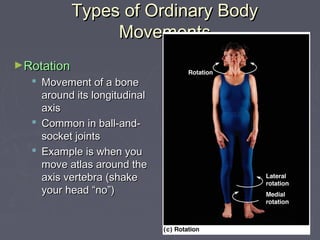
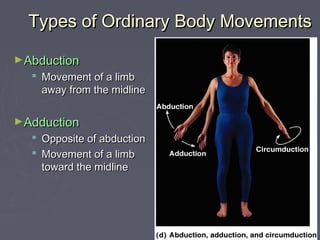
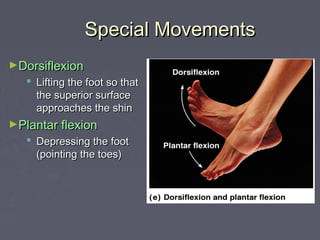
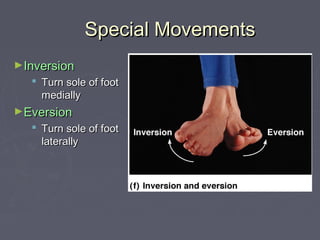
Muscles allow the body to move by connecting to bones at attachment points called origins and insertions. There are several types of basic movements including flexion, extension, rotation, abduction, and adduction. Flexion decreases joint angles while extension increases them. Rotation turns bones around their longitudinal axis. Abduction moves limbs away from the body midline while adduction moves them towards it. Some special movements are dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot, inversion and eversion of the ankle, supination and pronation of the forearm, and opposition of the thumb.