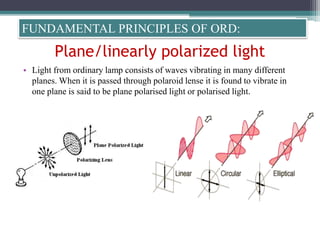
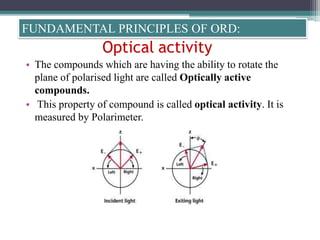
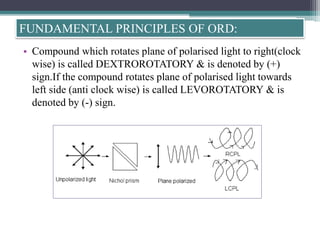
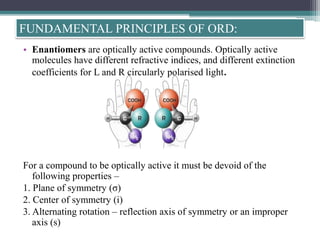
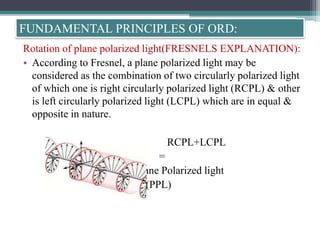
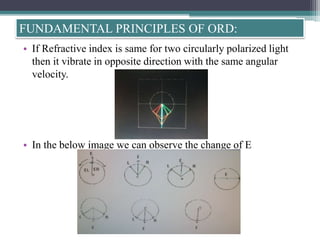
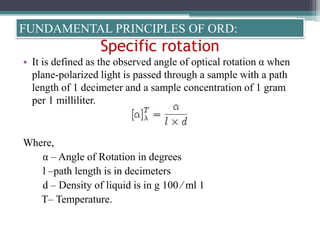
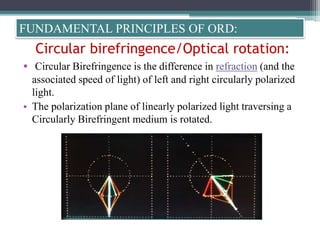
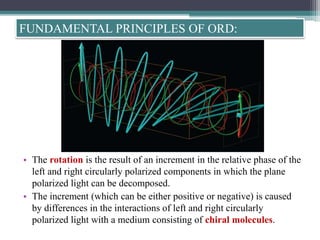
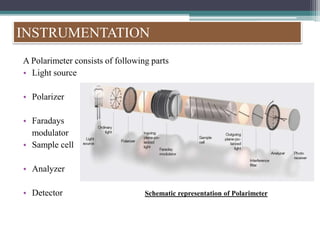
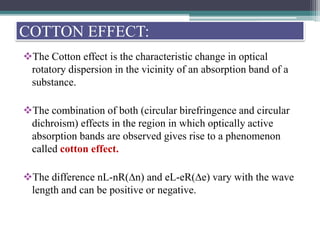
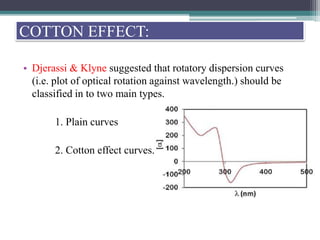
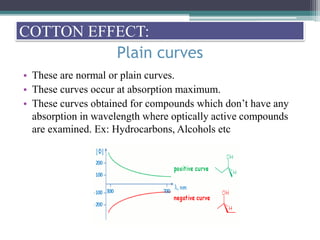
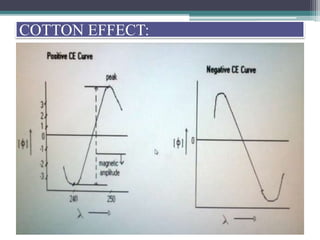
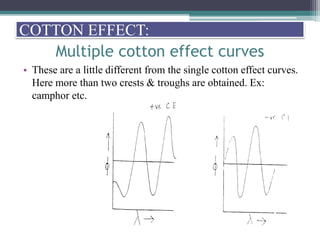
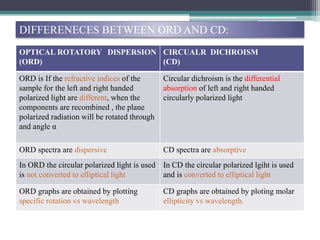
Optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) is the variation in optical rotation of a substance with changing wavelength of light. ORD can determine the absolute configuration of chiral molecules like metal complexes. It works by measuring how fast left and right circularly polarized light travels through a sample. A polarimeter measures the optical rotation as a function of wavelength in ORD spectroscopy. Key effects seen in ORD spectra include the Cotton effect, where peaks and troughs appear near absorption bands due to differences in how left and right polarized light interact with chiral molecules. ORD can be used to analyze chiral compounds and determine their stereochemistry.