CDMA Technology & IS-95
- CDMA uses spread spectrum techniques where signals are spread over a wide frequency band before transmission. IS-95 is a 2G mobile telecommunications standard that uses CDMA.
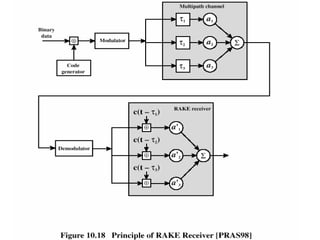
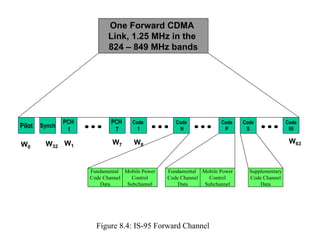
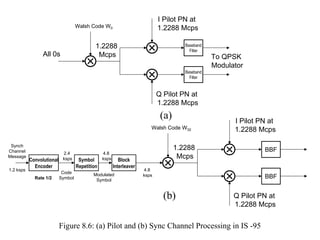
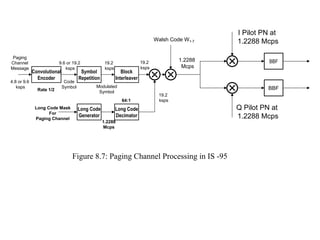
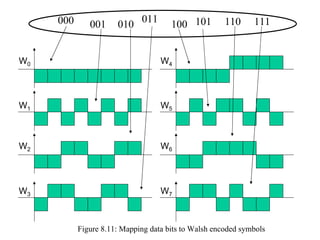
- IS-95 defines forward and reverse air interfaces with different channel structures using techniques like orthogonal codes, power control, and RAKE receivers.
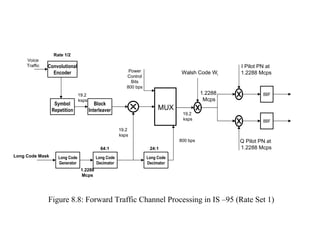
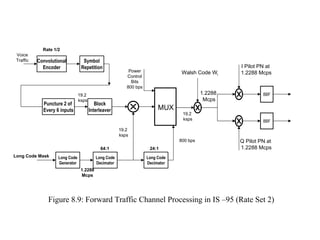
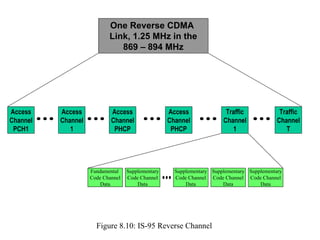
- The document discusses the technical details of the IS-95 forward and reverse channel structures including the pilot, sync, paging and traffic channels.