The document discusses the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and its relationship to the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) and discrete Fourier series (DFS). It begins by introducing the DTFT as a theoretical tool to evaluate frequency responses, but notes it cannot be directly computed. The DFT solves this issue by sampling the frequency spectrum. It then discusses how the DFS represents periodic discrete-time signals using complex exponentials, unlike the continuous-time Fourier series. The key properties of the DFS such as linearity, time-shifting, duality, and periodic convolution are also covered. Finally, it discusses how the continuous-time Fourier transform (CTFT) of periodic signals relates to the DFS through Poisson's sum

![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 2
Introduction
The DTFT is a theoretical tool to evaluate the frequency response of
signals and systems
Unfortunately, it cannot be computed using a digital computer
Solution: Sample the frequency spectrum DFT
Unlike the CTFT, the DTFT does not have a duality relationship, i.e. if
x(t) ⇔ X(jΩ), then X(t) ⇔ 2πx(-jΩ), but no such relationship exists
between x[n] and X(ejω)
As seen in the sequel, there is a duality relationship between x[n] and X[k]
Idea:
Sample the (continuous) function X(ejω)
Corresponding function in time now also becomes periodic (but still
discrete-time (this is the DFS)
Crop out one period of the sequence in time and frequency domain
DFT
However, there is an inherit periodicity in the time and frequency signals
(more later)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-2-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 3
Discrete-Fourier Series (DFS)
2
2
2
Define: , thus
Properties of :
is periodic with period (it is essentially cos and sin ):
Since is periodi
j k
k N
N
N
k k N k N
N
j
N N
N
N
N
N W e
W
W N W W W
W
W e
π
π −
± ±
−
=
• =
=
=
•
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
2
1
0
c with period , unlike the CTFS, the DFS representation of a
periodic signal needs only complex exponentials, i.e.
1
wh
N j kn
N
k
N
x n N
x n X k e
N
π
−
=
= ∑
[ ] [ ]
ere is the DFS coefficients of .
X k x n
]
[
~ n
x
n
[ ] [ ] N
period
rN
n
x
n
x ,
~
~ +
=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-3-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 4
Discrete-Fourier Series (DFS)
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
1
0
1
0
The DFS representation of thus becomes
Synthesis equation:
Analysis equation:
Note: The tilde in indicates
1
a
N
kn
N
k
N
kn
N
n
x n X k
x n
W
X k x n W
x
N
−
−
=
−
=
=
=
∑
∑
[ ]
period signal.
is periodic with period .
X k N
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-4-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 5
Is this relationship true?
To show that the analysis and synthesis equations are indeed true, we can derive
the analysis equation from the synthesis equation. But first, we need to show that
the following property is true:
1
0
1 1
0 0
, if
0, if
( ) (i) If , 1. So
1
(ii) If , 1, which can
N
k
N
k
k mkN
N N
N N
lk
N
k k
N
N mN
W
mN
Pf mN W W
W N
mN W
−
=
− −
= =
=
=
≠
= = =
= =
≠ ≠
∑
∑ ∑
1
0
1
0
be shown by using the geometric series
1
relation: . Then
1
1 1 1
0
1 1
Note that this property
k
k
n
n
N
N
k N
N
k N N
r
r
r
W
W
W W
+
=
−
=
−
=
−
− −
= = =
− −
∑
∑
[ ] [ ]
1
0
can be written more compactly as
1 N
k
N
k m
Y W mN
N
δ
− ∞
= =−∞
= = −
∑ ∑
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-5-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 6
How come the DFS relationship is true?
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
1
0
1
0
1
( )
Pick an where 0 1. Multiply both sides of the synthesis equation
by and sum from 0 to 1
1
N
kn
N
k
rn
N
N
rn
N
n
Pf x n X k W
N
r r N
W n N
x n W
−
−
=
−
=
=
≤ ≤ −
= −
=
∑
∑
[ ]
[ ]
1 1
0 0
1 1
( )
0 0
1
Now using the property from the last page, we know that
N N
kn rn
N N
n k
N N
r k n
N
k n
X k W W
N
X k W
N
− −
−
= =
− −
−
= =
=
∑∑
∑ ∑
( )
[ ] ( )
[ ]
[ ]
1
0
1 1 1
0 0 0
1,
1
0,
So,
1
(for )
0 0
N
r k n
N
n
N N N
r k n
N
k n k
k r mN
W
else
N
X k W X k r k mN
N
X
−
−
=
− − −
−
= = =
− =
=
= −
=
=
∑
∑ ∑ ∑
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
1
0
1 0 1
That is, QED
N
rn
N
n
X X k r
X r
X r x n W
−
=
+ + + = +
=
= ∑
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-6-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 7
Example: Periodic Rectangular Pulse Train
[ ]
4
5
4
10 10
10
0 10
sin
1 2
1
sin
10
k
k
j
kn
k
n
k
W
X k W e
k
W
π
π
π
−
=
−
= = =
−
∑
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-7-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 8
Properties of the DFS
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
1 1
2
1 2
2
1 2
Linearity:
then
Time Shift:
ax n bx n aX k
x n X k
x X
b k
n
X
k
↔
↔
+ ↔ +
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
If
then
Note that any shifts that are greater than or equal to the period, i.e. cannot
be distinguished in the time domain fro
km
N
x n X k
x n m W X k
m N
↔
≥
− ↔
1
1 1 2
1 2 1 1
1
m a shorter shift such that ,
where and are integers and 0 1. Or simply, modulo
i.e. is the remainder of / . So .
