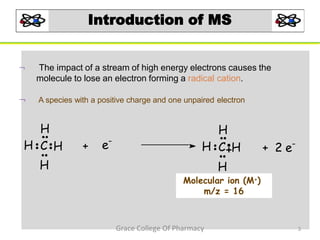
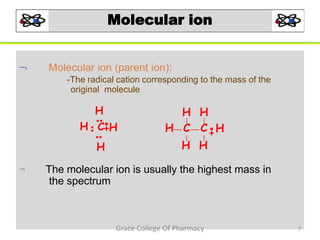
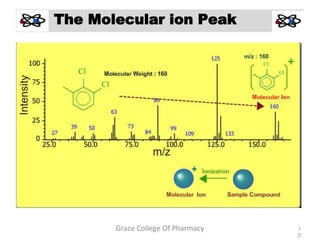
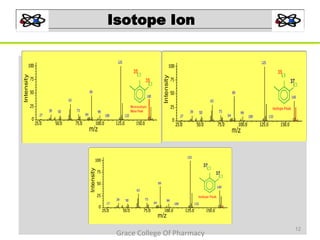
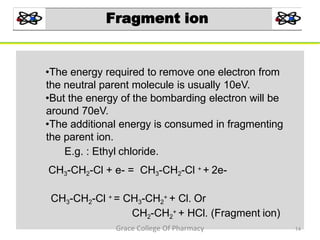
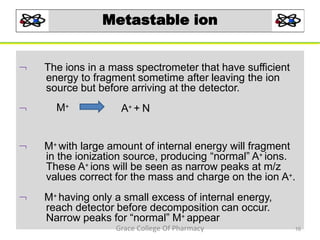
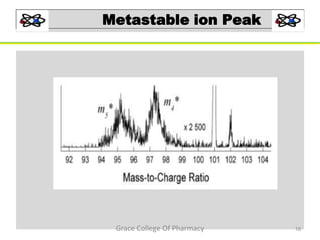
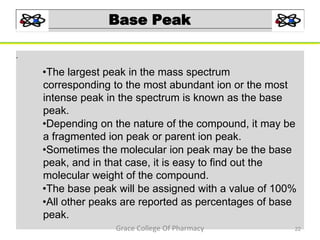
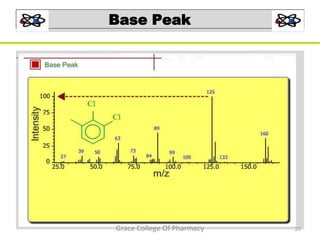
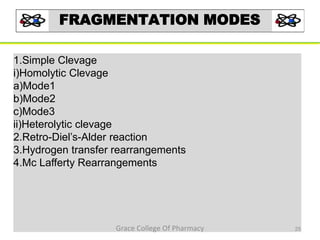
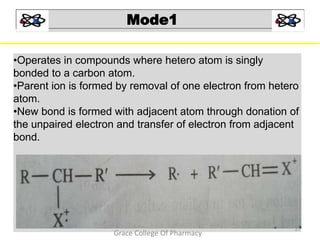
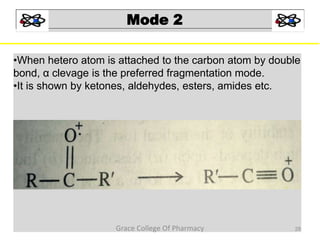
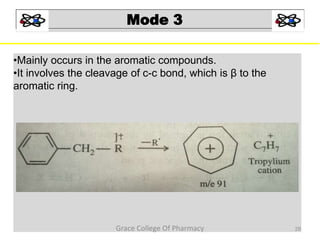
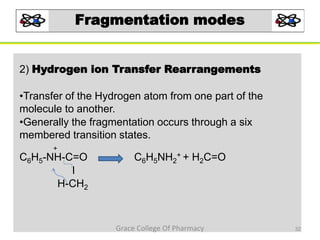
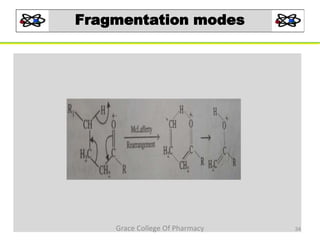
Mass spectrometry is a technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. It can be used to determine molecular masses and elucidate molecular structures of organic compounds. There are several types of ions produced including molecular ions, fragment ions, and isotope ions. Compounds undergo various fragmentation modes like homolytic cleavage, heterolytic cleavage, retro-Diels-Alder reactions, hydrogen transfers and McLafferty rearrangements. Mass spectrometry has applications in fields like drug development, environmental analysis, and clinical diagnosis.