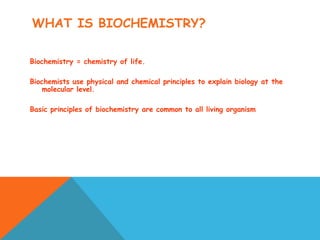
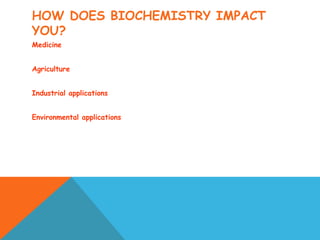
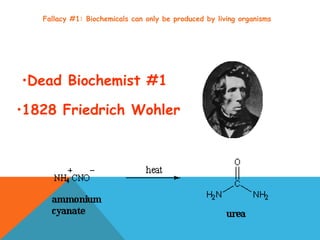
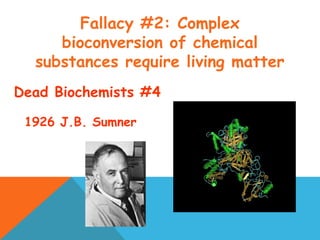
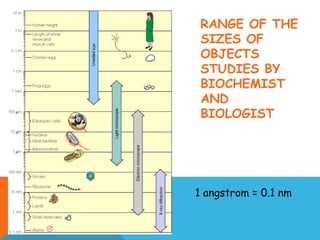
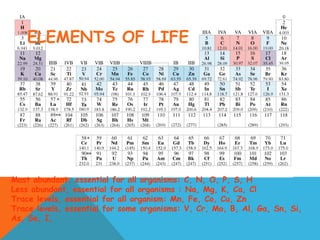
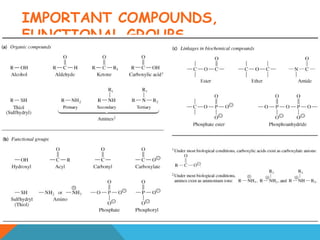
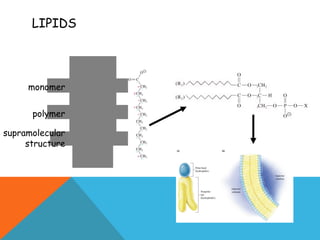
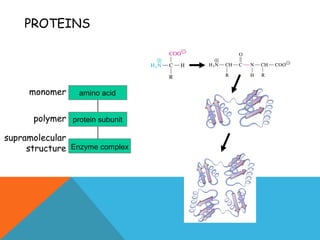
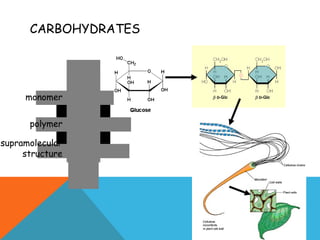
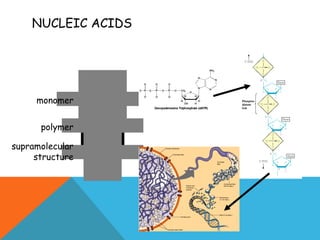
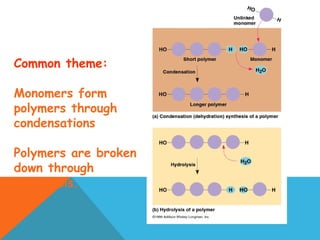
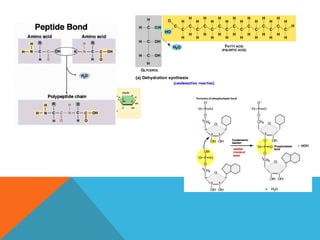
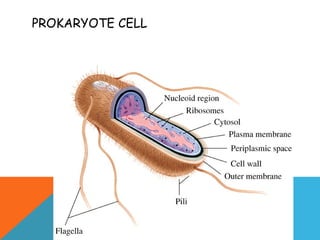
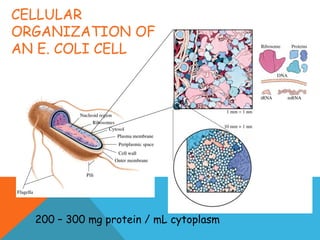
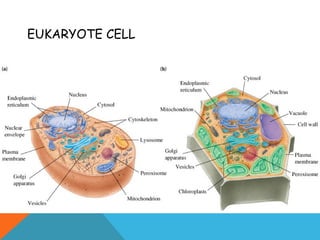
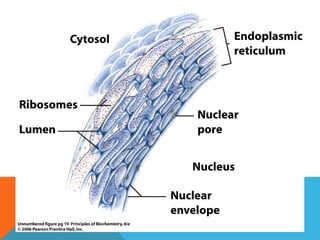
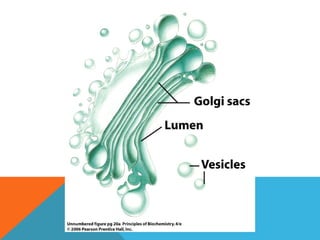
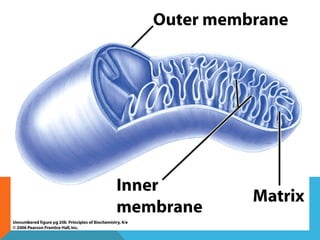
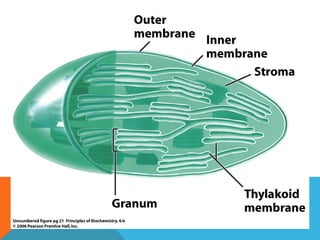
This document provides an introduction to biochemistry from Dr. Armaan Singh. It begins by emphasizing the importance of attending class, participating in clicker questions for extra credit, and seeing the professor during office hours. The document then defines biochemistry as the chemistry of life and explains how it impacts fields like medicine, agriculture, and industry. It proceeds to outline major areas of biochemistry like macromolecules, metabolism, genetics, and protein synthesis. The document concludes by discussing the cellular organization of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.