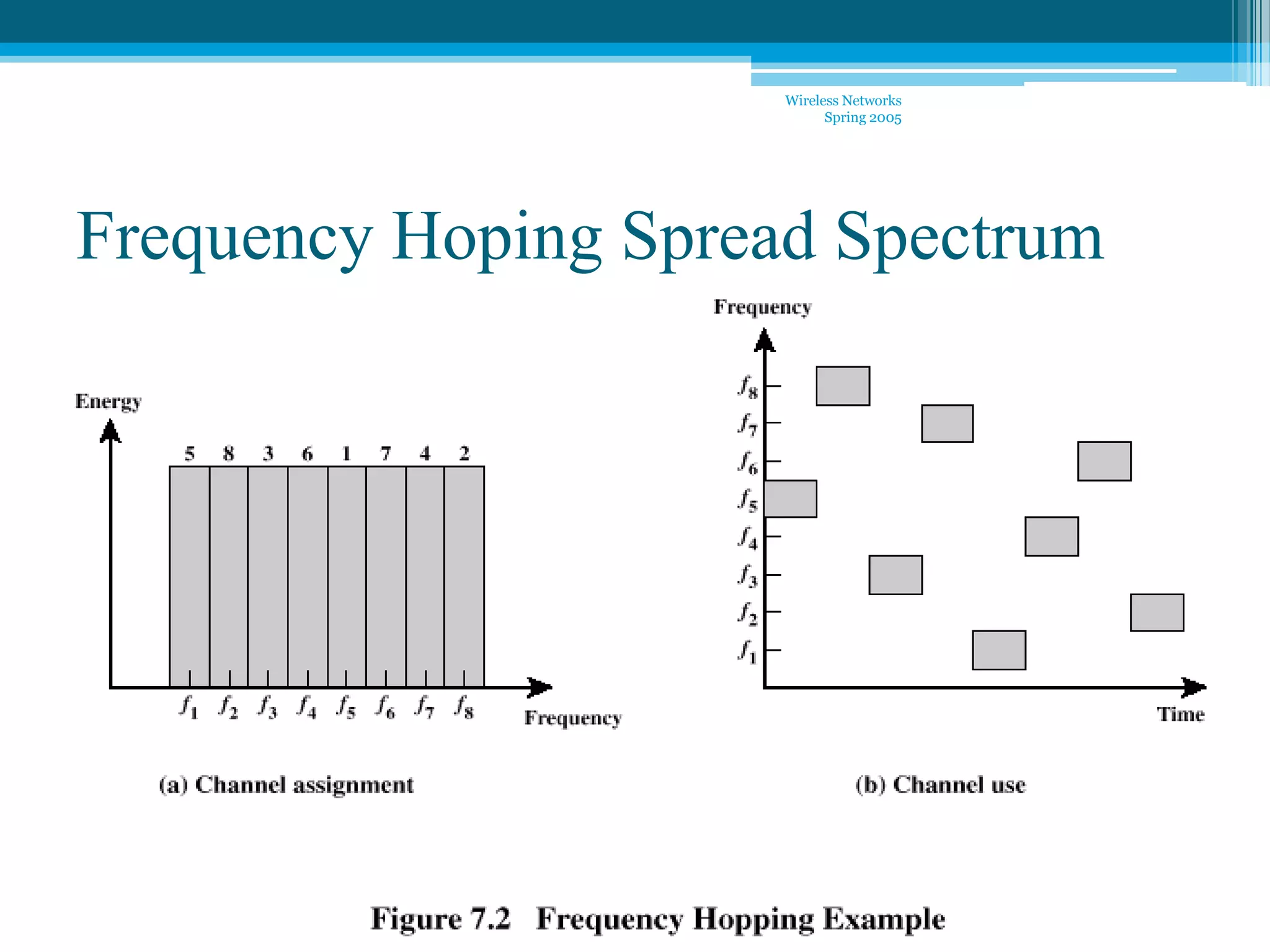
Spread spectrum communication uses wideband noise-like signals that are hard to detect, intercept, or jam. It spreads data over multiple frequencies. There are two main techniques: direct sequence spread spectrum multiplies a data signal by a pseudorandom code, and frequency hopping spread spectrum modulates a narrowband carrier that hops between frequencies. Spread spectrum provides benefits like resistance to interference and jamming, better signal quality, and inherent security. It finds applications in wireless networks, Bluetooth, and CDMA cellular systems.