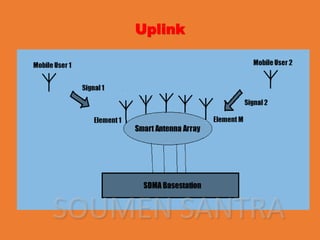
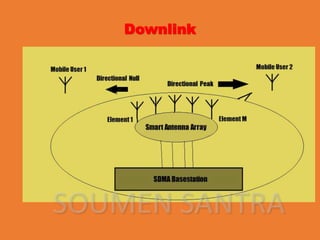
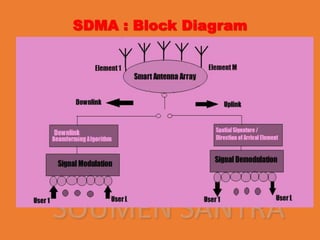
Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA) is a communication method that allows multiple users to share a single channel by creating parallel spatial channels using advanced smart antenna technology, enhancing system capacity, speed, and quality. It operates in both uplink and downlink modes, focusing on user data to minimize interference. While SDMA improves transmission quality and is free from interference, it also involves high costs and complex construction.