The document provides an introduction to the muscular system, including:
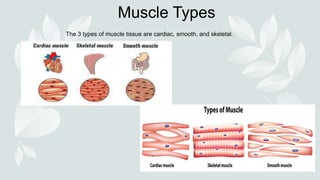
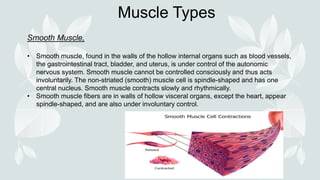
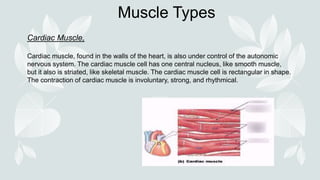
- The three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
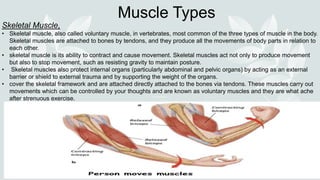
- Skeletal muscle is voluntary and allows movement, while smooth and cardiac muscles are involuntary.
- Muscles are named based on size, shape, direction, location, number of origins, and action.
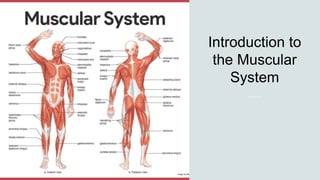
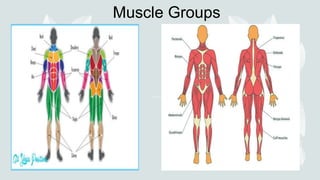
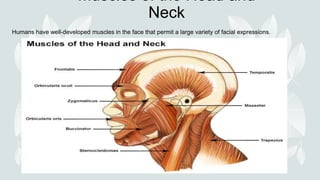
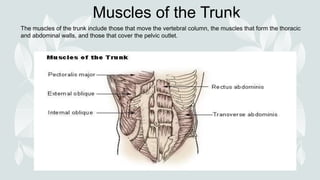
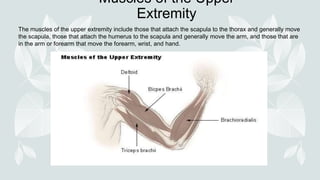
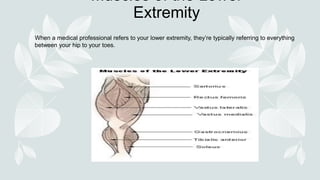
- The four major muscle groups are those of the head/neck, trunk, upper extremities, and lower extremities.
- Key functions of muscles include motion, posture, joint stability, and heat production.





![Special attention:
•If you activate the muscle in its lengthened state, then it gradually stretches further then relaxes more; eventually
becoming stronger. So, activate muscles that are stretched in a pose.
•When a muscle is stretched long enough, then the muscle relaxes eventually. So always hold the posture longer
[at least 15 seconds].
•If you activate or tense one muscle, the surrounding group of muscles is also fired and eventually leads to better
strength and stability.
•Counter poses: In yoga you can use counter poses to successfully create balance. Vinyasas are counter poses
[Upward dog/ downward dog]. It is important to use counter poses too in your classes since they balance and
reset the muscles. For example, forward bends followed by back bends, side bends by doing on both sides,
internal rotation by external rotation.
•As you move from one pose to the next during a yoga session, try to enter and exit the pose with grace and
elegance. A smoother, gentler, and more controlled movement strengthens the body, quiets the mind induces
relaxation and control.
•Creating internal heat within your body gives you more flexibility and helps your body release toxins.
•Active stretching is where you assume a position and hold it by using the relative muscle groups. It builds up
strength in muscles involved.
•Passive stretching is where you assume and hold a pose with the help or support of parts of your body, partner,
blocks, or other assistance. It helps with cooling down and reduces post-workout soreness and tension.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/muscularsystem-210129055752/85/Muscular-system-17-320.jpg)