Embed presentation
Download to read offline





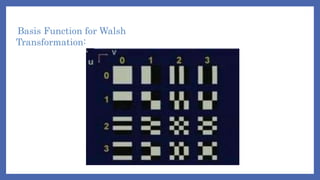


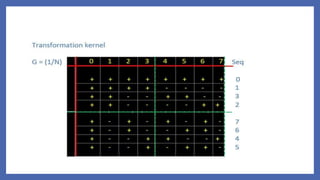
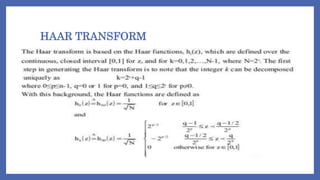
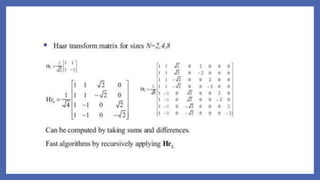


The document compares the Walsh and Haar transforms used in digital image processing. It outlines the mathematical formulations for both forward and inverse transforms, highlighting the similarities and differences in terms of energy compaction and speed of computation. While the Walsh transform features more complex energy distribution, the Haar transform is noted for its speed and orthogonality, albeit with a weaker energy compaction for images.












