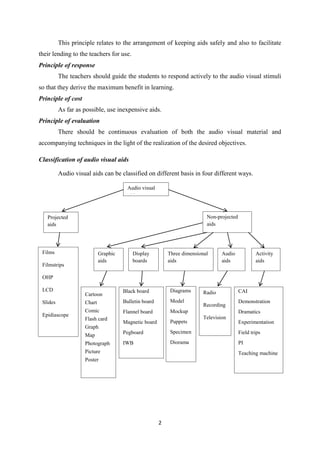
The document discusses different types of audio-visual aids used in education. It describes projected aids like films, filmstrips, epidiascope, overhead projector, and LCD projector which are used to project images onto a screen. Films are effective as they engage both visual and auditory senses but have disadvantages of high cost and dependence on others. Overhead projectors allow teachers to face students while teaching and modify content easily. The document also provides principles and classification of audio-visual aids used in classrooms.