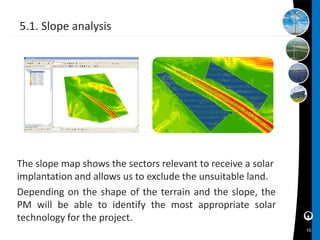
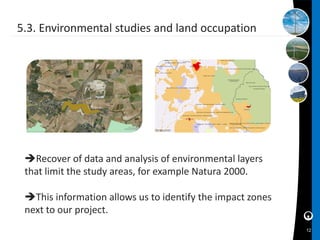
This document discusses how geographic information systems (GIS) can be used to plan and site solar energy projects. It describes Eolfi, a company that develops solar and wind projects. GIS tools like spatial analysis and elevation data are used to identify optimal locations based on slope, aspect, shadows, environmental constraints, and grid connectivity. The GIS model enables evaluation of potential sites and informs siting decisions to reduce costs and environmental impacts. In conclusion, the document states that GIS provides a practical and reliable way to map suitable areas and make more efficient siting decisions.