The document discusses the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm.
1) The FFT is a set of techniques that exploits symmetries in the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to make its computation much faster. The speedup increases with larger DFT sizes.
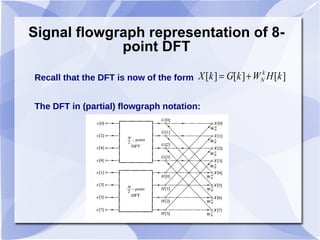
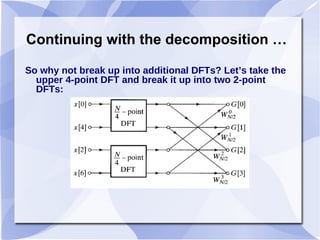
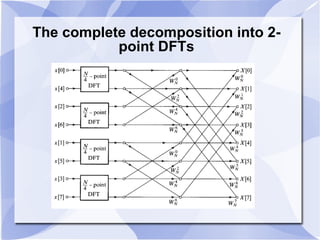
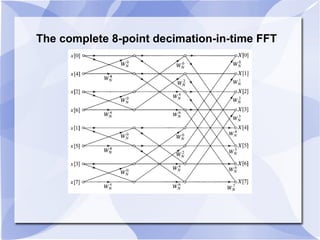
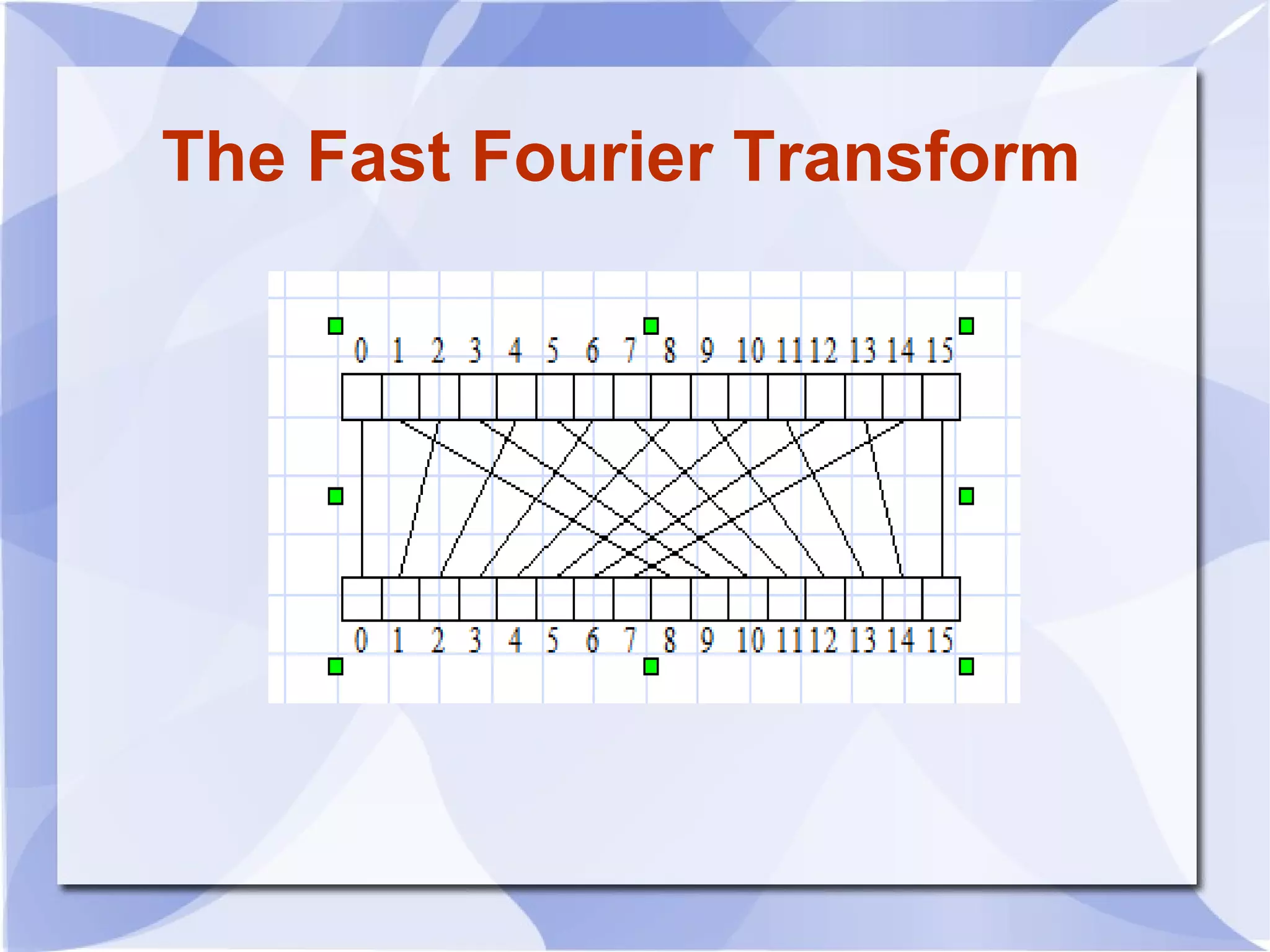
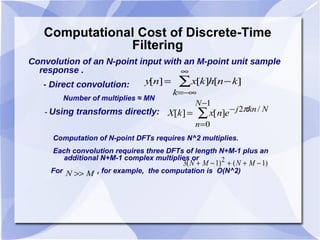
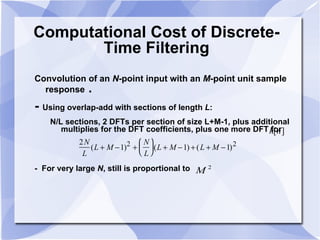
2) The Cooley-Tukey algorithm decomposes an N-point DFT into smaller DFTs by splitting the indices, resulting in an algorithm that is proportional to NlogN operations rather than N^2.
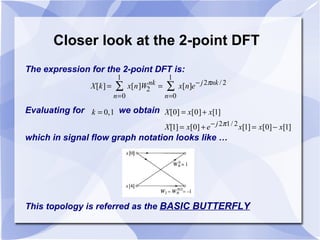
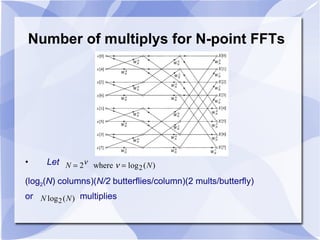
3) The algorithm can be represented as a series of "butterfly" operations, with each butterfly requiring only 2 multiplications. This reduces the number of multiplications needed compared to direct computation of the DFT.


![The Cooley-Tukey decimation-in-time algorithm Splitting indices in time , we have obtained But and So N/2 -point DFT of x[2r] N/2 -point DFT of x[2r+1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fftppt-110603180956-phpapp01/85/Fft-ppt-6-320.jpg)