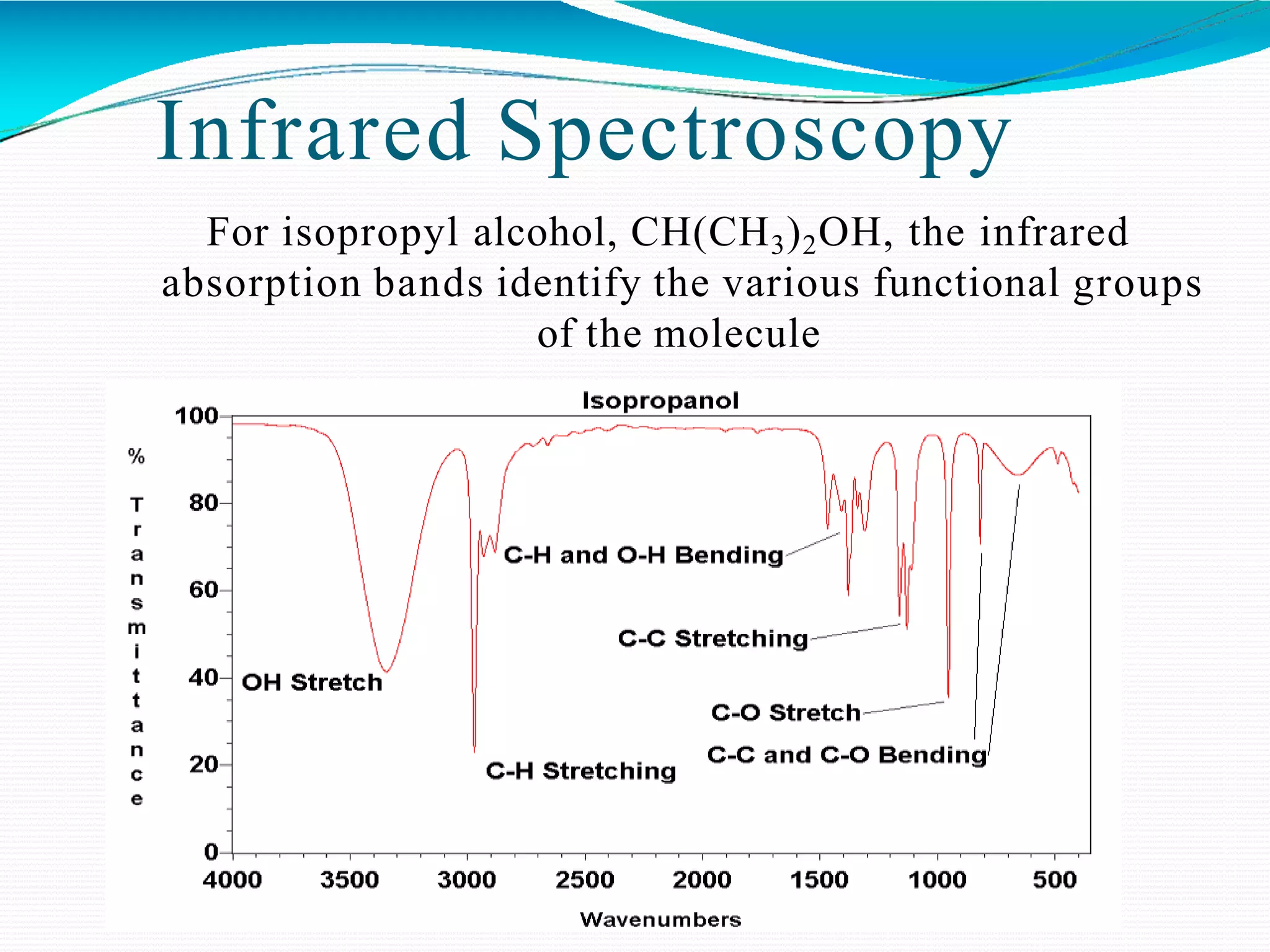
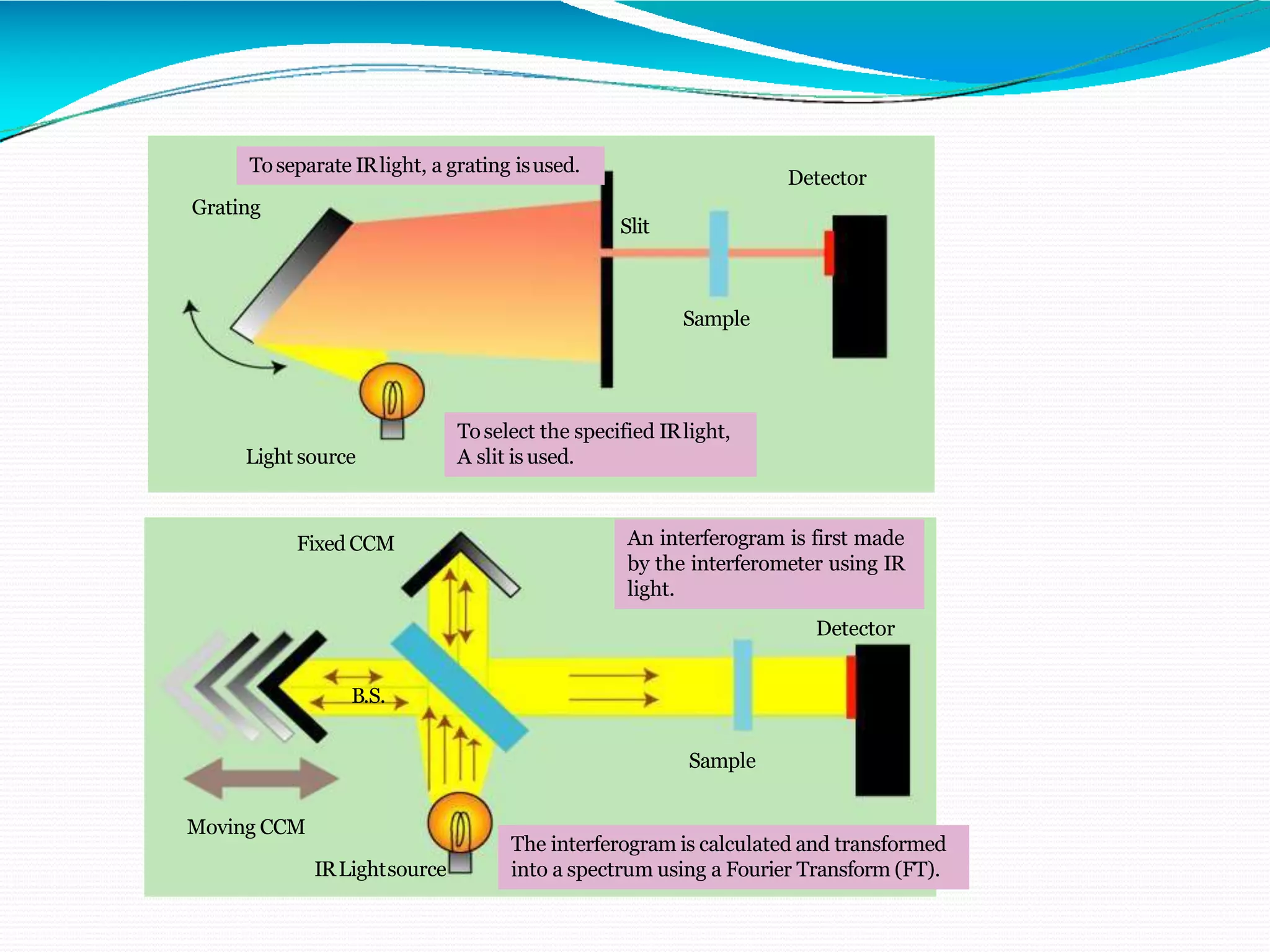
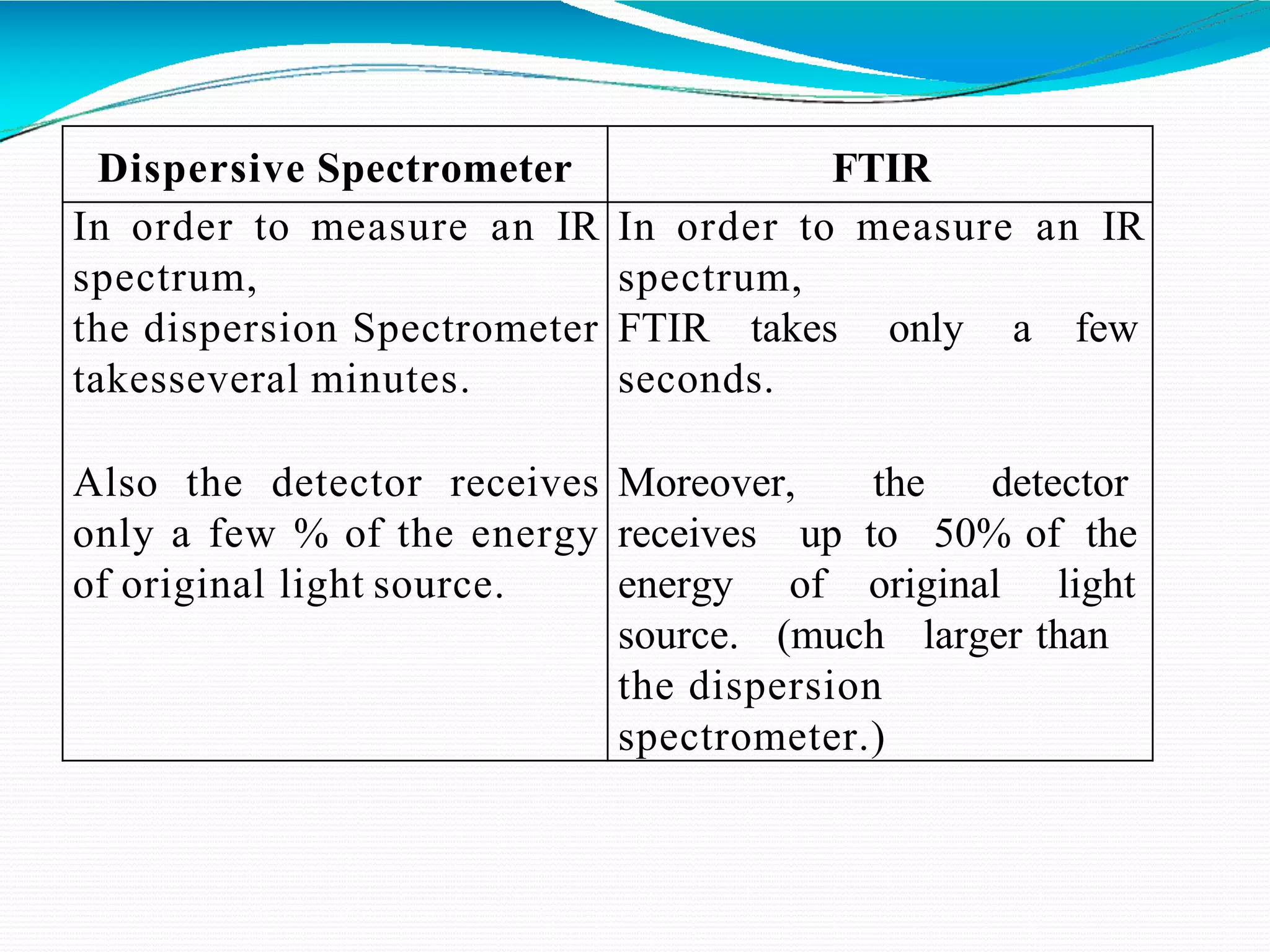
