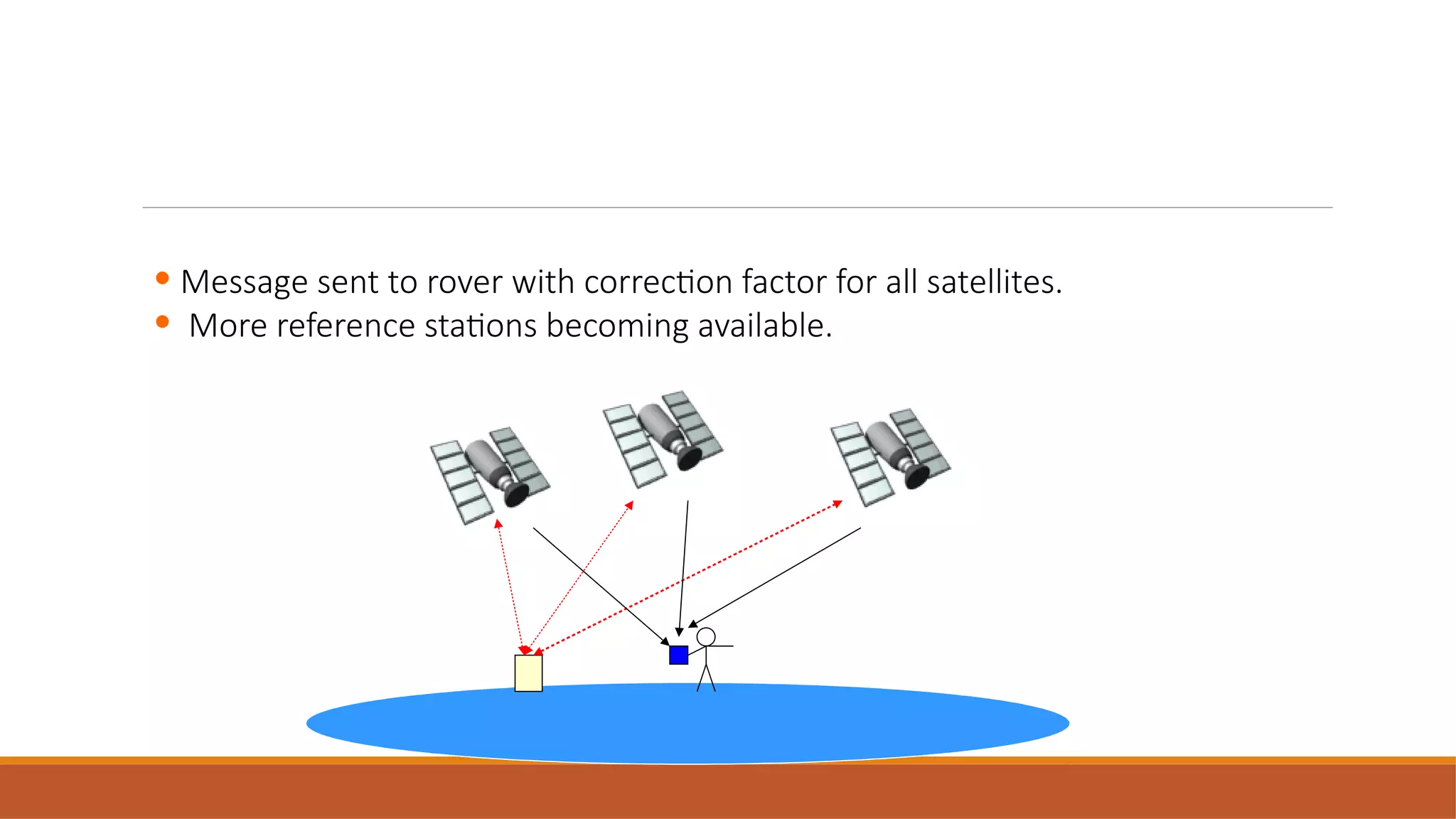
This document discusses differential GPS (DGPS), which improves the accuracy of GPS positioning. It works by using a stationary GPS receiver at a known location to calculate error corrections, which are transmitted to a roving receiver to improve its position accuracy. DGPS can reduce GPS errors from sources like atmospheric delays, satellite orbit issues, and multipath effects, providing sub-meter accuracy compared to the 5-10 meter accuracy of standard GPS. It allows real-time position correction or post-processed correction through data from a fixed base station.