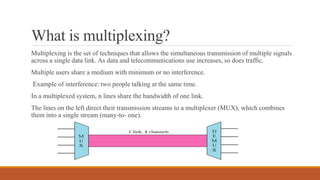
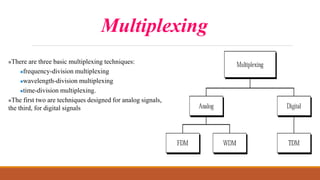
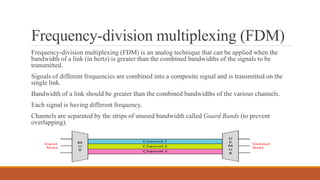
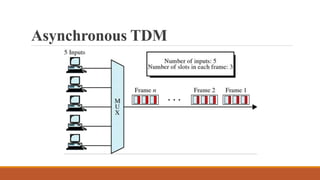
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a digital multiplexing technique that allows multiple signals to share a single data link by allocating unique time slots to each signal. There are two main types of TDM - synchronous TDM where each device is given the same fixed time slot to transmit data, whether it has data or not, and asynchronous TDM where time slots are flexible and allocated dynamically based on which devices have data ready to transmit. TDM is commonly used in telephone networks, digital audio systems, and cellular networks to efficiently transmit multiple calls or signals over the same medium.