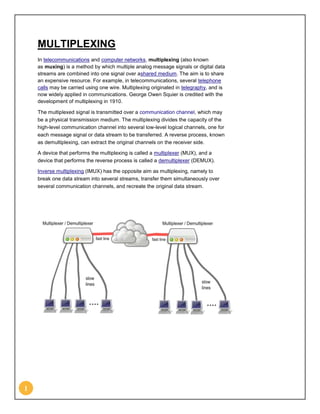
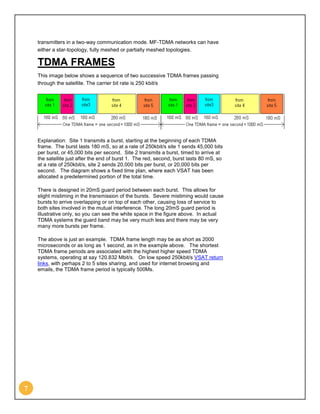
Time division multiplexing (TDM) is a technique used in telecommunications to transmit multiple signals over a shared medium. It involves dividing a signal into multiple time slots and assigning each slot to a different signal. TDM was initially developed for telegraphy in 1870 and is now widely used. It is used in digital networks like TDM telephone networks and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) networks to efficiently allocate bandwidth to multiple signals or data streams. Common examples of TDM include digitally transmitting multiple telephone calls over the same cable or interleaving left and right stereo signals in an audio file.