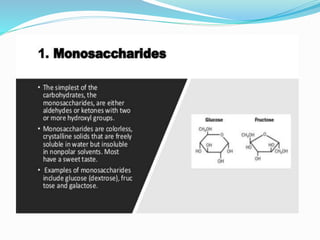
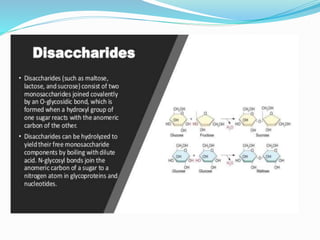
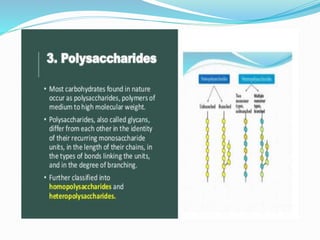
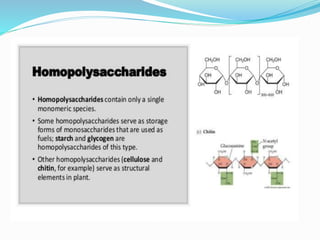
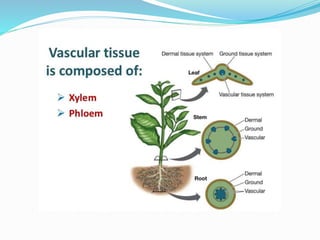
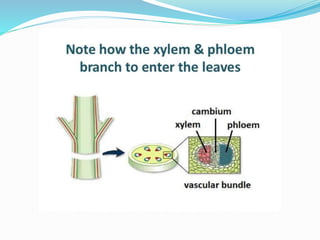
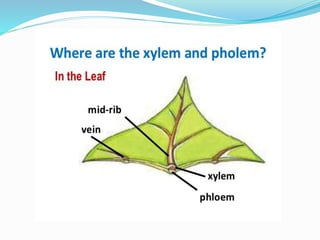
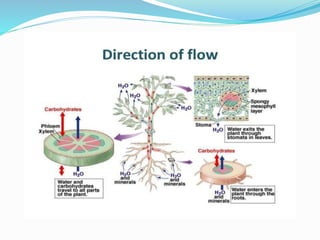
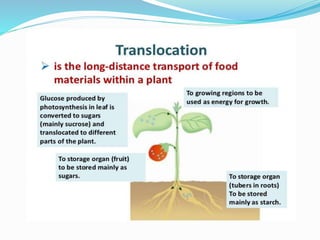
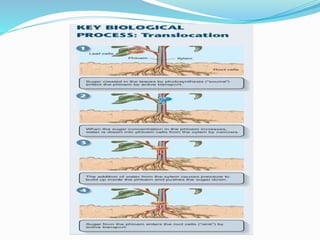
Carbohydrates are organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, essential as they provide energy and structure in living organisms. They are classified into monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides, with significant roles in both diet and pharmaceutical applications. Diseases related to carbohydrate metabolism include diabetes and lactose intolerance, highlighting their importance in health and nutrition.