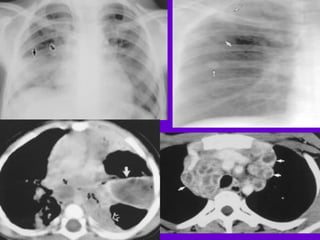
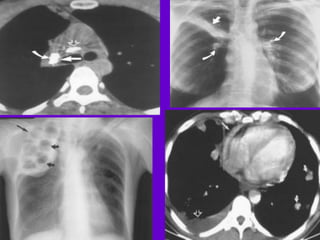
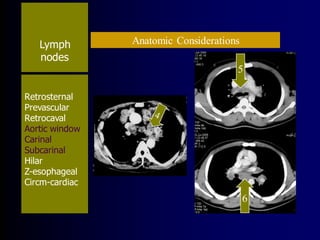
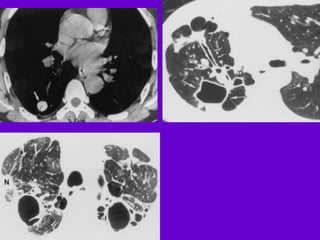
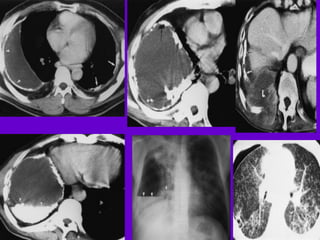
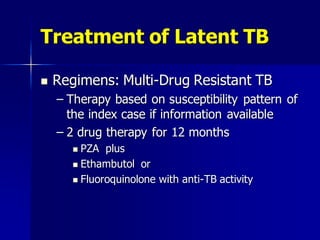
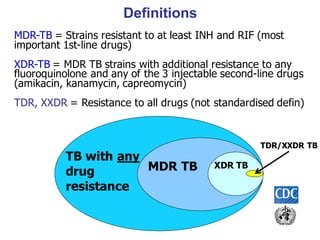
The document provides an overview of tuberculosis (TB) including epidemiology, diagnosis, and laboratory testing. Some key points:
- TB infects millions worldwide each year and is a leading cause of death. Rates are highest in developing countries.
- Diagnosis involves sputum smear microscopy, culture, and molecular testing like PCR. Smear microscopy has low sensitivity but high specificity. Culture is more sensitive but slower.
- Rapid culture methods like BACTEC and MGIT can detect TB in 2-8 days compared to 6-8 weeks for traditional culture.
- Molecular tests like PCR that detect TB DNA sequences like IS6110 can identify TB in smear-negative cases and distinguish TB from