Since the DFS coefficients sequence is also
km
km
N N
m m m m N
m m m N m m N
m m N W W
= +
≤ ≤ − =
=
[ ] [ ]
periodic, we have a similar result for
the shift in the DFS coefficients by an integer
, i.e.
If
then n
N
x n X k
W
↔
[ ] [ ]
x n X k
↔ −
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-8-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 9
Properties of the DFS (cont’d)
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
Duality:
If
then (Prove later)
Symmetry
If
X n Nx k
x n X k
x n X
↔
↔ −
↔
[ ]
[ ]
{ } [ ] [ ] [ ]
( )
[ ]
{ } [ ] [ ] [ ]
( )
*
*
then
1
Re
2
1
Im
2
e
o
x n X k X k X k
j x n X k X k X
k
k
↔ = + −
↔ = − −
[ ] [ ] [ ]
( ) [ ]
{ }
[ ] [ ] [ ]
( ) [ ]
{ }
*
*
Also
1
Re
2
1
I
2
m
e
o
x n x n x n X k
x n x n x n j X k
= + − ↔
= − − ↔
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-9-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 10
Properties of the DFS (cont’d)
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
*
Symmetry (cont'd):
If is real,
then
X k X k
x n X k X k
X k X k
= −
∠ = −∠ −
= −
[ ]
{ } [ ]
{ }
[ ]
{ } [ ]
{ }
Re Re
Im Im
X k X k
X k X k
= −
=
− −
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-10-320.jpg)
![Proof of Duality
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 11
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
1 1 1
0 0 0
1
0
1
0
1 1
, then
Compare this to the analysis eqn: , th
Proof:
Since
en we see that
N N N
kn kn kn
N N N
k k k
N
kn
N
n
N
kn
N
k
x n X k W x n X k W Nx n X k W
N N
X k x n W
Nx k X n W
− − −
−
= =
−
=
−
=
= −
= ⇒ −
=
=
− =
∑ ∑ ∑
∑
∑
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-11-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 12
Properties of DFS: Periodic Convolution
(Circular Convolution)
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
1
1 2 1 2
0
1
3 1 2 1 2
1
0
2
Periodic Convolution:
If , are periodic sequences with period
then
These convolution equation
1
s l
N
m
N
x m x
x n x n
n m X k X k
x n x n x n X X k
N
N
−
=
−
=
− ↔
= ↔ −
∑
∑
ook very similar to the ones from
DTFT, but there is a very subtle difference here. That is, the
sum in the convolution here is only for a single period!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-12-320.jpg)
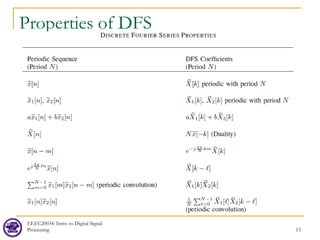
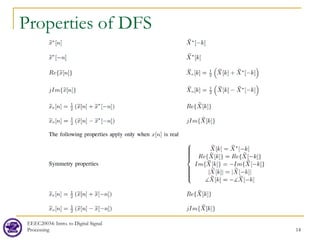
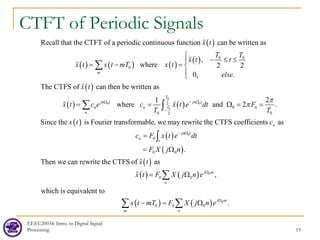
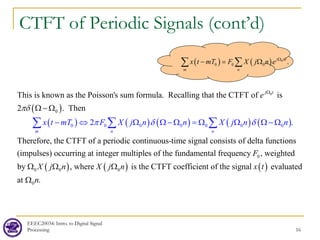
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 17
Fourier Transform of Periodic Signals
Recall from Chapter 2 that the DTFT of a periodic sequence is represented by
impulse train. This is because periodic signal has neither uniform convergence
nor mean-square convergence since it is not absolutely summable nor square
summable. As n±∞, the sequence does not go to zero
With the knowledge about the DFS, we will show that DFS is actually a
sampled version of the DTFT (via examples below)
Recall from above that the CTFT of a periodic signal requires the use of
impulse train in the frequency domain with impulse values weighted by the
CTFS coefficients for the signal
Similarly, in discrete-time domain, the DTFT of a periodic sequence is
represented by a impulse train in the frequency domain weighted by impulse
values proportional to the DFS coefficients for the sequence, i.e.
Note the has periodicity of 2π because is periodic with N and the
impulses are spaced at integer multiples of 2π/N
( ) [ ]
2 2
j
k
k
X e X k
N N
ω π π
δ ω
= −
∑
( )
j
X e ω
[ ]
X k
( ) ( ) ( )
0 0 0 0
m n
x t mT X j n n
δ
− ⇔ Ω Ω Ω − Ω
∑ ∑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-17-320.jpg)
![Example 1
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 18
[ ] [ ]
Here, we want to show that the DFS coefficients are a sampled version of the DTFT.
