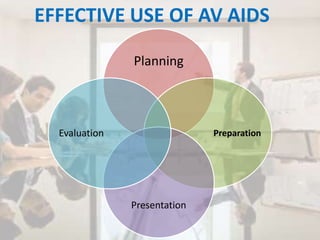
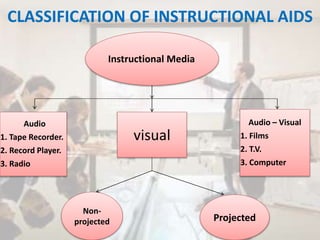
The document discusses the definition, purpose, principles, and importance of audio-visual aids in education, highlighting how they enhance learning by capturing attention and providing clear, vivid images. It outlines characteristics of effective instructional aids, guidelines for planning, preparation, presentation, and evaluation, as well as classifications and advantages of different types of aids. The document also addresses some limitations of audio-visual aids, including financial hurdles and technical difficulties.