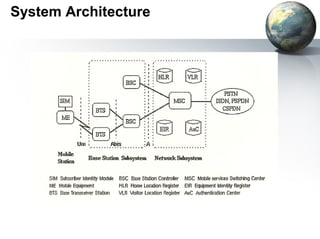
The document discusses GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication), including its definition as a 2G cellular standard, system architecture with components like the mobile station, base station subsystem, and network subsystem, basic features like call waiting and advanced features like roaming, future developments like UMTS, and advantages like international roaming capabilities and efficient use of spectrum.