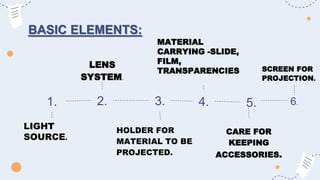
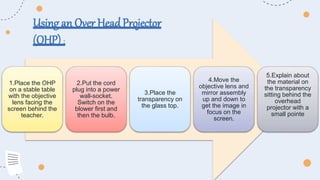
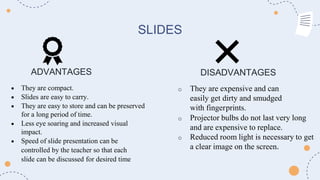
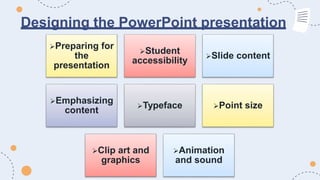
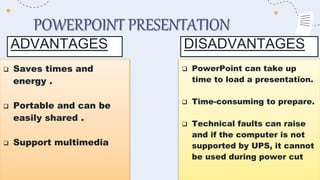
Projected aids such as slides, filmstrips, overhead projectors, and LCD projectors allow visual elements to be projected for a whole audience to see. They are commonly used in educational settings to enhance engagement and convey information effectively. Key advantages include their ability to present ideas visually and keep the audience's attention, as well as allow instructors to control the pace of presentation. Proper use of projected aids maximizes their educational impact.