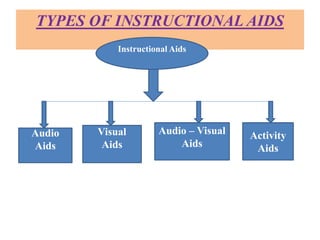
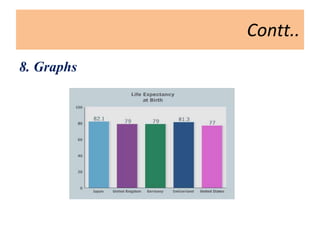
This document discusses instructional aids, which are materials used to aid in transferring information from an instructor to students. It defines instructional aids as devices that assist teachers in the teaching and learning process. The document categorizes instructional aids into audio aids, visual aids, audiovisual aids, and activity aids. It discusses the importance, uses, selection, preparation, and advantages of using instructional aids to enhance the learning process.