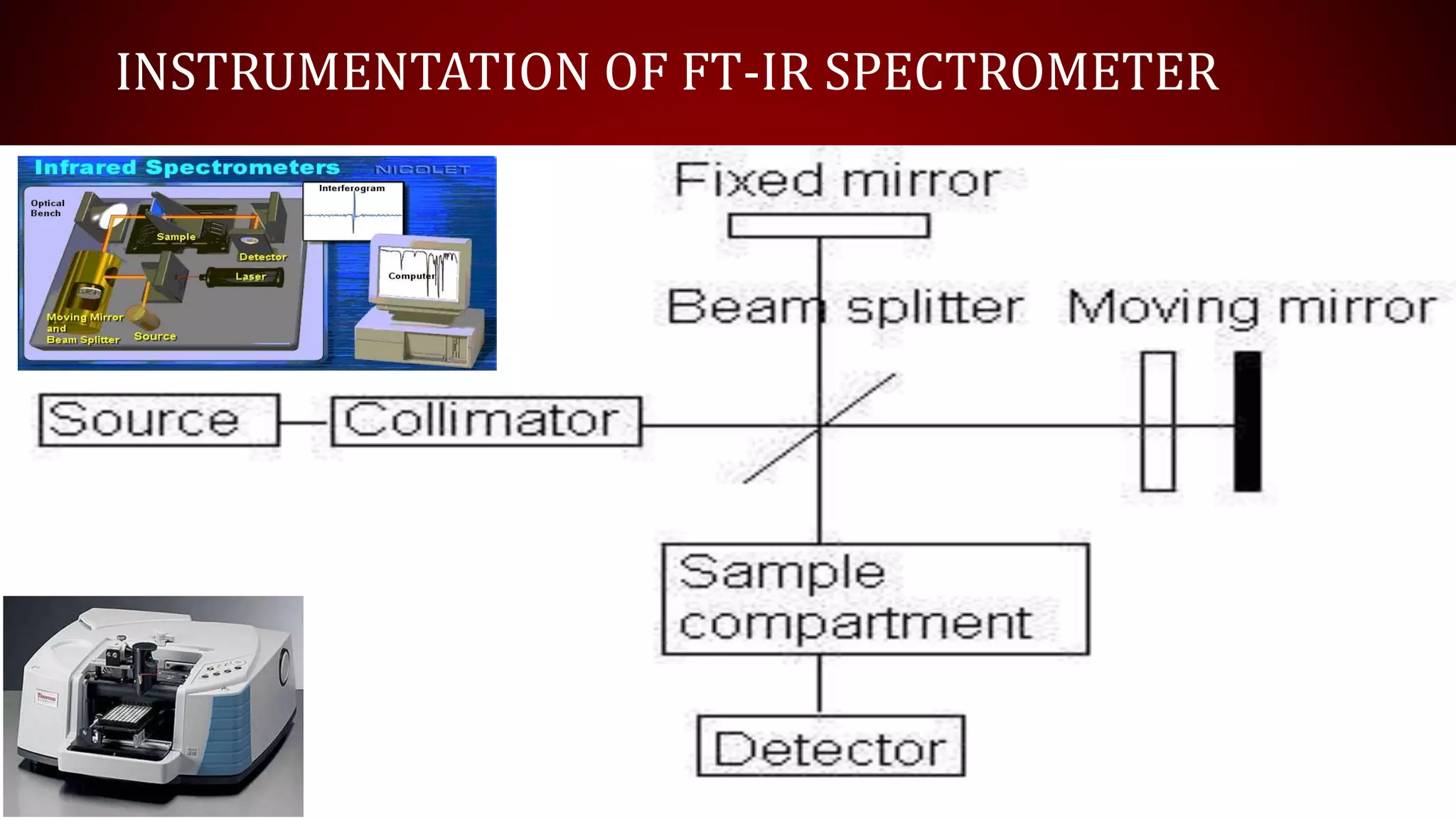
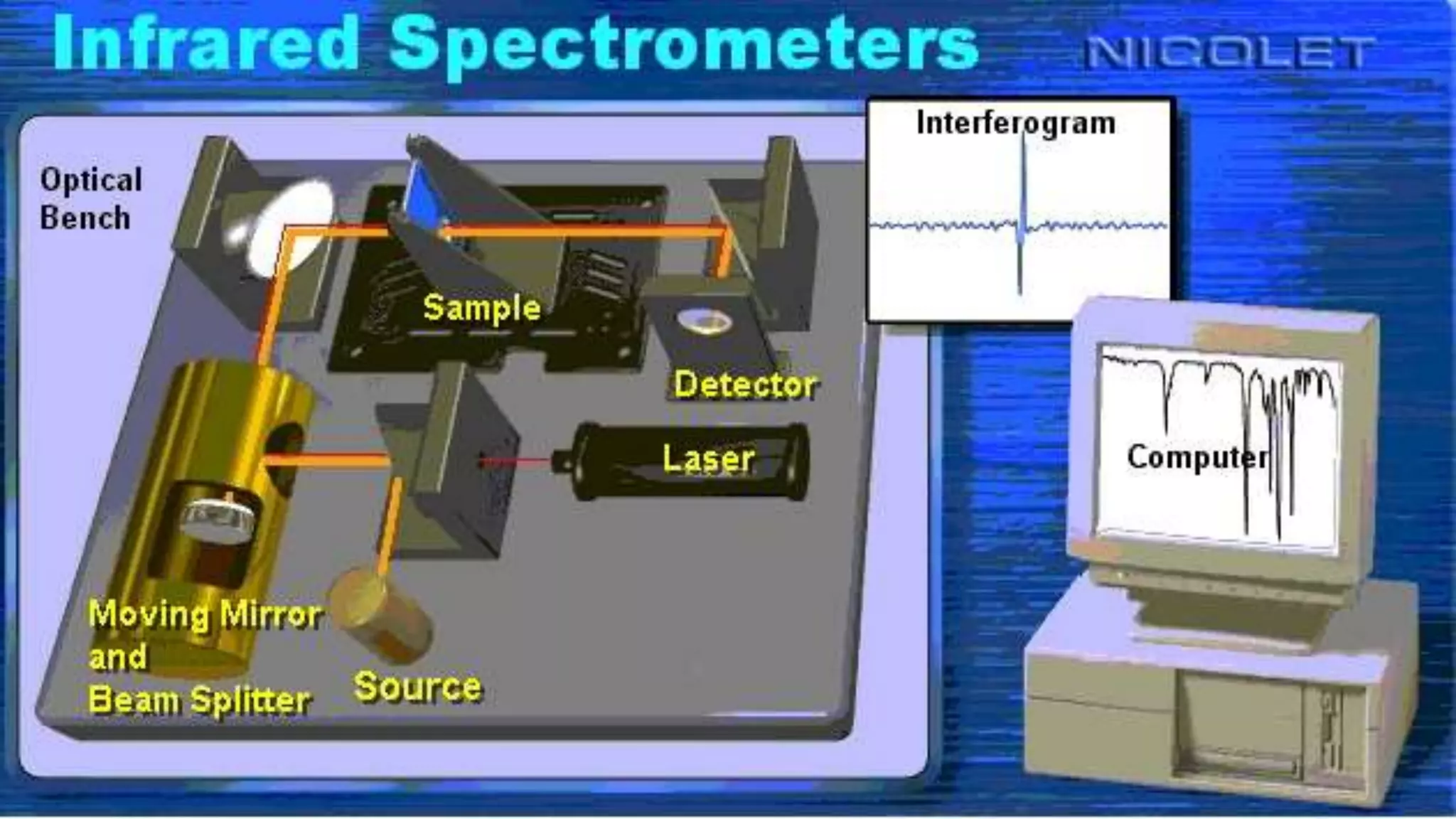
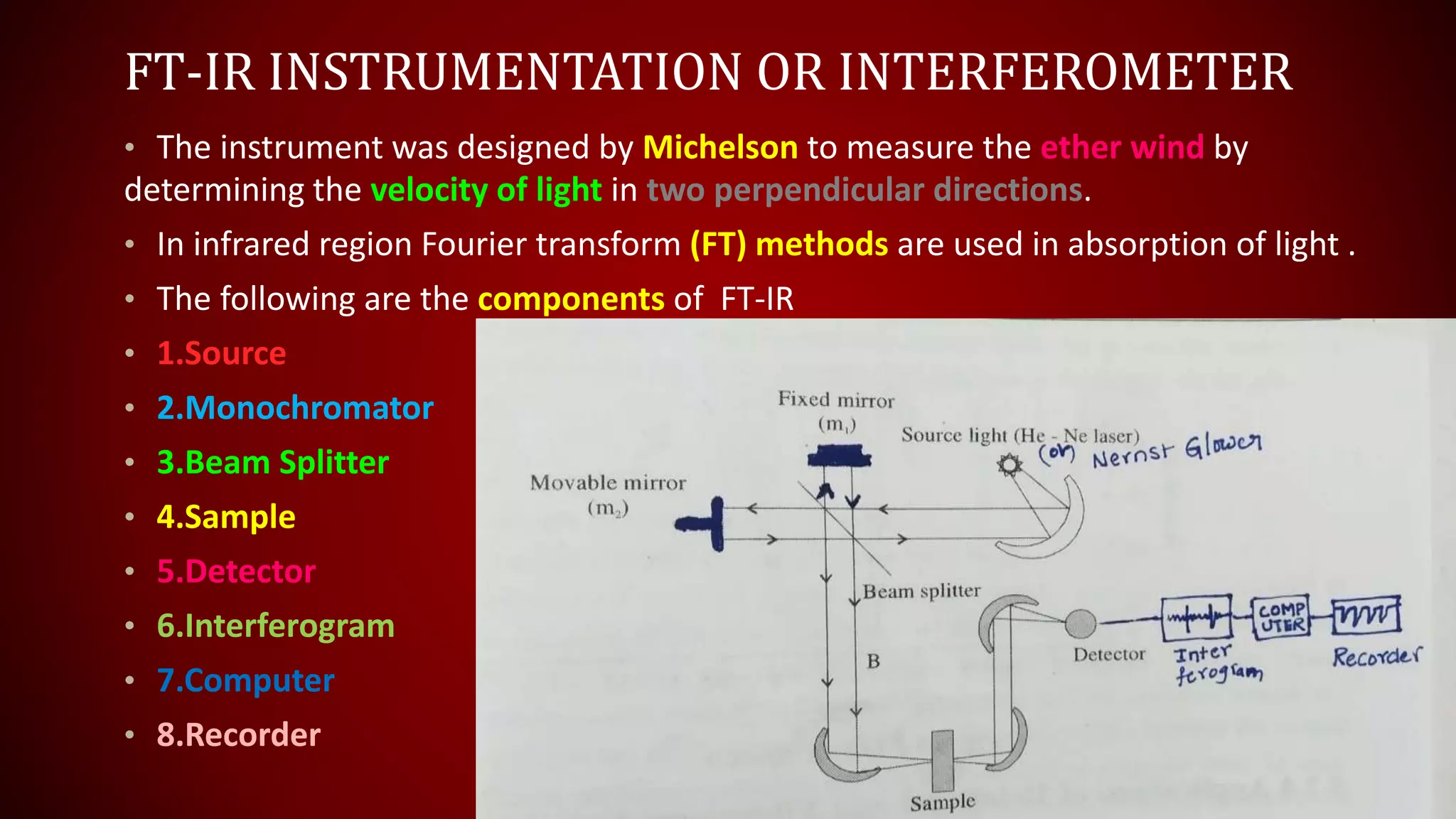
FT-IR spectroscopy uses a Michelson interferometer to measure the absorption of infrared light by molecules. The key components are a source, beam splitter, two mirrors, sample, detector, and computer. Infrared light from the source is split at the beam splitter, reflected by the mirrors, and recombined to generate an interferogram, which is Fourier transformed by the computer into an infrared absorption spectrum. FT-IR spectroscopy can be used to determine molecular structure in gases, explore interstellar composition, perform quantitative analysis, and identify functional groups and bonds based on their characteristic vibrational frequencies.