Consider the periodic impulse train
.
From the analysis equatio
r
p n n rN
δ
= −
∑
[ ]
[ ]
( )
n of the DFS, we see that
1, .
Therefore, the Fourier transform of is
2 2
.
Now
j
k
P k k
p n
k
P e
N N
ω π π
δ ω
= ∀
= −
∑
[ ]
consider the aperiodic sequence x n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-18-320.jpg)
![Example 1 (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 19
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ]
Now convolve with we get
* *
.
r
r
x n p n
x n x n p n x n n rN
x n rN
δ
= = −
= −
∑
∑
[ ]
( ) ( ) ( )
( )
Using the convolution property, the Fourier transform of is
2 2
j j j
j
k
x n
X e X e P e
k
X e
N N
ω ω ω
ω π π
δ ω
=
= −
∑
2
2 2
.
j k
N
k
k
X e
N N
π
π π
δ ω
= −
∑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-19-320.jpg)
![Example 1 (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 20
( ) [ ]
[ ] ( )
[ ]
2
2
2 2
Therefore, comparing this equation to ,
we see that
.
From this example, we see that the DFS coefficient of the
j k
j
k
j
N
k
N
X
k
X e X k
N N
X
X e X e
k
k
ω
π
ω
π
ω
π π
δ ω
=
= =
= −
∑
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
signal
is equal to the DTFT of the corresponding aperiodic signal , sampled at
2
.
Since the DTFT of is periodic in with 2 , the DFS of resulting
sequence is periodic in with period
x n
x n
k
N
x n x n
k N
π
ω
ω π
=
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-20-320.jpg)
![Example 2
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 21
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
Consider the periodic sequence
1, 10 4 10
0, 5 10 9 10
with . It is obvious that a single period of is
1, 0 4,
0,
x n
r n r
x n
r n r
r x n
n
x n
e
≤ ≤ +
=
+ ≤ ≤ +
∈
≤ ≤
=
, with 10
lse
N
=
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-21-320.jpg)
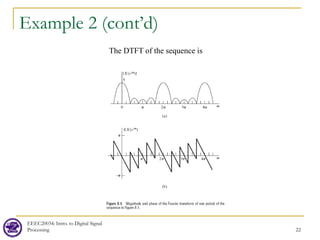
![Example 2 (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 23
[ ]
( ) ( )
( )
[ ] ( )
4
2
0
2
2
The Fourier transform of is given by
sin 5 / 2
.
sin / 2
Since , we substitute 2 /10
(since 10, not 4) to obtain
j j n j
n
j k
j
N
k
N
x n
X e e e
X k X e X e k
N
ω ω ω
π
ω
π
ω
ω
ω
ω π
− −
=
=
= =
= = =
=
∑
[ ]
[ ]
( )
( )
2(2 )
10
the DFS coefficients of , which is
sin / 2
sin /10
k
j
x n
k
X k e
k
π
π
π
−
=
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-23-320.jpg)
![Sampling the Fourier Transform
As seen from the above, is
periodic in k with period N. Since the
Fourier transform is equal to the z-
transform evaluated on the unit circle,
can be obtained by sampling X(z) at N
equally spaced points on the unit
circle
We have seen that is the DFS
coefficient of and is a
sampled version of the DTFT of x[n].
So we formally derive the relationship
between x[n] and (as we have
seen before, x[n] represents one of
period of ).
We can actually draw parallels in the
relationship between x[n] and
with that of X(jΩ) and X(ejω)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 24
[ ]
X k
[ ]
X k
[ ] ( ) 2
2
k
j
N
k
j
N
z e
X k X z X e
π
π
=
= =
[ ]
X k
[ ]
x n
[ ]
X k
[ ]
x n
[ ]
x n
[ ]
x n
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-24-320.jpg)
![Comparison With Uniform Sampling
in Time
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 25
[ ] ( )
[ ] [ ] ( ) 2
DTFT
sampling
IDFS
?
|
j
j
k
N
X e
X k X
n
n e
x
x
ω
ω
π
ω=
→ →
↓
← ← =
( ) ( )
[ ] ( )
CTFT
sampling ?
