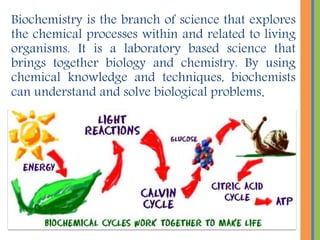
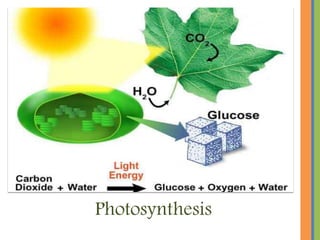
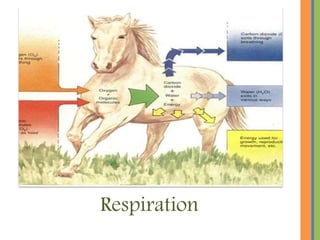
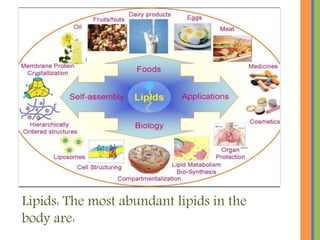
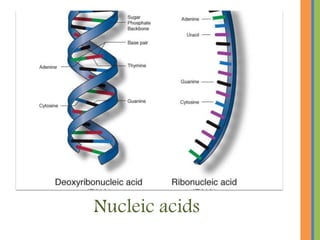
Biochemistry is the science that studies chemical processes in living organisms, combining biology and chemistry to address biological issues. Key topics include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, detailing their structures, functions, and roles in metabolism. The document emphasizes the significance of these biomolecules in energy storage, cellular function, and maintaining life.