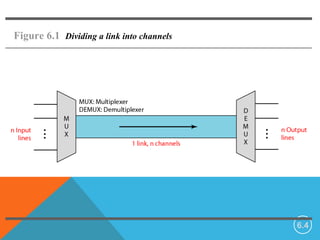
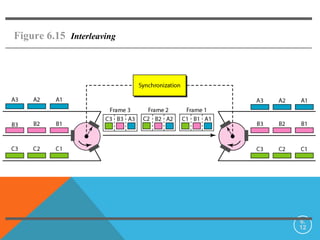
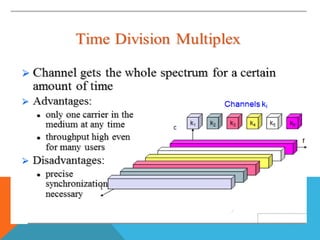
Bandwidth utilization techniques allow multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over a single data link. Multiplexing divides the bandwidth into channels that can be assigned to different signals. There are two primary multiplexing techniques: frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) and time-division multiplexing (TDM). FDM is an analog technique that combines signals by assigning each to a different frequency band. TDM is a digital technique that combines signals by assigning each short time slots in a repeating sequence. TDM makes more efficient use of the available bandwidth than FDM.