DTFT j
x t X j
x n X e ω
→ → Ω
↓
→ →
Compare to:
Aperiodic sequence:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-25-320.jpg)
![Relationship Between x[n] and
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 26
[ ] [ ]
( )
[ ]
[ ]
1
0
1
2
0
1
2
0
2
1
(IDFS)
1
(Sampling)
1
(FT)
1
N
kn
N
k
N
j kn
N
k
k N
N
j m kn
N
k m k
N
j km
kn
N
N
k m
x n X k W
N
X e W
N
x m e W
N
x m e W
N
ω
π
ω
ω
π
ω
π
−
−
=
−
−
=
=
− ∞
− −
= =−∞ =
∞ −
−
=−∞
=
=
=
=
∑
∑
∑ ∑
∑
[ ]
[ ] ( )
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
1
0
1
0
1 1
0 0
1
1 1
(recall that )
*
r
N
N
km kn
N N
m k
N N
k n m k
N N
m k k m
n m rN
r
r
x m W W
N
x m W W mN
N N
x n n rN
x n rN
δ
δ
δ
−
=
−
−
=
− −
− −
= =
− +
=
= = −
∑
= +
= +
∑
∑ ∑
∑ ∑ ∑ ∑
∑
∑
[ ]
x n
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-26-320.jpg)
![Aliasing in Time
In Figure 8.8, we show that if we sample
X(ejω) with high enough N, then x[n] can be
recovered from by extracting one period
of . But if we do not sample with
enough N (Figure 8.9), then we will have
aliasing in time. In that case, we will not be
able to recover x[n] from
If x[n] has finite length and we take a
sufficient number of equally spaced samples
of its Fourier Transform (a number greater
than or equal to the length of x[n]), then x[n]
is recoverable from
Two ways (equivalently to define the DFT):
1) N samples of the DTFT of a finite duration
sequence x[n]
2) Or, make the period replica of x[n]
Take the DFS of
Pick up one segment of
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 27
[ ]
x n
[ ]
x n
[ ]
x n
[ ]
x n
[ ]
x n
[ ]
X k
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
k
X
DFS
n
x
k
X
DFT
n
x
~
~
segment
one
periodic
]
[
→
→
↑
↓
→
→
[ ]
x n
Figure 8.8 (a) Finite-length sequence x[n]. (b)
Periodic sequence corresponding to sampling the
Fourier transform of x[n] with N = 12.
Figure 8.9 Periodic sequence corresponding to
sampling the Fourier transform of x[n] in Figure 8.8(a)
with N = 7.
[ ]
x n
[ ]
x n
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-27-320.jpg)
![Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 28
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
( )
( )
( )
: length , 0 1
Make the periodic replica:
modulo
r
N
x n N n N
x n x n rN
x n N
x n
∞
=−∞
≤ ≤ −
= +
≡
≡
∑
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] ( )
( )
1
0
Keep one segment (finite duration)
, 0 1
That is,
0, otherwise
N
kn
N
n
N
X k x n W
X k k N
X k X k X k
−
=
=
≤ ≤ −
=
∑
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-28-320.jpg)
![DFT (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 29
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
1
0
1
0
: , 0 1
1
, 0 1
:
N
kn
N
n
N
kn
N
k
Analysis eqn
Sy
X k x n W k N
x n X k W
nthe n
s N
s qn
N
i e
−
=
−
−
=
= ≤ ≤ −
= ≤ ≤ −
∑
∑
Remarks:
• DFT formula is the same as DFS formula. Indeed, many properties of DFT are
derived from those of DFS.
• Keep in mind that X[k] is equal to samples of the X(ejω), and if the synthesis
equation is evaluated outside the interval 0 ≤ n ≤ N-1, then the result will not be
zero but a periodic extension of x[n]. This inherent periodicity is always present!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-29-320.jpg)
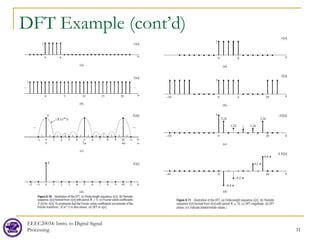
![DFT Example
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 30
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
1, 0 4
Consider the sequence:
0,
Let be the periodic extension of .
For the first case, let
1, 5 4 5
0,
and for the second case, let
1, 10 4 10
0
n
x n
else
x n x n
r n r
x n
else
r n r
x n
≤ ≤
=
≤ ≤ +
=
≤ ≤ +
=
, else
In two cases, we can see that if we sample faster, then more information about
the original DTFT can be shown, i.e. both DFTs (N=5 and N=10) contain same
amount of information, but the extra information shown in the N=10 case is just
hidden in the N=5 case. Remember, to get the 10-point DFT, we have simply
zero-padded the original sequence, nothing more.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-30-320.jpg)
![IDFT Matrix
The IDFT and DFT is a linear transform
The computation can thus be represented using a matrix multiplication
The (n,k)th element of an N×N matrix N-point IDFT matrix WN is
This is a symmetric (but complex-valued) matrix
Example:
DFT coeff. vector xk = WN
Hx, where xk is a N×1 vector containing the DFT coefficients X[k],
and x is a N×1 vector containing the time domain sequence x[n]
The DFT matrix can be generated by matlab using the function dftmtx. Note that this
generates a unnormalized version of the DFT matrix, i.e. WN is only an orthogonal matrix,
NOT orthonormal, so WN WN
H = NIN not IN
Properties of the IDFT matrix
WN = WN
T, i.e. WN is symmetric
WN
H = WN
*
WN
-1 = WN
*
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 32
[ ]
2
1 j kn
N
nk
N e
N
π
W
2 4
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
,
1 1 1 1 1 1
1
1
1
1
2
2
j j
j j
− −
= =
− − −
− −
W W](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-32-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 33
Properties of the DFT
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
1
1
2 2
2
1
2 1 1 2
Linearity:
(
then
Circular Shift:
length= max ,
ax n bx n aX k bX
x n X k
x k
k N N
n X
↔
+ ↔ +
↔
[ ] [ ]
( )
( ) [ ]
[ ] ( )
( )
If
then
also
km
N
N
n
N N
x n m W X k
W x n X k
x n X k
−
− ↔
↔
↔ −
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-33-320.jpg)
![Proof of Circular Shift Property
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 34
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] ( )
( ) [ ] ( )
( )
[ ]
[ ]
2
1
1 1 1 1
1
1
Let
From the definition of the DFT, we know that
Then, the DFS of is
k
j m
km
N
N
N N
j
X k e X k W X k
x n x n X k X k
x n
X k e
π
−
−
= =
= ↔ =
=
( )
( )
( )
( ) ( )
( ) [ ]
[ ] [ ]
2 2 2
1
.
