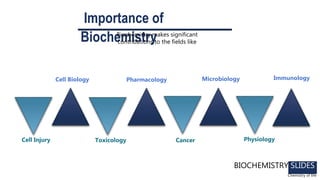
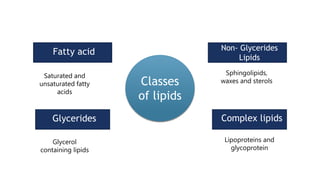
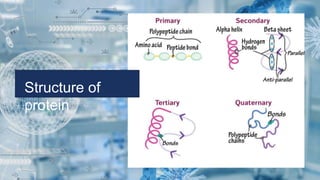
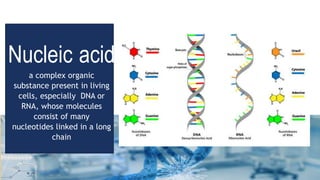
Biochemistry is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, focusing on cellular components like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. It plays a critical role in various fields such as cancer biology, immunology, and pharmacology. The document details the classification of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, emphasizing their structure and functions.