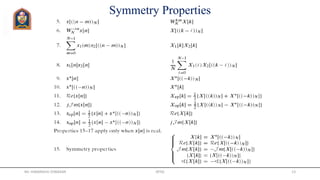
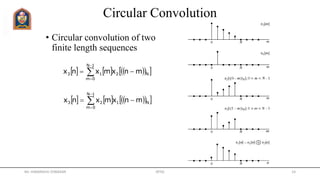
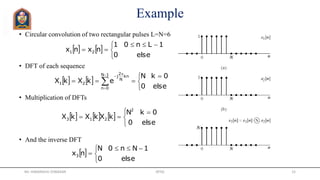
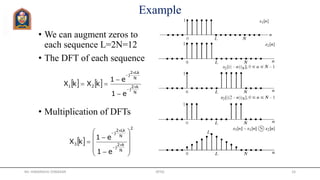
The document discusses the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT). It explains that the DFT represents a finite-length sequence by the samples of its Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT). These samples are called the DFT coefficients of the sequence. The DFT provides a transformation between the time and frequency domains. It has various properties like linearity, duality, and relationships between shifting sequences and their DFTs. Circular convolution in the time domain can be computed as multiplication of DFT coefficients in the frequency domain. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts.


![Sampling the Fourier Transform
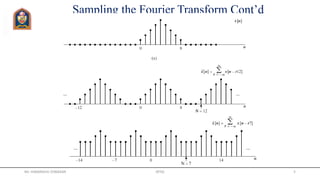
• Consider an aperiodic sequence with a Fourier transform
• Assume that a sequence is obtained by sampling the DTFT
• Since the DTFT is periodic resulting sequence is also periodic
• We can also write it in terms of the z-transform
• The sampling points are shown in figure
• could be the DFS of a sequence
• Write the corresponding sequence
kN/2j
kN/2
j
eXeXkX
~
jDTFT
eX]n[x
kN/2j
ez
eXzXkX
~
kN/2
kX
~
1N
0k
knN/2j
ekX
~
N
1
]n[x~
Mr. HIMANSHU DIWAKAR JRTGI 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thediscretefouriertransformdsp4-170119084954/85/The-discrete-fourier-transform-dsp-4-3-320.jpg)
![Sampling the Fourier Transform Cont’d
• The only assumption made on the sequence is that DTFT exist
• Combine equation to get
• Term in the parenthesis is
• So we get
m
mjj
emxeX
1N
0k
knN/2j
ekX
~
N
1
]n[x~
kN/2j
eXkX
~
mm
1N
0k
mnkN/2j
1N
0k
knN/2j
m
kmN/2j
mnp~mxe
N
1
mx
eemx
N
1
]n[x~
r
1N
0k
mnkN/2j
rNmne
N
1
mnp~
rr
rNnxrNnnx]n[x~
Mr. HIMANSHU DIWAKAR JRTGI 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thediscretefouriertransformdsp4-170119084954/85/The-discrete-fourier-transform-dsp-4-4-320.jpg)

![The Discrete Fourier Transform
• Consider a finite length sequence x[n] of length N
• For given length-N sequence associate a periodic sequence
• The DFS coefficients of the periodic sequence are samples of the DTFT of x[n]
• Since x[n] is of length N there is no overlap between terms of x[n-rN] and we can
write the periodic sequence as
• To maintain duality between time and frequency
• We choose one period of as the Fourier transform of x[n]
1Nn0ofoutside0nx
r
rNnxnx~
NkXNmodkXkX
~
kX
~
else0
1Nk0kX
~
kX
NnxNmodnxnx~
Mr. HIMANSHU DIWAKAR JRTGI 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thediscretefouriertransformdsp4-170119084954/85/The-discrete-fourier-transform-dsp-4-7-320.jpg)
![The Discrete Fourier Transform Cont’d
• The DFS pair
• The equations involve only on period so we can write
• The Discrete Fourier Transform
• The DFT pair can also be written as
1N
0k
knN/2j
ekX
~
N
1
]n[x~
1N
0n
knN/2j
e]n[x~kX
~
else0
1Nk0e]n[x~
kX
1N
0n
knN/2j
else0
1Nk0ekX
~
N
1
]n[x
1N
0k
knN/2j
1N
0n
knN/2j
e]n[xkX
1N
0k
knN/2j
ekX
N
1
]n[x
]n[xkX DFT
Mr. HIMANSHU DIWAKAR JRTGI 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thediscretefouriertransformdsp4-170119084954/85/The-discrete-fourier-transform-dsp-4-8-320.jpg)
![Example
• The DFT of a rectangular pulse
• x[n] is of length 5
• We can consider x[n] of any
length greater than 5
• Let’s pick N=5
• Calculate the DFS of the
periodic form of x[n]
else0
,...10,5,0k5
e1
e1
ekX
~
5/k2j
k2j
4
0n
n5/k2j
Mr. HIMANSHU DIWAKAR JRTGI 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thediscretefouriertransformdsp4-170119084954/85/The-discrete-fourier-transform-dsp-4-9-320.jpg)
![Example Cont’d
• If we consider x[n] of length 10
• We get a different set of DFT
coefficients
• Still samples of the DTFT but in
different places
Mr. HIMANSHU DIWAKAR JRTGI 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thediscretefouriertransformdsp4-170119084954/85/The-discrete-fourier-transform-dsp-4-10-320.jpg)