Then it follows that shifting property of the DFS that
.
Then from the definition of the DFT
N
k k k
m j m j m
N N N
N N
X k e X k e X k
x n x n m
π π π
− −
= =
= −
[ ] ( )
( )
[ ]
[ ] ( )
( )
1
1
.
Therefore,
, 0 1
0, .
: This is a circular shift, not linear shift. (Linear shift of a periodic sequence
N
N
x n m x n m
x n x n m n N
x n
else
Remark
− = −
= − ≤ ≤ −
=
= circular shift of a finite sequence.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-34-320.jpg)
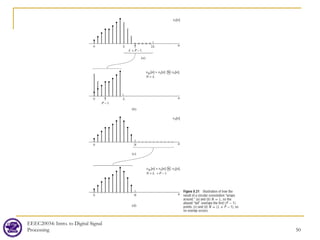
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 35
Example: Circular Shift
[ ] ( )
( )
[ ] [ ] ( )
( )
[ ]
6
1 6
1
We have . We want to obtain
2 2 . This is shown in
Figure 8.12(c). Figure 8.12(d) shows a single
period of .
x n x n
x n x n x n
x n
=
= + = +
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-35-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 36
Duality Property of the DFT
[ ] [ ]
[ ] ( )
( )
Duality:
If
then , 0 1
N
X n Nx k k
x X
N
n k
↔ − ≤ ≤ −
↔
Example:
Consider the finite length sequence x[n]
shown in Figure 8.13(a). Figures 8.13(b)
and 8.13(c) show the real and imaginary
part of X[k]. To show the duality property,
we relabel the k-axis in Figures 8.13(b)
and (c) to be n-axis, shown in Figures
8.13(d) and (e). According to the duality
property, Figure 8.13(f) shows the DFT of
the complex-valued sequence of Figures
8.13(d) and (e).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-36-320.jpg)
![Symmetry Properties of the DFT
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 37
[ ] ( )
( ) [ ] ( )
( ) [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] ( )
( )
( )
( )
* *
* *
* *
*
and , and and
, we have
, 0 1
Since N N
DFT
N
DFT
N
x n x n X k X k x n X k
x n X k
x n X k N
n
n
x
= ↔ −
− ↔
←
→ − ≤ ≤ −
←
−
[ ]
*
, 0 1
X n N
k
→ ≤ ≤ −
Table 8.1: DFS properties](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-37-320.jpg)
![Symmetry Properties of the DFT
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 38
[ ]
It shows decomposition of periodic sequence into sum of a conjugate symmetric and a
conjugate antisymmetric sequence.
This suggests decomposition of finite-duration se into
quen the two fi
ce x n
•
•
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
nite-duration
sequences of duration corresponding to one period of the conjugate symmetric and
conjugate antisymmetric components of . Denote these components of as
and
Wi
ep op
N
x n x n
x n x n
•
[ ] ( )
( ) [ ] [ ] [ ]
( )
[ ] [ ] [ ]
( )
[ ] [ ]
*
*
1
th , the conjugate symmetric part being ,
2
1
and conjugate antisymmetric part being , define
2
, 0
e
N
o
ep e
x n x n x n x n x n
x n x n x n
x n x n n N
= = + −
= − −
= ≤ ≤
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
1
, 0 1
I.e. both and are finite-duration sequences
op o
ep op
x n x n n N
x n x n
−
= ≤ ≤ −
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-38-320.jpg)
![EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 39
Symmetry Properties of the DFT
[ ] ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( )
[ ] ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( )
( )
( ) ( ) ( )
( )
*
*
Then
1
, 0 1
2
1
, 0 1
2
Since both sequences are finite, and since and for 0 1
then we can wri
ep N N
op N N
N N
x n x n x n n N
x n x n x n n N
n N n n n n N
= + − ≤ ≤ −
= − − ≤ ≤ −
− = − = ≤ ≤ −
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
{ }
[ ]
{ }
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
{ }
[ ]
{ }
*
*
1
, 1 1
2
Re 0 , 0
1
, 1 1
2
te these
Im 0 ,
sequences as
ep
op
x n x N n n N -
x n
x n
x n x N n n N -
x n
j x
+ − ≤ ≤
=
=
− − ≤ ≤
=
( )
( ) [ ] [ ] [ ]
( ) [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
( ) [ ]
* *
* *
0
This avoids the use of . They are also n
1
2
1
nor , r
ot e
esp.
