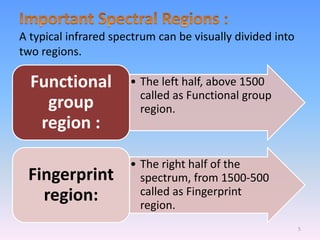
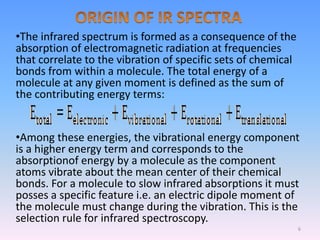
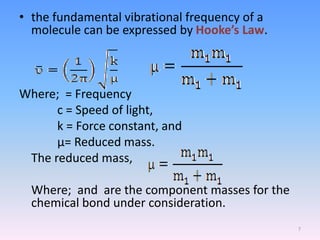
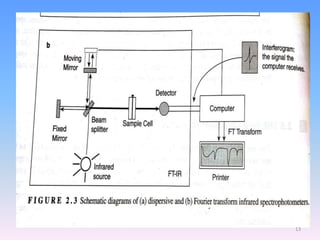
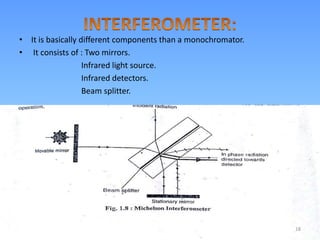
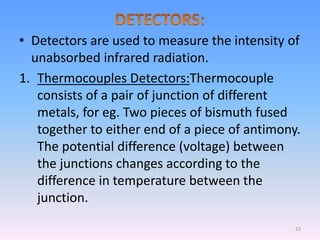
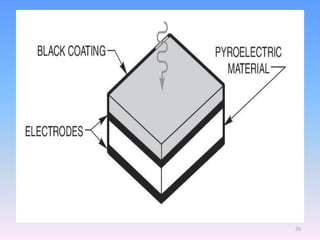
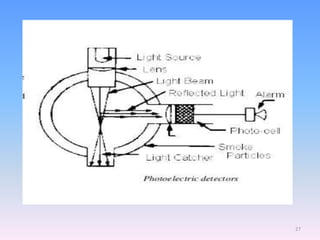
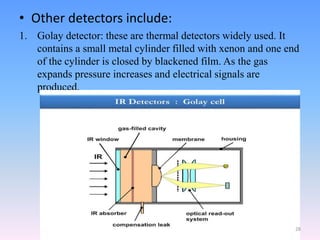
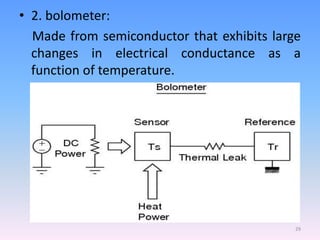
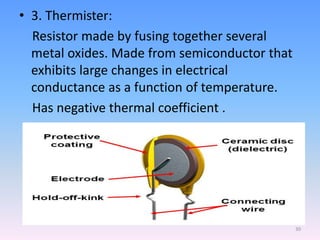
Infrared spectroscopy is a technique that uses infrared light to determine the functional groups present in molecules based on the vibrations of atoms. It works by passing infrared radiation through a sample and measuring the absorption of specific wavelengths, which correspond to vibrations between bonds of different atoms. The peaks in an infrared spectrum can identify functional groups and chemical bonds based on the wavelength of absorption. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is now commonly used as it allows simultaneous detection of all infrared wavelengths for faster analysis.