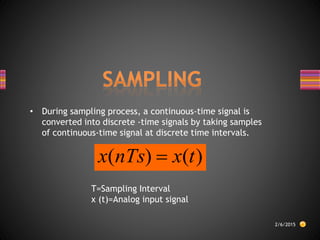
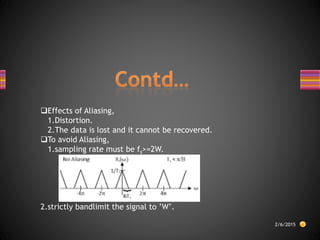
The document discusses sampling theory and analog-to-digital conversion. It begins by explaining that most real-world signals are analog but must be converted to digital for processing. There are three steps: sampling, quantization, and coding. Sampling converts a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal by taking samples at regular intervals. The sampling theorem states that the sampling frequency must be at least twice the highest frequency of the sampled signal to avoid aliasing. Finally, it provides an example showing how to calculate the minimum sampling rate, or Nyquist rate, given the highest frequency of a signal.