qual to
2
e e
N
o o
n x n x n x n x n
x n x n x n x n
n
+ − =
= − −=
=
−
−
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-39-320.jpg)
![Symmetry Properties of the DFT
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 40
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
{ } [ ] ( )
( )
, for 0 1
We also have
1
Re
2
e o e
ep
o
ep o
N
p
x n x n x n x n x n x
x n X k X k X
n x n n N
x n x n
= + ⇒ = = + ≤ ≤ −
=
↔
+
=
⇒
+
( )
( )
{ }
[ ]
{ } [ ] ( )
( ) ( )
( )
{ }
[ ] [ ]
{ } [ ] [ ]
{ }
*
*
1
Im
2
Re Im
N
op N N
ep op
k
j x n X k X k X k
x n X k x n j X k
−
↔ = − −
↔ ↔
⇒](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-40-320.jpg)
![Symmetry Properties of the DFT
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 41
[ ] [ ] ( )
( )
[ ] ( )
( )
[ ]
{ } ( )
( )
[ ]
{ } ( )
( )
{ }
[ ]
{ } ( )
( )
{ }
[ ]
{ } [ ] ( )
( ) ( )
( )
{ }
[ ]
{ } [ ] ( )
( )
*
*
If real, , 0 1
Re Re
Im Im
1
Re
2
1
Im
2
N
N
N
N
N
ep N N
op N
x n X k X k k N
X k X k
X k X k
X k X k
X k X k
x n X k X k X k
x n X k X k
= − ≤ ≤ −
= −
⇒
∠ = −∠ −
= −
⇒
=
− −
↔ = + −
↔ =
( )
( )
{ }
*
N
X k
− −
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-41-320.jpg)
![Circular Convolution of the DFT
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 42
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
3
1
3 2 1
0
1
1 2
0
From the DFS circular convolution: ircular convolution for
the DFT
, c
, 0 1
N
m
N
m
x n x m x n m
x m x n m n
x N
x
n
−
=
−
=
= −
= − ≤ ≤ −
=
∑
∑
( )
( ) ( )
( )
( )
( )
[ ] [ ] ( )
( )
[ ] [ ]
1
3
1
1
1 2
2
0
2
0
1
for
, 0 1.
Since 0 1, then
, 0 1.
N
N N
m
N
N
N
m
m
x n x
m x n m n N
m m N
n N
x n x
m x n m
n
−
=
−
=
=
− ≤ ≤ −
= −
≤
−
≤
−
≤ ≤
=
∑
∑
[ ] ( )
( )
[ ] [ ]
1
0
2 1
2 1
, 0 1
where -point circular convoluti
denotes on
Also,
N
N
m
n N
x n x n
x m x n m
N
−
=
= −
≤ ≤ −
=
∑
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
1
1 2 2
X
n k
n x k X
x ↔](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-42-320.jpg)
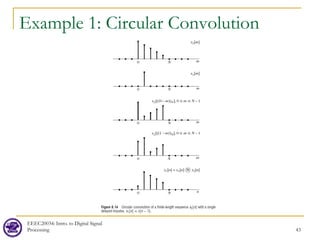
![Example 2: Circular Convolution (Aliasing)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 44
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ]
1 2
1
1 2
0
2
3 1 2
3
-point circular convolution of two
constant sequences of length . Let
6 for and . Let
, then
, 0,
0,
, 0,
0,
, 0 1
Note the res
N
kn
N
n
N
N
L x n x n
N L
N k
X k X k W
else
N k
X k X k X k
else
x n N n N
−
=
=
=
=
= = =
=
=
⇔ = ≤ ≤ −
∑
ult we get in Figure 8.15 is
different from that of linear convolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-44-320.jpg)
![Example 2: Circular Convolution (Alias-free)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 45
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
1 2
1 2
3 1 2
If we now perform a 2 -point circular convolution
with and by appending zeros to both
sequences, then
1
.
1
So the result becomes
1
1
Lk
N
k
N
LK
N
k
N
N L
x n x n L
W
X k X k
W
W
X k X k X k
W
=
−
= =
−
−
= =
−
2
,
where .
N L
=
Now the result in Figure 8.16 matches the result we
would have obtained if we were to perform linear
convolution between x1[n] and x2[n].
Therefore, unlike the relationship between linear
convolution and multiplication for the DTFT, linear
convolution and DFT multiplication may result in
different sequences depending on the number of points of
DFT we perform. This is due to the inherent periodic
nature of the 2 sequences x1[n] and x2[n].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-45-320.jpg)
![Linear Convolution Using DFT
Why use the DFT? There are fast DFT algorithms (FFT), so it
might be more computational efficient to do all your processing in
the transformed domain, followed by inverse operation to transform
the result back into time-domain. However, we do not want the
result of circular convolution, but rather, that of linear convolution.