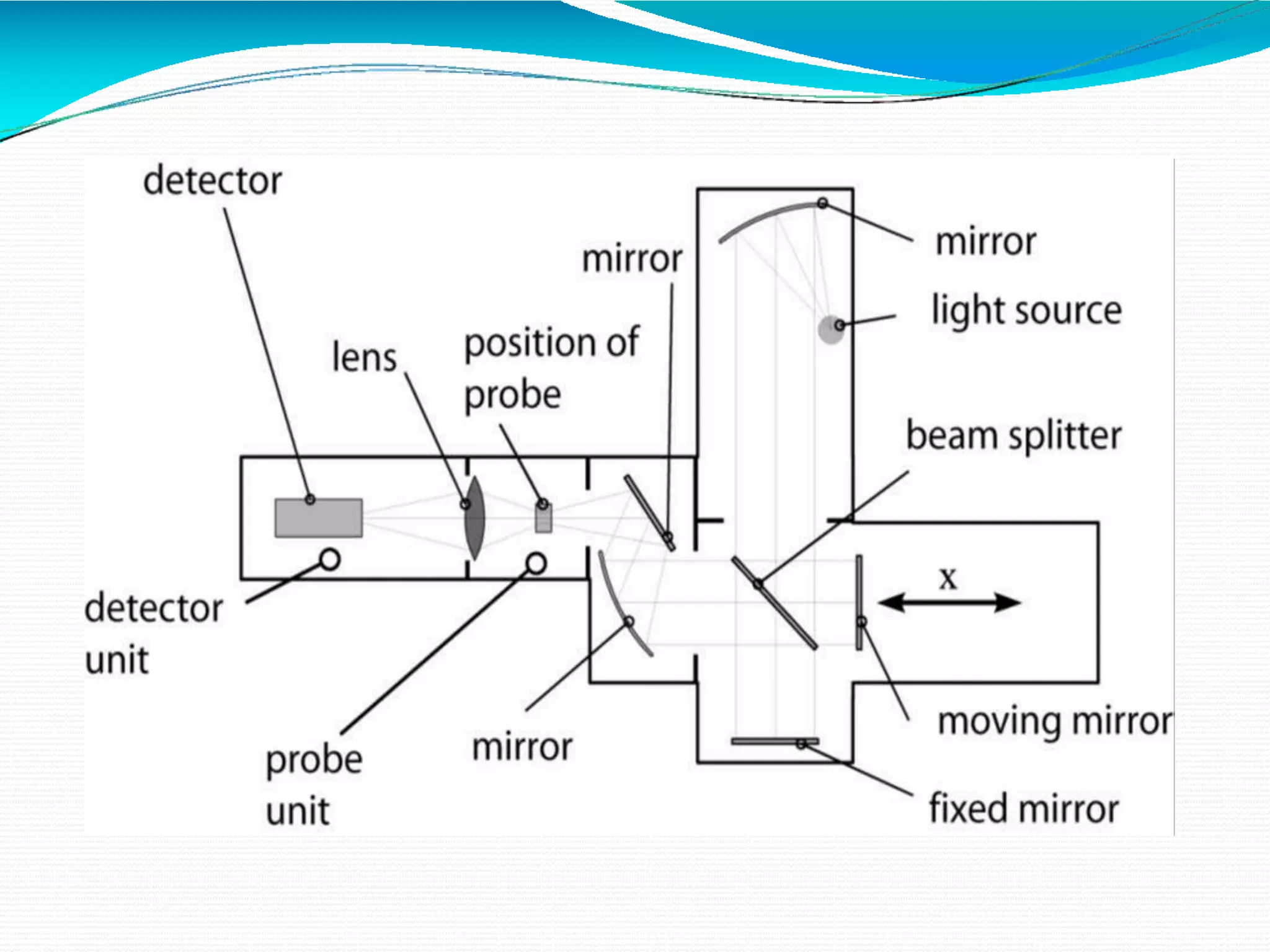
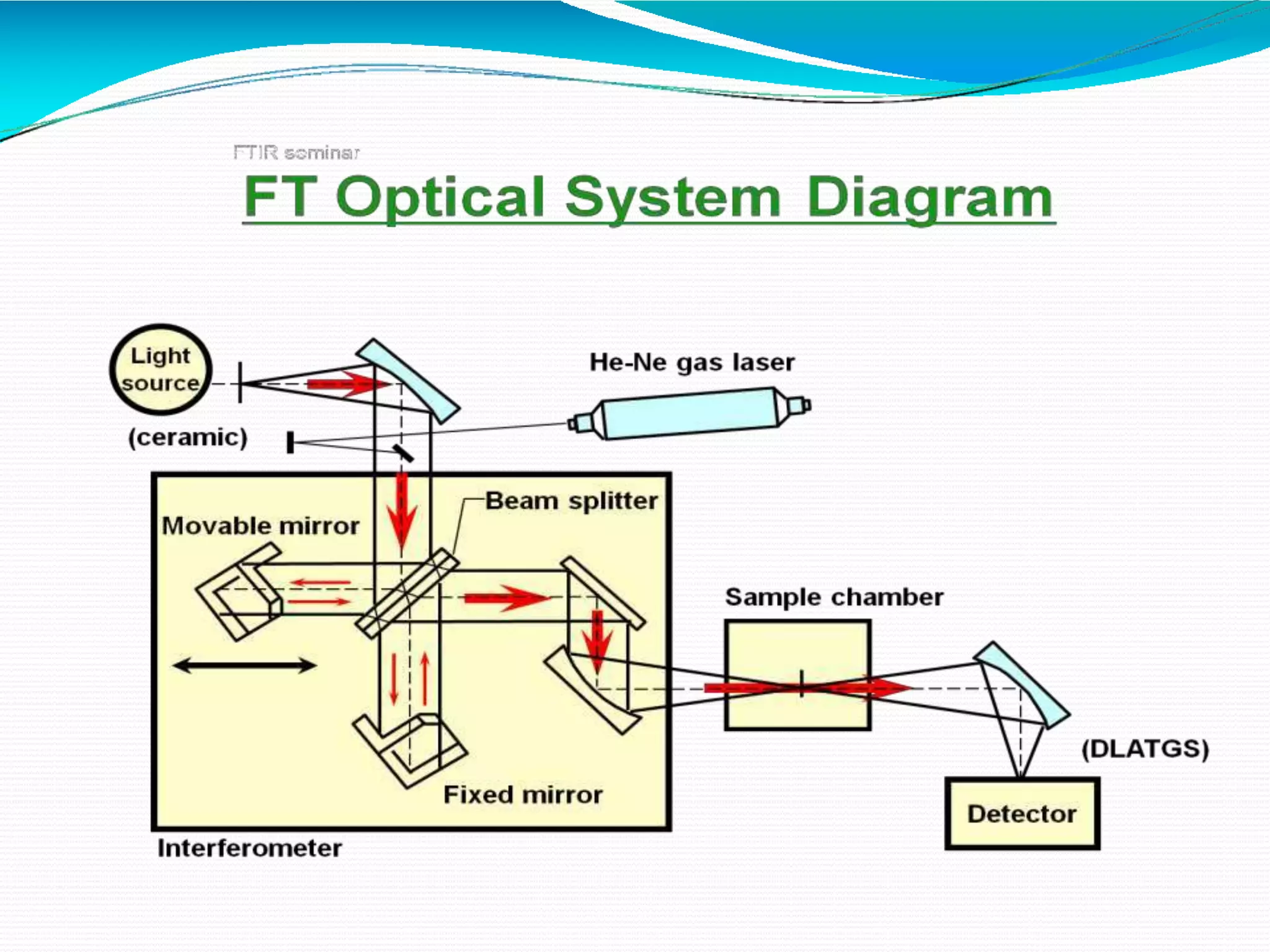
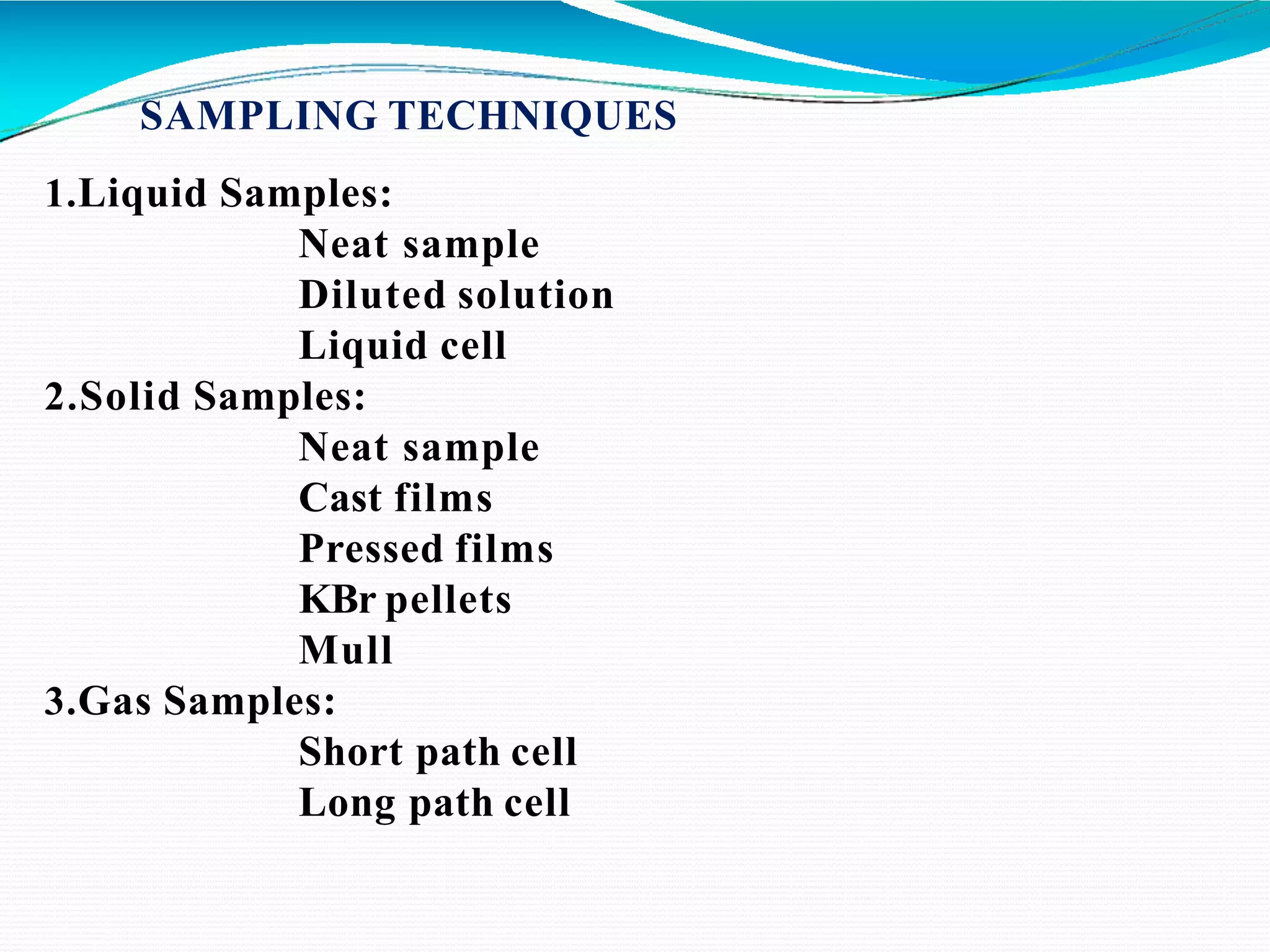
