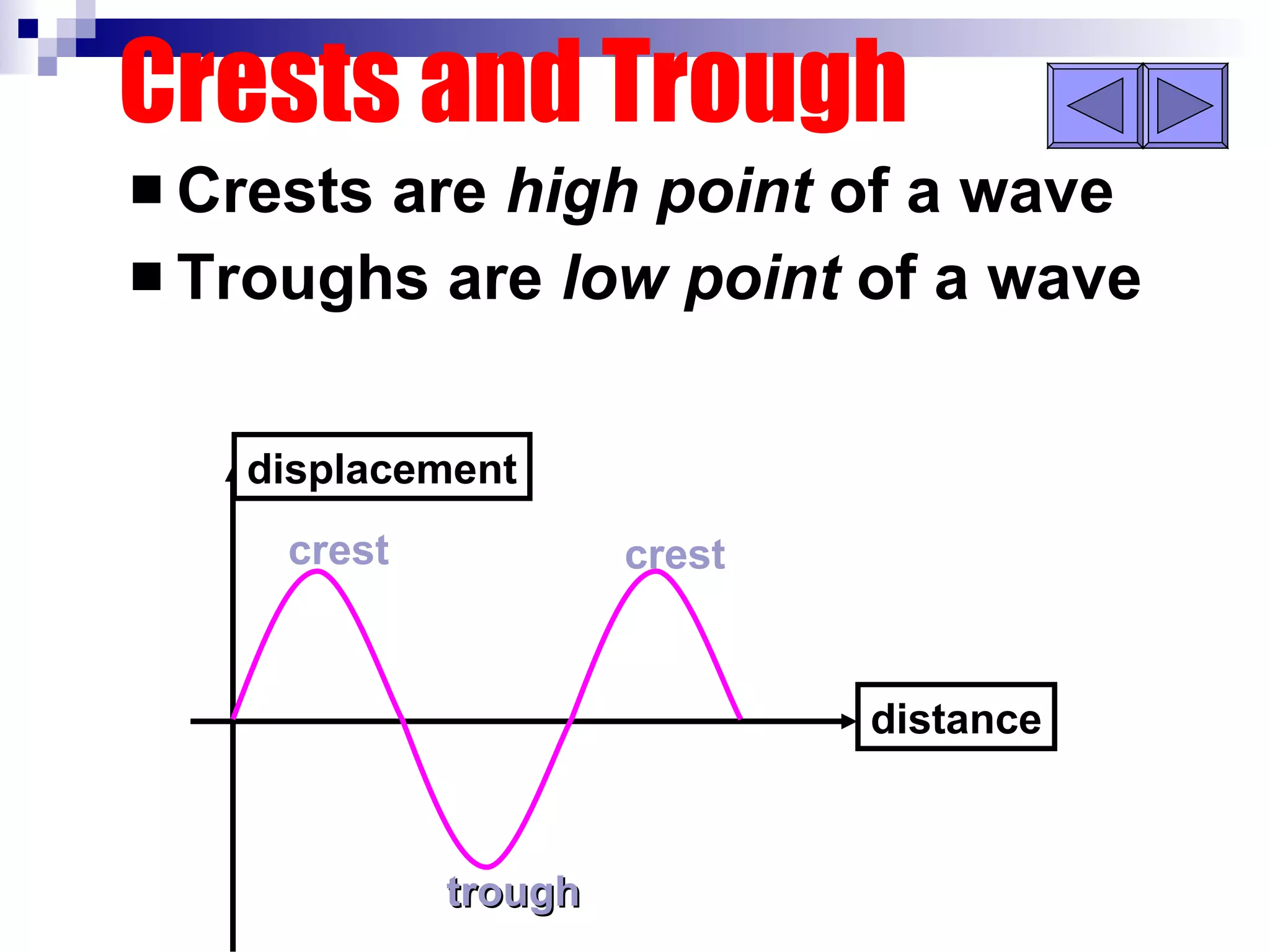
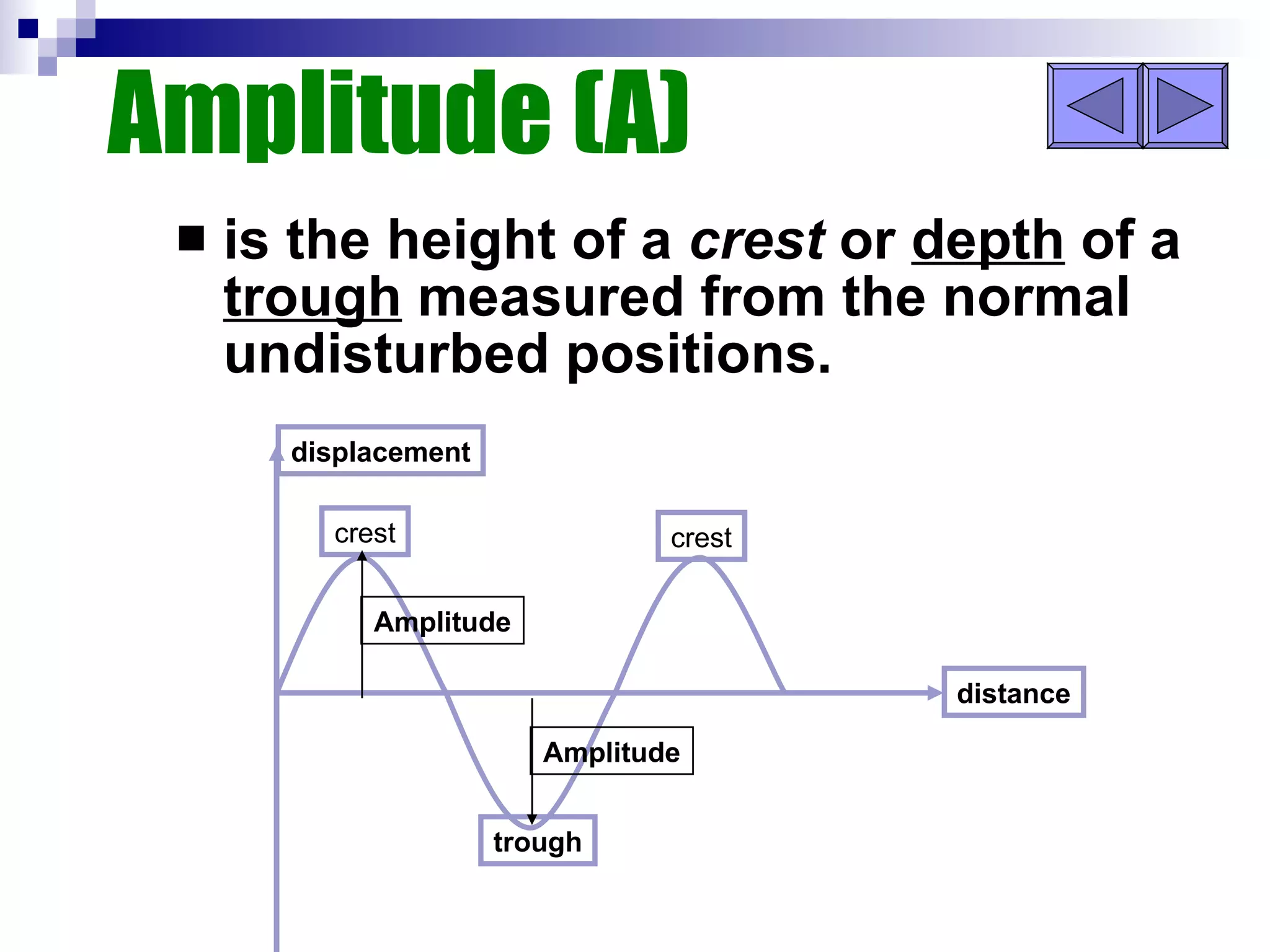
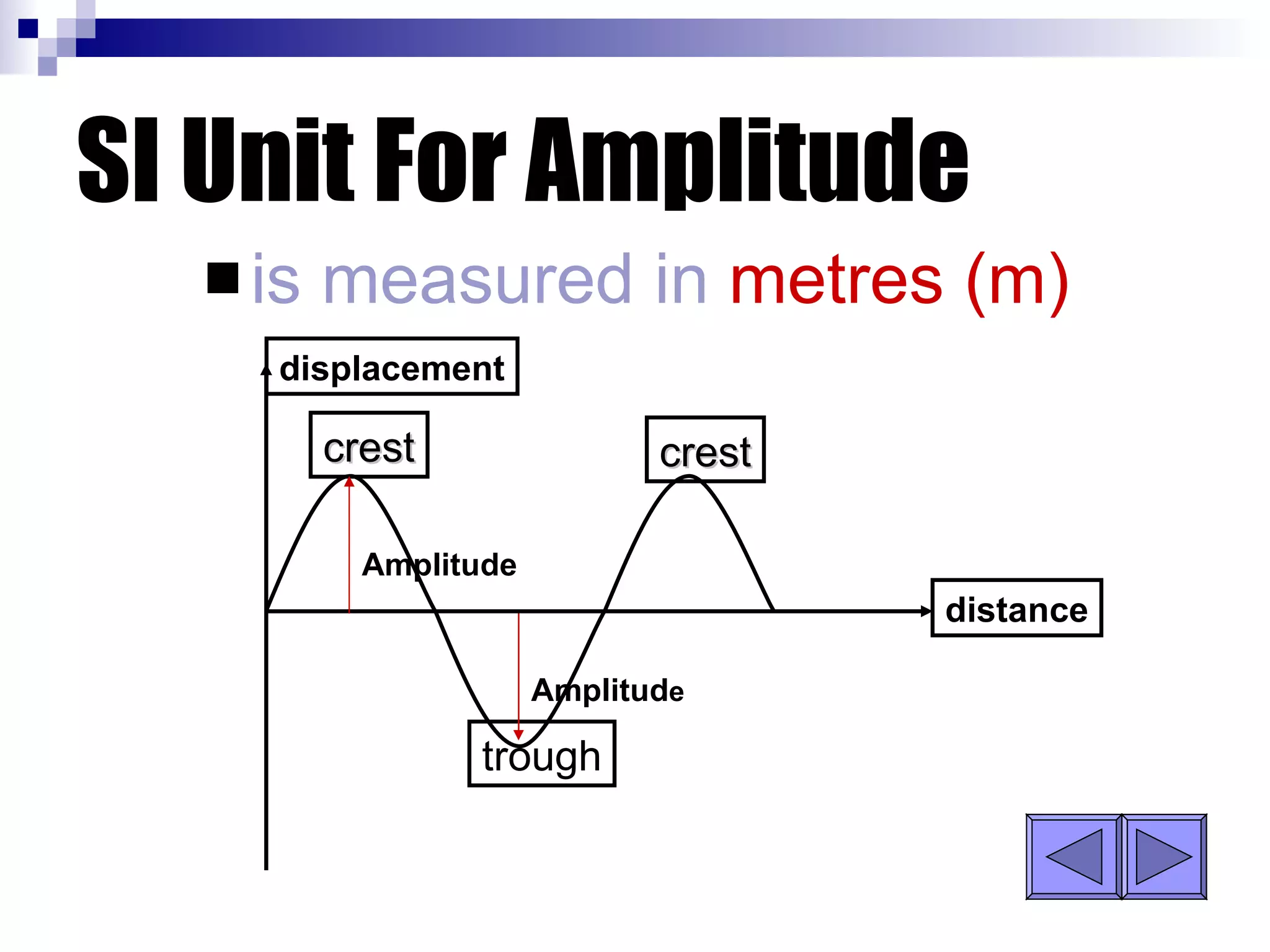
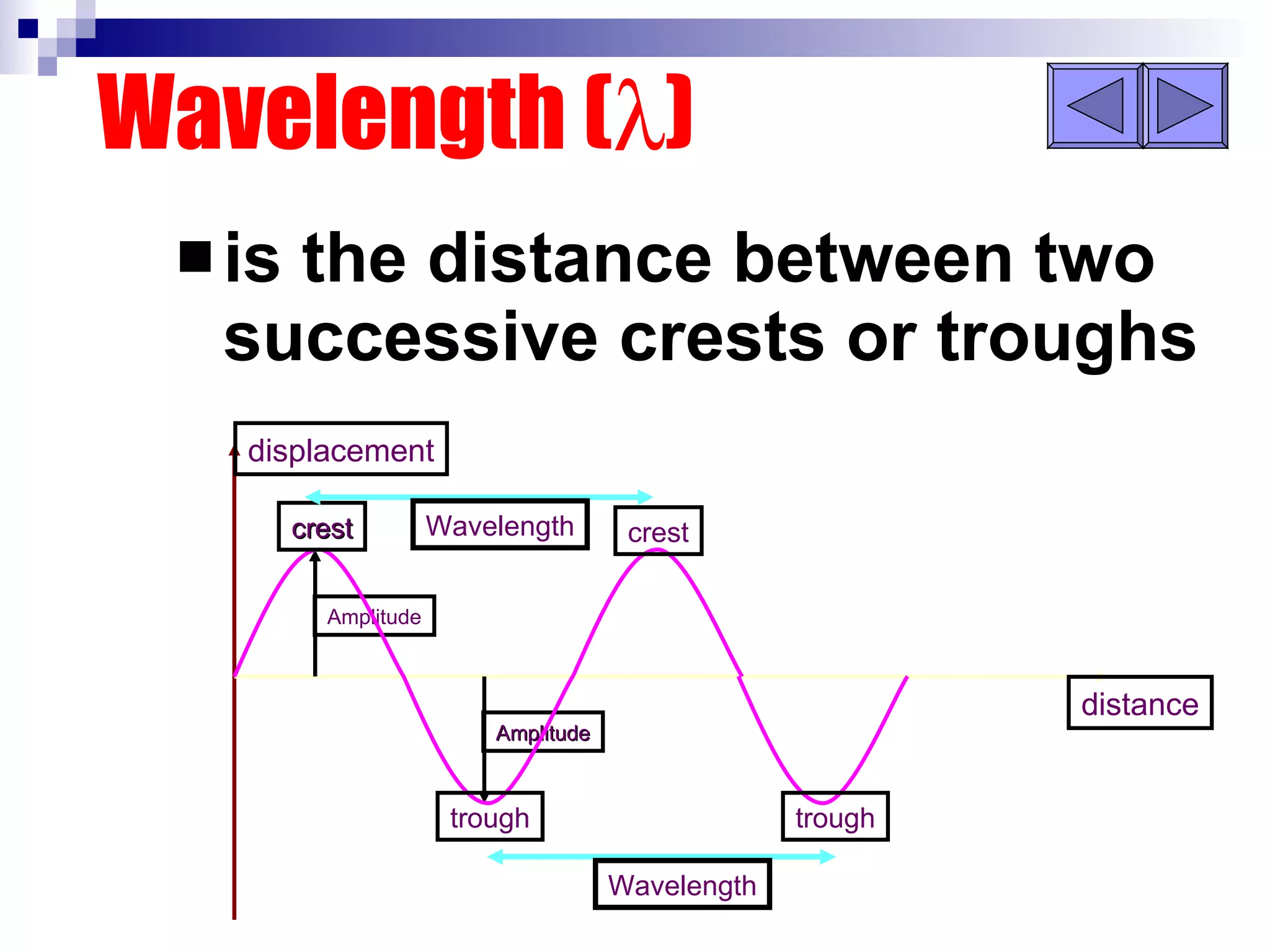
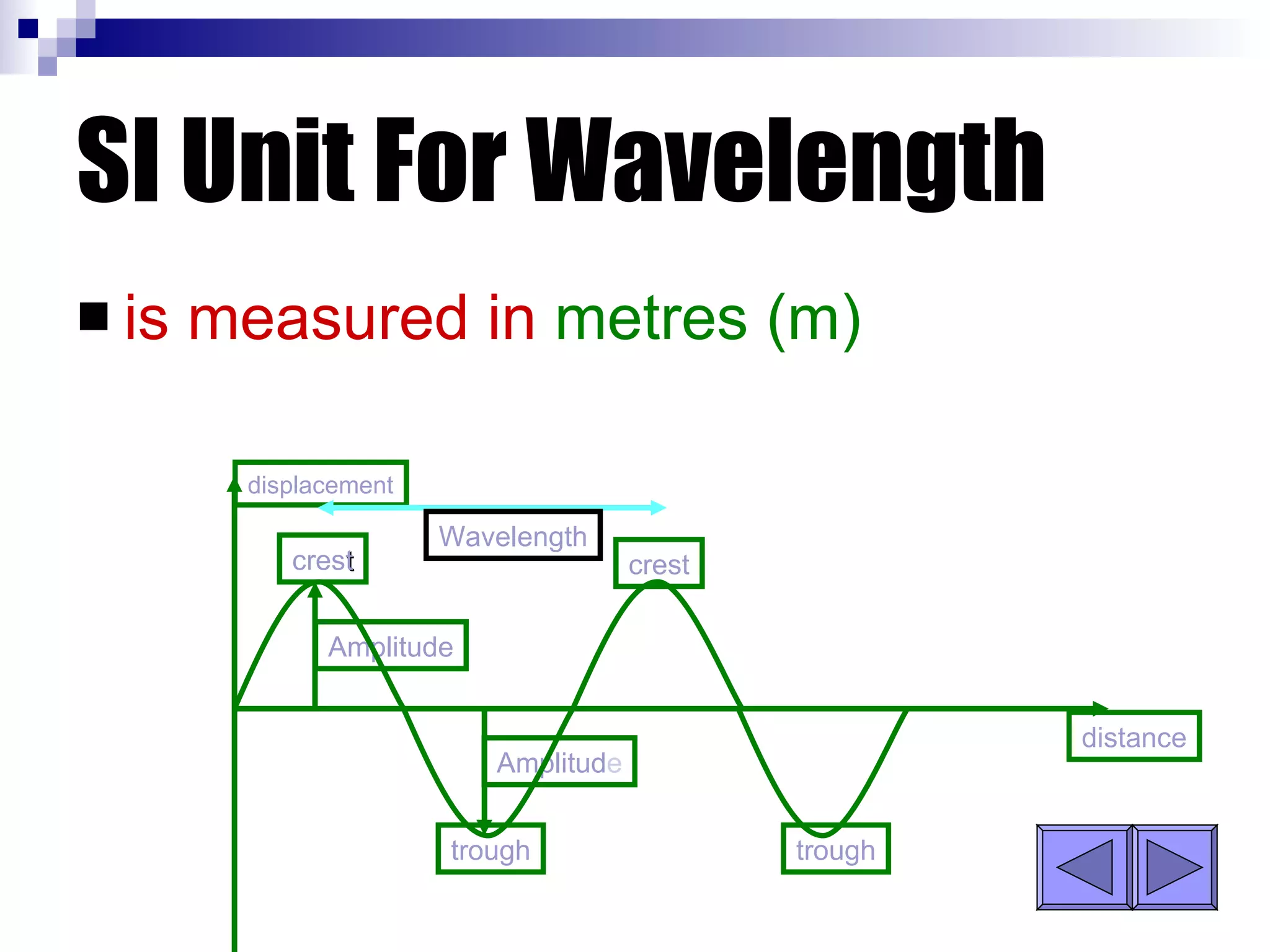
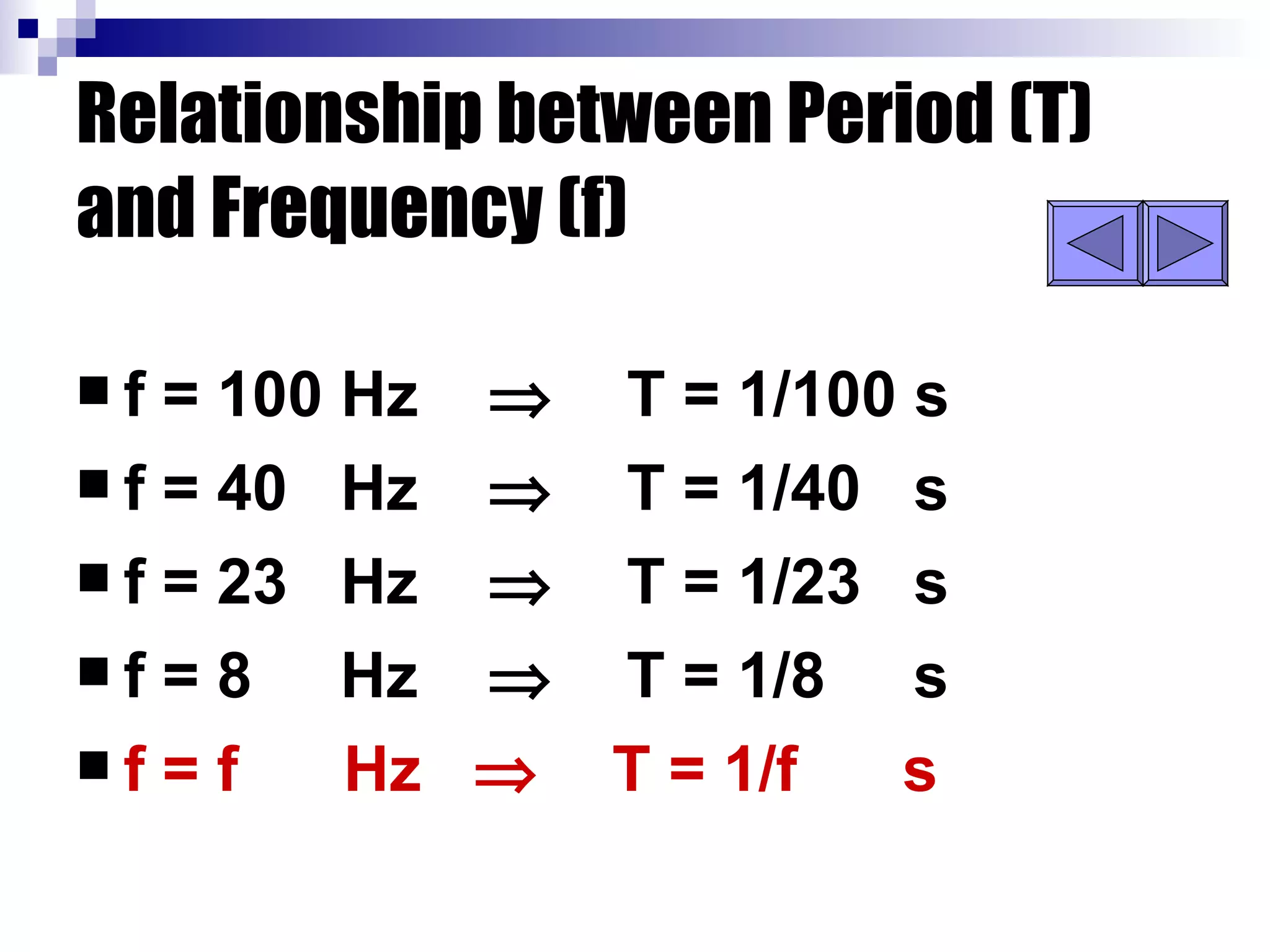
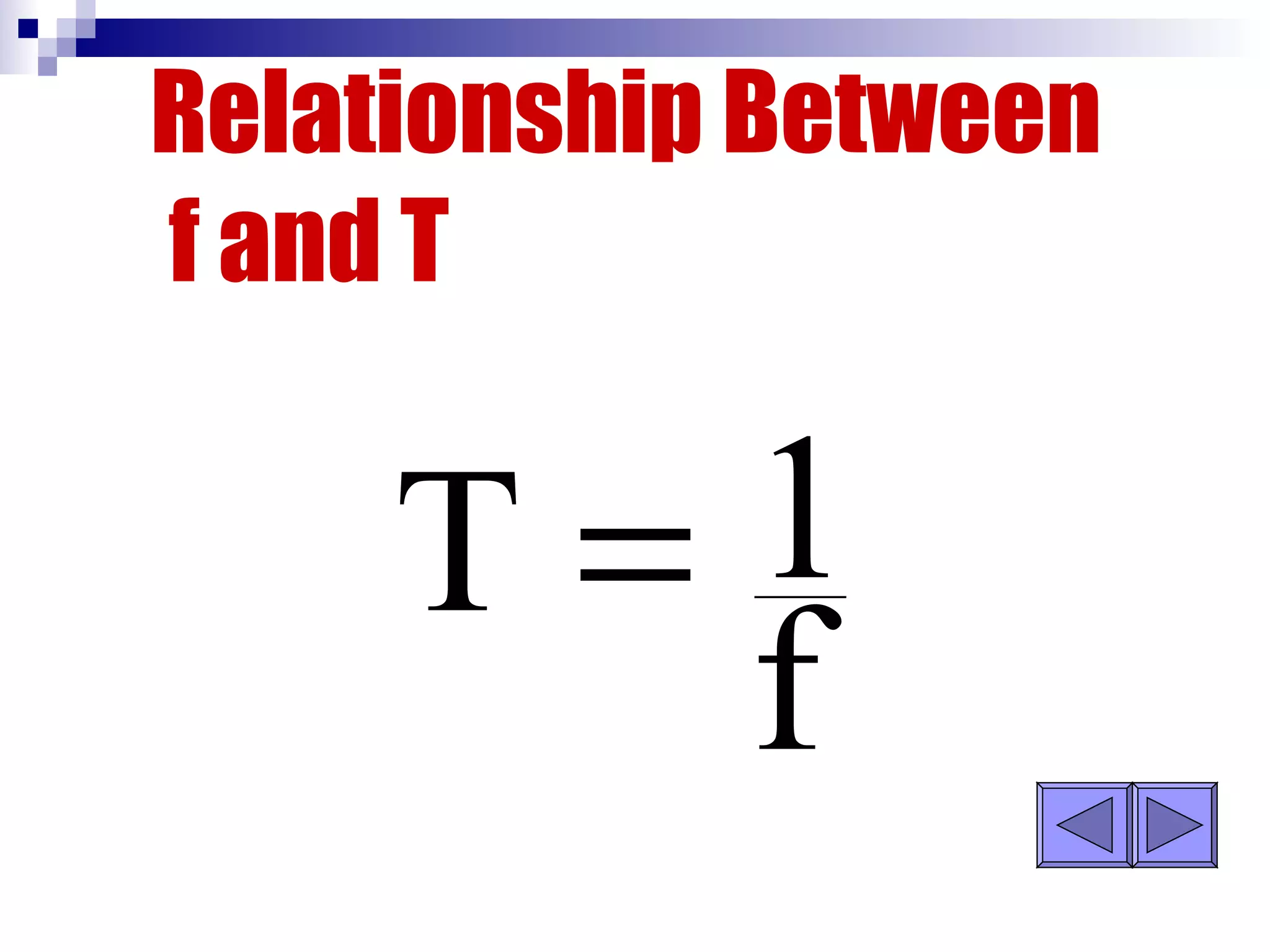
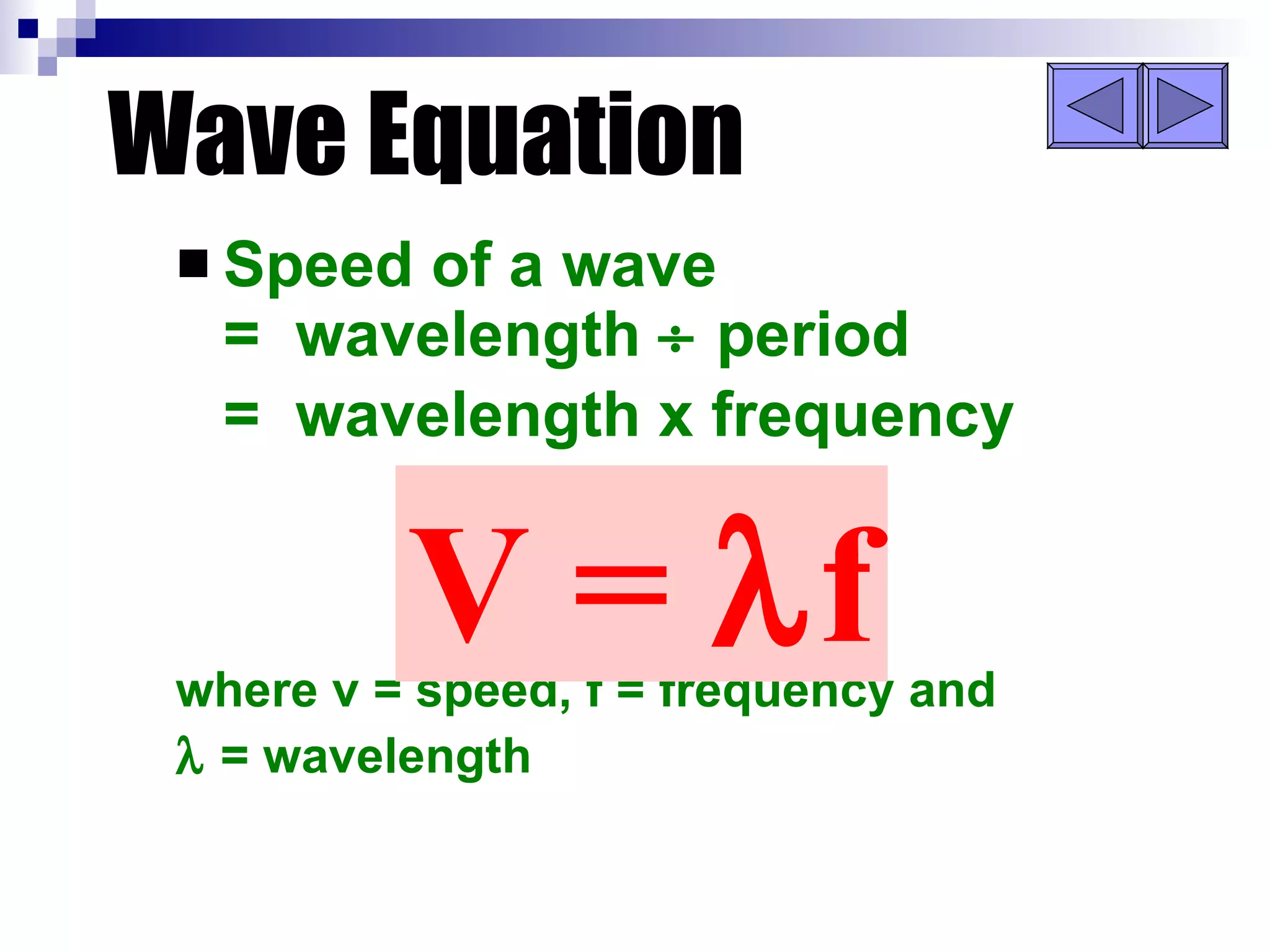
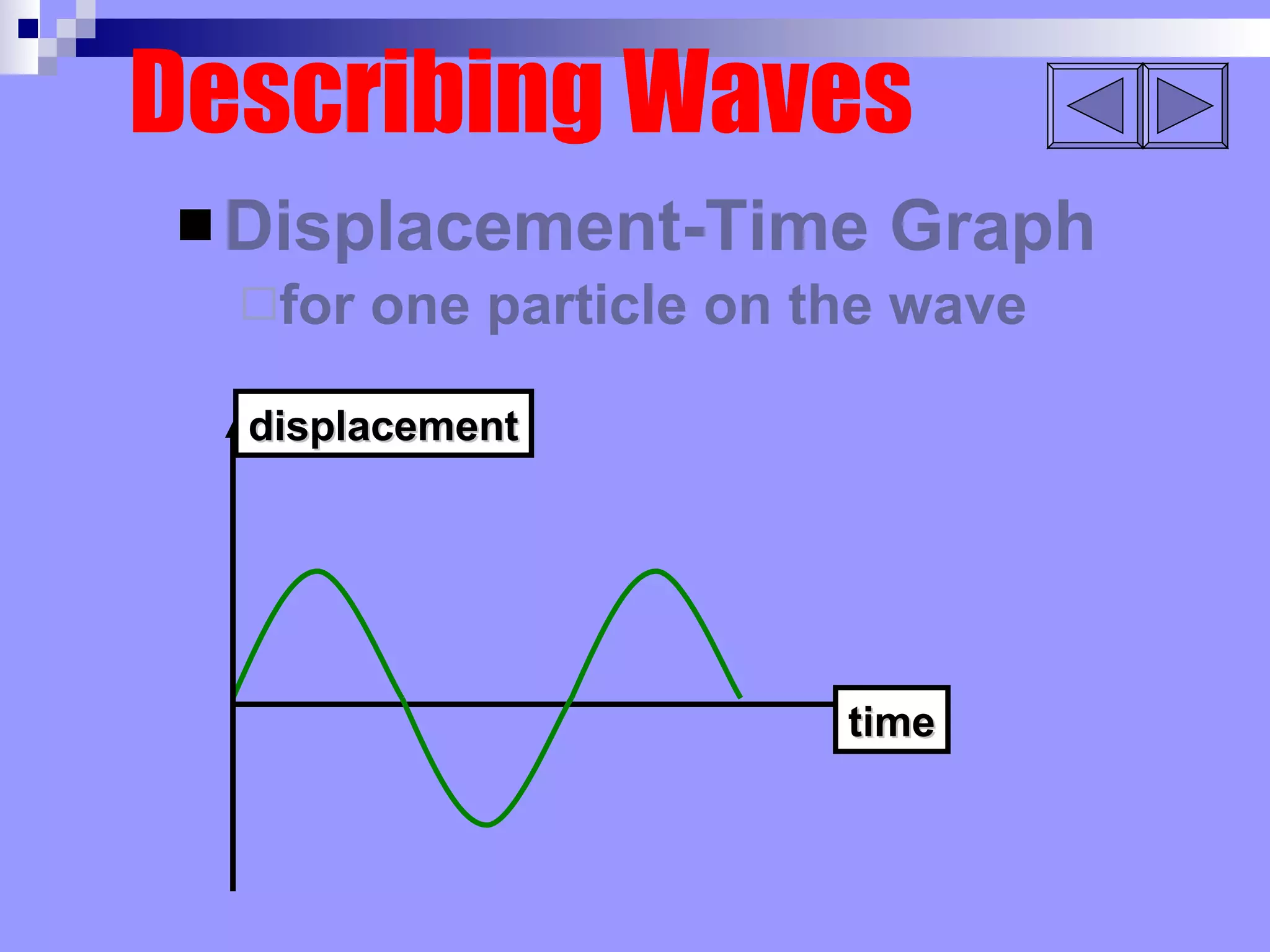
Waves can be transverse or longitudinal. Transverse waves have vibrations perpendicular to the direction of travel, like water waves. Longitudinal waves have vibrations parallel to travel, like