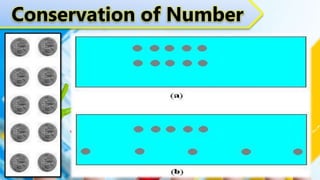
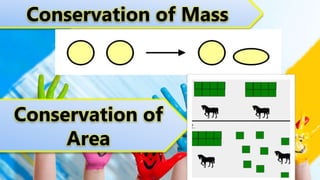
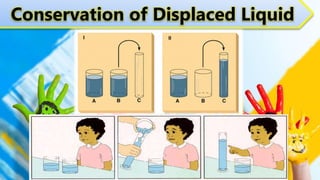
Early childhood from ages 2-6 is a period of rapid cognitive development. Children progress through Piaget's pre-operational stage, developing the ability for representational thought and pretend play. However, at this stage children have limitations in logical thinking and reasoning. They do not understand the concept of conservation or how to make logical inferences. Memory skills also develop during this stage, with recognition abilities stronger than recall. Vygotsky's sociocultural theory emphasizes that cognitive development occurs through social interactions and guided learning from adults and more capable peers.