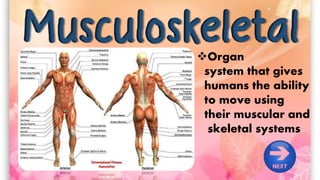
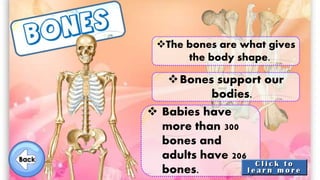
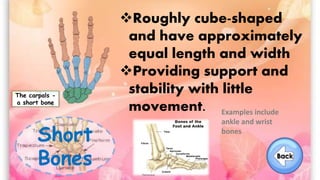
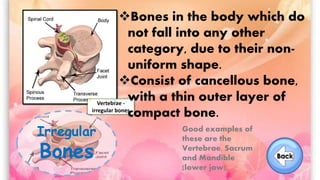
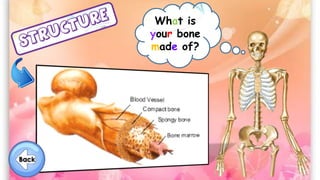
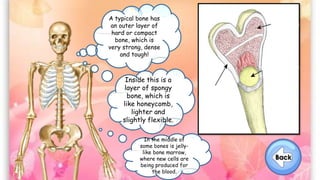
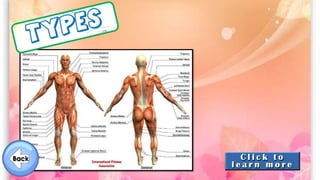
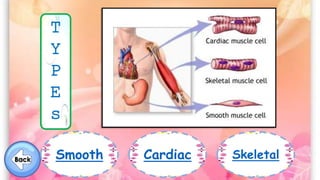
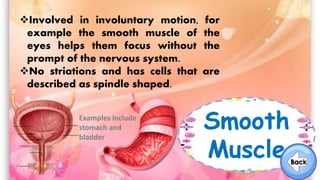
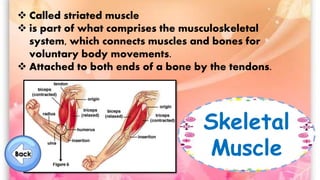
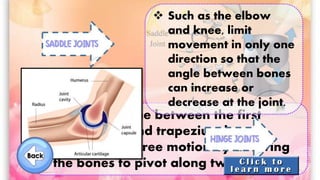
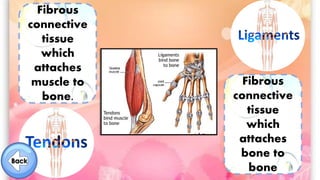
The document discusses the human musculoskeletal system, detailing the types of bones (long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid) and their functions such as providing support, protection, and enabling movement. It also explains the different types of muscles (smooth, cardiac, and skeletal) that facilitate movement, and describes joints, ligaments, and tendons that connect bones and muscles. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of bones and muscles in maintaining body structure and function.