As seen in the preceding example, this can be accomplished by
choosing the appropriate value for N.
How do we do it?
1. Compute the N-point DFT of x1[n] and x2[n], separately
2. Compute the product X3[k] = X1[k]X2[k]
3. Compute the N-point IDFT of X3[k]x3[n]
Problems
Aliasing
Very long sequence
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-46-320.jpg)
![Aliasing
Let x1[n] be an length L sequence
Let x2[n] be an length P sequence
In order to avoid aliasing, N ≥ L+P-1
where x3[n] is the result of the linear
convolution between x1[n] and x2[n].
x3p[n] is of this form because of the
inherent periodicity of x1[n] and x2[n].
So when the circular convolution is
performed, the tail of x1[n]/x2[n] will
wrap around to the head of
x1[n]/x2[n]. Therefore, aliasing in time
will occur if N < L+P.
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 47
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ]
3 1 2
3 , 0 1,
0,
p
r
x n x n x n
x n rN n N
else
=
− ≤ ≤ −
=
∑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-47-320.jpg)
![Aliasing (Partial Distortion)
If N=L=P, then all the
samples of x3p[n] are
corrupted by aliasing.
However, if P < L=N, then
only some of the samples in
x3p[n] are corrupted, while
the rest of it will equal to
x3[n]. Specifically, the first
P-1 points of the result are
incorrect, while the
remaining points are
identical to those that would
be obtained from linear
convolution (see Figure
8.21).
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-48-320.jpg)
![Aliasing (cont’d)
x1[n] pad with zeros
length N
x2[n] pad with zeros
length N
Interpretation: (Why call
it aliasing?)
X3[k] has a (time domain)
bandwidth of size L+P-1.
That is, the nonzero values
of x3[n] can be at most L+P-
1. Therefore, X3[k] should
have at least L+P-1
samples. If the sampling rate
is insufficient, aliasing
occurs on x3[n].
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-49-320.jpg)

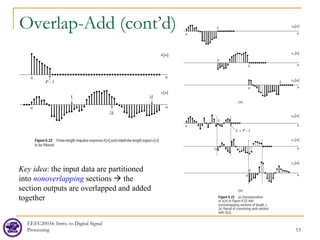
![Overlap-Add
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 52
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
Partition the long sequence into
sections of shorter length. For example, the filter
impulse response has finite length and the
input data is nearly "infinite"
no
.
n-overlapping
Let r
h n P
x n
x n x n
= [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
0
, 0 1
where
0, otherwise
The system (filter) output is a linear convolution.
Since linear convolution is a time-invariant
operation, then
r
r
rL
x n rL n L -
x n
∞
=
−
+ ≤ ≤
=
∑
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
0
0
0
where
r r
k
r
k r
r
r k
x n rL h n y n rL
r r r
r
y n x n h n
x k h n k
x k rL h n k
x k rL h n k
y n rL y n x n h n
∞
=
∞
=
− ∗ = −
∞
=
= ∗
= −
= − −
= − −
=
− =
∗
∑
∑∑
∑∑
∑
Remark: The convolution length is L+P-1. That is, the L+P-1 point DFT is
used. yr[n] has L+P-1 data points, among them, (P-1) points should be
added to the next section. Hence, the input sequences are each padded with
extra zeros at the end to make them both to have length L+P-1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-52-320.jpg)

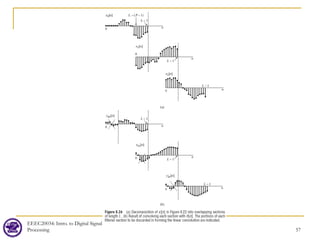
![Overlap-Save (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 55
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
Let be of length .
Let be of length ( )
Then, contains 1 incorrect
points at the beginning.
Therefore, we divide into sections
of length but each section overlaps
the preceding section
r
r
h n P
x n L L P
y n P
x n
L
>
−
[ ] ( ) ( )
by 1 points,
that is, we define the sequence of each
section to be
1 1 , 0 -1
r
P
x n x n r L P P n L
−
= + − + − − ≤ ≤
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-55-320.jpg)
![Overlap-Save (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 56
[ ] [ ]
Then, circularly convolve each section, , with . Since the first -1
samples are incorrect, after the (circular) convolution has taken place, simply
discard these samples. The remaining samples f
r
x n h n P
[ ]
[ ] ( )
[ ]
[ ]
0
rom successive sections are
put adjacent to each other to form the final output , i.e.