sound waves. The characteristics of all waves include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, period, and speed. Wavelength is the distance between two peaks, frequency is the number of waves passing a point per second, and speed equals wavelength times frequency.




![Generating of Longitudinal Waves [slinky spring]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-9-2048.jpg)











![Nov 1998 5. The diagram shows a coil spring along which a longitudinal wave is moving. (a) Mark on the diagram a distance equal to the wave length of the wave. [1] (b) Label on the diagram with the letter C where the coils of the spring are compressed. [1] Wave length C (continue in next slide) C C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-33-2048.jpg)
![(c) Is the wave on the spring more like a sound wave or a light wave? [1] Nov 1998 (Cont. …) Q 5 Sound wave, because sound wave is a longitudinal wave but light wave is a transverse wave..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-34-2048.jpg)
![Nov 1997 5. The diagram below shows a transverse wave travelling a rope. (a) Mark on the diagram which is equal to (i) the wavelength, (ii) the amplitude of the wave. Label your answers. [2] (b) If the wavelength is 0.8m and the frequency is 2 Hz, what is the speed at which the wave moves along the rope ? [2] wavelength amplitude v = f = 0.8 x 2 = 1.6 ms -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-35-2048.jpg)
![Nov 1996 6(a) Explain the difference between a transverse and a longitudinal wave. [2] (b) State one example of each type of wave. Transverse Longitudinal [2] Light Sound Transverse wave is a wave that its direction of