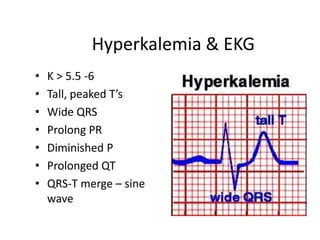
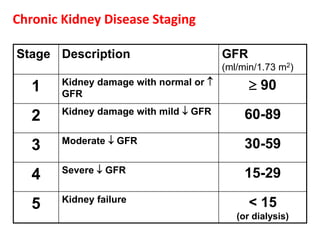
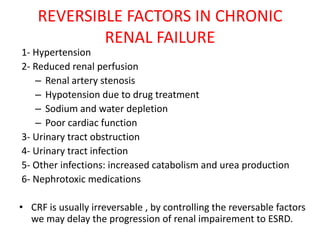
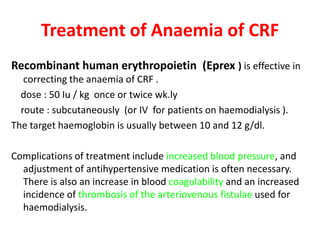
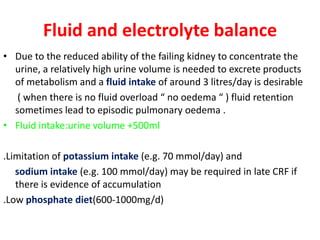
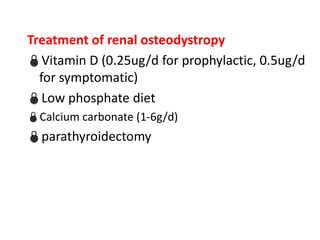
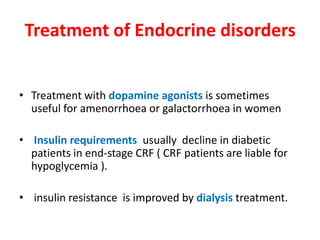
Chronic renal failure refers to the irreversible deterioration of renal function over years. It initially presents as biochemical abnormalities and eventually leads to uraemic symptoms as the excretory, metabolic and endocrine functions of the kidneys fail. Common causes include diabetes, hypertension, and glomerulonephritis. Management involves identifying and treating the underlying disease, slowing progression, managing complications, and renal replacement therapy for end-stage disease.