1 1
where
, 1 1
r
r
rp
r
y n
y n y n r L P P
y n P n L
y n
∞
=
= − − + + −
− ≤ ≤ −
=
∑
[ ]
,
0,
where is the result of the circular convolution for the section.
th
rp
else
y n r
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-56-320.jpg)
![Overlap-Save: Matrix Representation
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 58
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ]
If you recall, assuming that 3 and 5, the linear convolution between
and can be written in matrix form as
0 0
1 1 0
2 2 1 0
3 2 1 0
4 2 1 0
5 2
6
P L h n
x n
y h
y h h
y h h h
y h h h
y h h h
y h
y
= =
=
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
0
1
2
3
1 4
2
Since convolution is a commutative operation, we can also write
x
x
x
x
h x
h
=
y Hx
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
0 0
1 1 0
2 2 1 0 0
3 3 2 1 1
4 4 3 2 2
5 4 3
6 4
y x
y x x
y x x x h
y x x x h
y x x x h
y x x
y x
=
=
y Xh](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-58-320.jpg)
![Overlap-Save: Matrix Representation (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 59
For N = L, the N-point circular convolution will be equal to the linear
convolution except for the initial P-1 points in the result. The figures
above show the (periodic extension with 2 periods only) impulse responses
of x[n] (blue) and h[n] (red). Therefore, the circular convolution can be
written in matrix form as
x[n]
h[n]
1st block 2nd block 1st block 2nd block
[ ] [ ] ( )
( )
[ ] [ ]
[ ] ( )
( )
[ ] [ ]
1
0
1
0
, 0 1.
, 0 1
N
N
m
N
N
m
y n x m h n m
h
h m x n
n N
x n n
n N
h n x n
m
−
=
−
=
= − ≤ ≤ −
= −
≤ ≤ −
=
=
∑
∑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-59-320.jpg)
![h[0]
h[-1]
h[-2]
h[-1]
h[-2]
h[0]
h[0]
h[-1]
h[-2]
h[-1]
h[-2]
h[0]
Overlap-Save: Matrix Representation (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 60
x[4]
x[3]
x[0]
x[4]
x[3]
x[0]
[ ] [ ] ( )
( )
1
0
, 0 1
N
N
m
y n x m h n m n N
−
=
= ≤
≤
− −
∑
h[n] is regarded as a finite-duration sequence, but for
ease of visualization, we create another cycle
n=0
n=1
n=2
h[0]
h[-1]
h[-2]
h[-1]
h[-2]
h[0]
At n = 2 (3 and 4), output
of circular convolution
equals to that of linear
convolution due to the 2
zeros inserted in each
cycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-60-320.jpg)
![Overlap-Save: Matrix Representation (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 61
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
3
2 1 0 4
2 1 0 0
2 2 1 0 1
3 2 1 0 2
4 2 1 0 3
4
0 0
1 0 1
2
2 1
2 1 0 2
3 2 1 0
4 1
0
1
2 0
2
0
1
x
h h h x
h h h x
y h h h x
y h h h x
y h h h x
x
h x
h h x
y h h h x
y h h h x
h h
y
h h
y h
y
y h
y
=
⇔ =
[ ]
[ ]
3
4
x
=
=
y
y Hx
add](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-61-320.jpg)
![x[0]
x[-1]
x[-4]
Overlap-Save: Matrix Representation (cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 62
x[0]
x[-1]
x[-4]
x[0]
x[-1]
x[-4]
[ ] [ ] ( )
( )
1
0
, 0 1
N
N
m
y n h m x n m n N
−
=
= ≤
≤
− −
∑
h[0] h[1]
h[2]
h[1]
h[2]
x[n] is regarded as a finite-duration sequence, but for
ease of visualization, we create another cycle
n=0
x[0]
x[-1]
x[-4]
n=1
x[-4]
x[0]
x[-1]
x[-4]
n=2
x[0]
x[-1]
x[-4]
x[0]
x[-1]
x[-4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-62-320.jpg)
![Overlap-Save: Matrix Representation
(cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 63
shift
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
Due to the commutative property of the convolution, I can also write
this as
4 3 2 1 0 1
0 4 3 2 1 2
2 1 0 4 3 2 0
3 2 1 0 4 3 0
4 3 2 1 0 4 0
0
1
y
y
y
x x x x x h
x x x x x h
y x x x x x
y x x x x x
y x x x x x h
=
⇔
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
4 3 2 1
0 0
1 0 1
2 2 1 0 2
3 3 2 1 0 0
4 4 3 2 1 0 0
4
0
1 3 2
4 3
4
x x x x
x x x
x x
x h
x x h
y x x x h
y x x x x
y x x x x
x
y
x
=
y
y = Xh
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-63-320.jpg)
![Overlap-Save: Matrix Representation
(cont’d)
EEEC20034: Intro. to Digital Signal
Processing 64
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
Note that 0 and 1 are corrupted by samples from the previous block.
These are the first 1 samples of the output. Only 2 2 , 3 3
and 4 4 are valid. Also, 5 and 6 (not shown) will be
y y
P y y y y
y y y y
− =
=
=
( ) [ ]
2
corrupted
by the next block, so they will be discarded as well.
For any circulant matrix , it can be diagonalized by IFFT matrix , i.e.
, where the , element of is , for
1
N
j kn
N
N N kn
H
N H N k n e
N
π
=
=
H W
W W
H W Λ W
,
0,1, -1. That is, the diagonal elements of contains the DFT coefficients
of the first column vector of .
: This can always be done regardless of the values of as long as
is circulan
H
k n
N
=
… Λ
H
Note H
H
t, i.e. structure requirement is the only requirement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec07dft-230606124451-085c3e9b/85/lec07_DFT-pdf-64-320.jpg)