vibration is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. It can travel through vacuum. Longitudinal wave is a wave that its direction of vibration is parallel to the direction of propagation. It needs medium to travel.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-36-2048.jpg)
![9.(a) Explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves, referring in your answer to the direction in which the waves travel. [2] GCE ‘O’ LEVEL Nov 1995 Transverse waves are waves that their direction of vibration is perpendicular to their direction of propagation. Longitudinal waves are waves that their direction of vibration is parallel to their direction of propagation. (continue on next slide)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-37-2048.jpg)
![9.(b) The speed of sound in water is 1500m/s. What is a wave length of a sound wave of frequency 250Hz travelling through water ? [2] Since v = f therefore 1500 = 250 = 1500 / 250 = 6.0 m (Cont. …) Q. 9 Nov 1995](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-38-2048.jpg)
![Nov 1993 6. The diagram shows the air pressure at different distances from a loudspeaker. (continue on next slide) (a) Mark carefully on the diagram: [2] (i) a distance which is the wavelength of the sound wave; (ii) the amplitude of the sound waves. wavelength amplitude](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-39-2048.jpg)
![6(b) If the wavelength of a sound wave of frequency 250 Hz is 1.4 m, calculate the speed of the wave. [2] (Cont. …) Q. 6 Nov 1993 since v = f therefore, = 1.4 x 250 = 350 ms -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-40-2048.jpg)
![5.(a) With the aid of a diagram, explain what is meant by the frequency and wavelength of a wave. [5] GCE O Nov 1990 (b) What is a longitudinal wave ? [2] Frequency is the number of vibrations per second. Wavelength is the distance from a point on a wave to its next corresponding point. It usually denote as .. Longitudinal wave is a wave that its direction of vibration always parallel to the direction of propagation. (continue in next slide)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/longitudinalandtransversewaves-100907055401-phpapp01/75/Longitudinal-and-transverse-waves-41-2048.jpg)