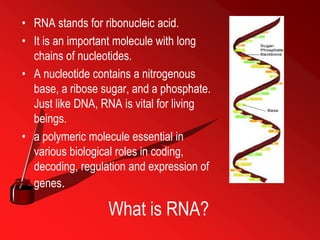
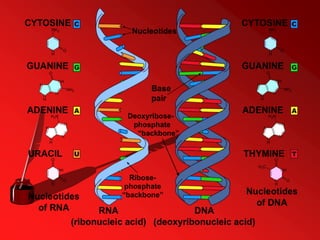
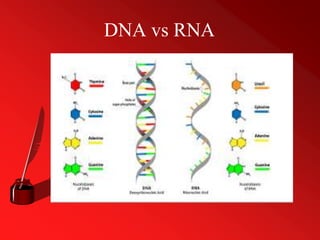
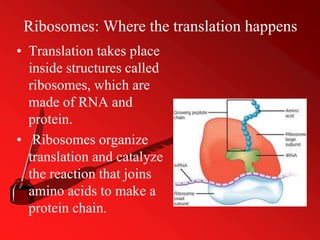
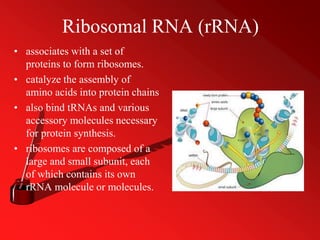
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a crucial molecule composed of long chains of nucleotides, serving essential roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and gene expression. It differs from DNA as a single-stranded molecule that contains ribose sugar and uracil instead of thymine and plays various roles including messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) in protein synthesis. Additionally, RNA can act as enzymes known as ribozymes, showcasing its versatility in biological processes.