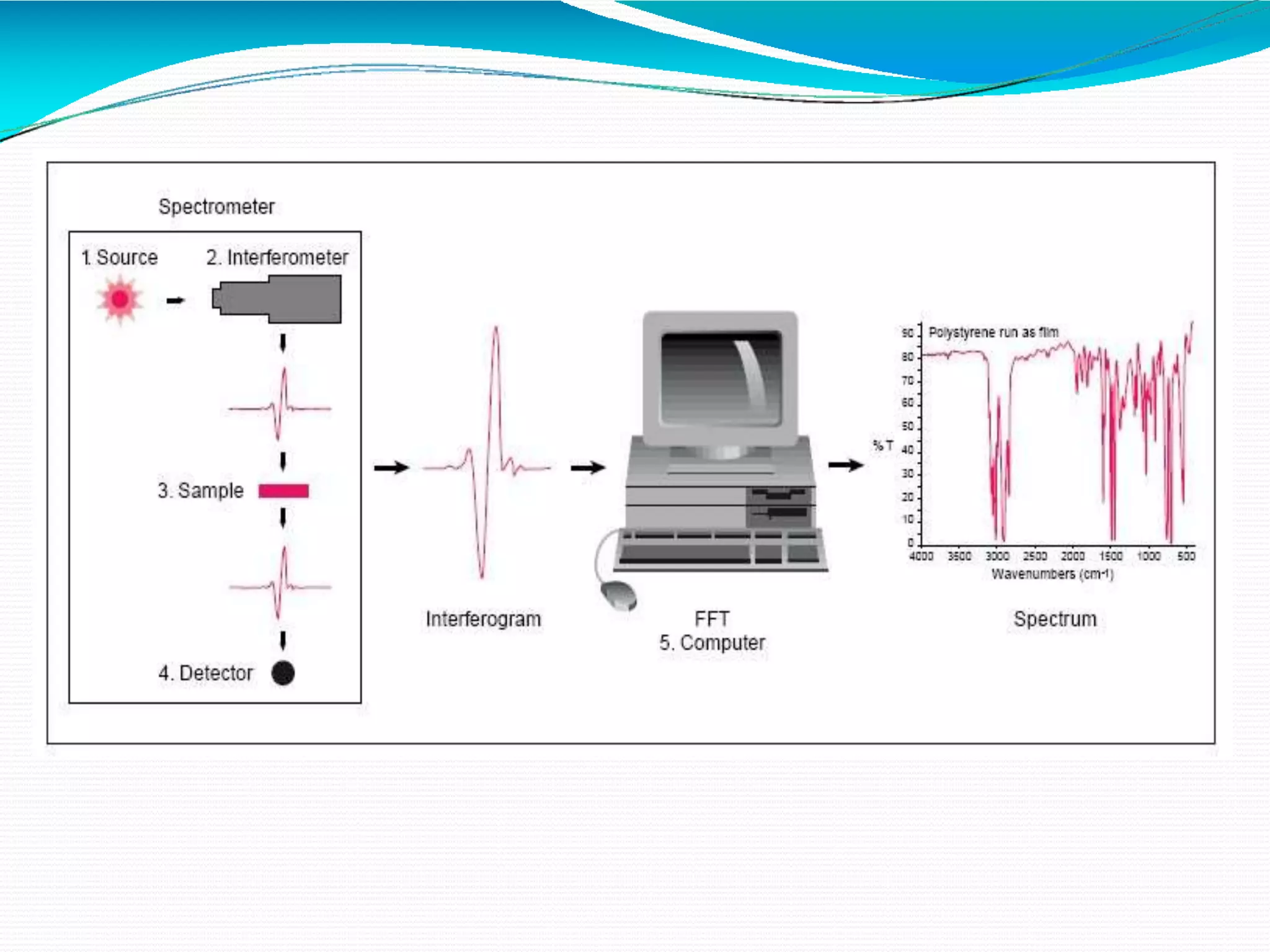
The document provides an overview of Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, explaining its principles, advantages, and the differences from dispersive infrared spectrometers. FT-IR utilizes an interferometer for rapid and sensitive measurements, allowing simultaneous collection of all infrared frequencies, which enhances efficiency and accuracy in identifying materials. Sampling techniques for various states of matter (liquid, solid, and gas) are also discussed, along with the instrumental process involved in obtaining infrared spectra.