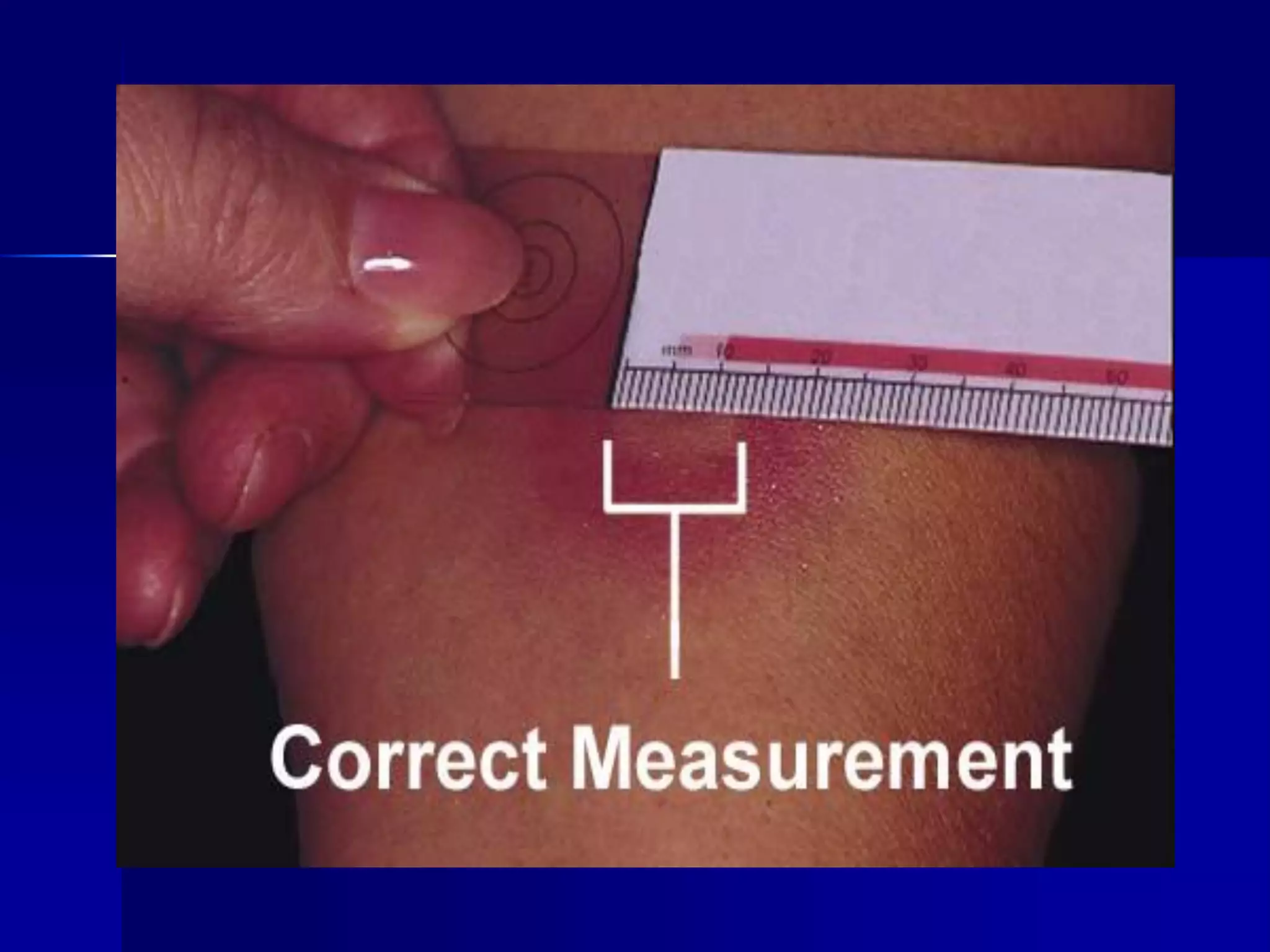
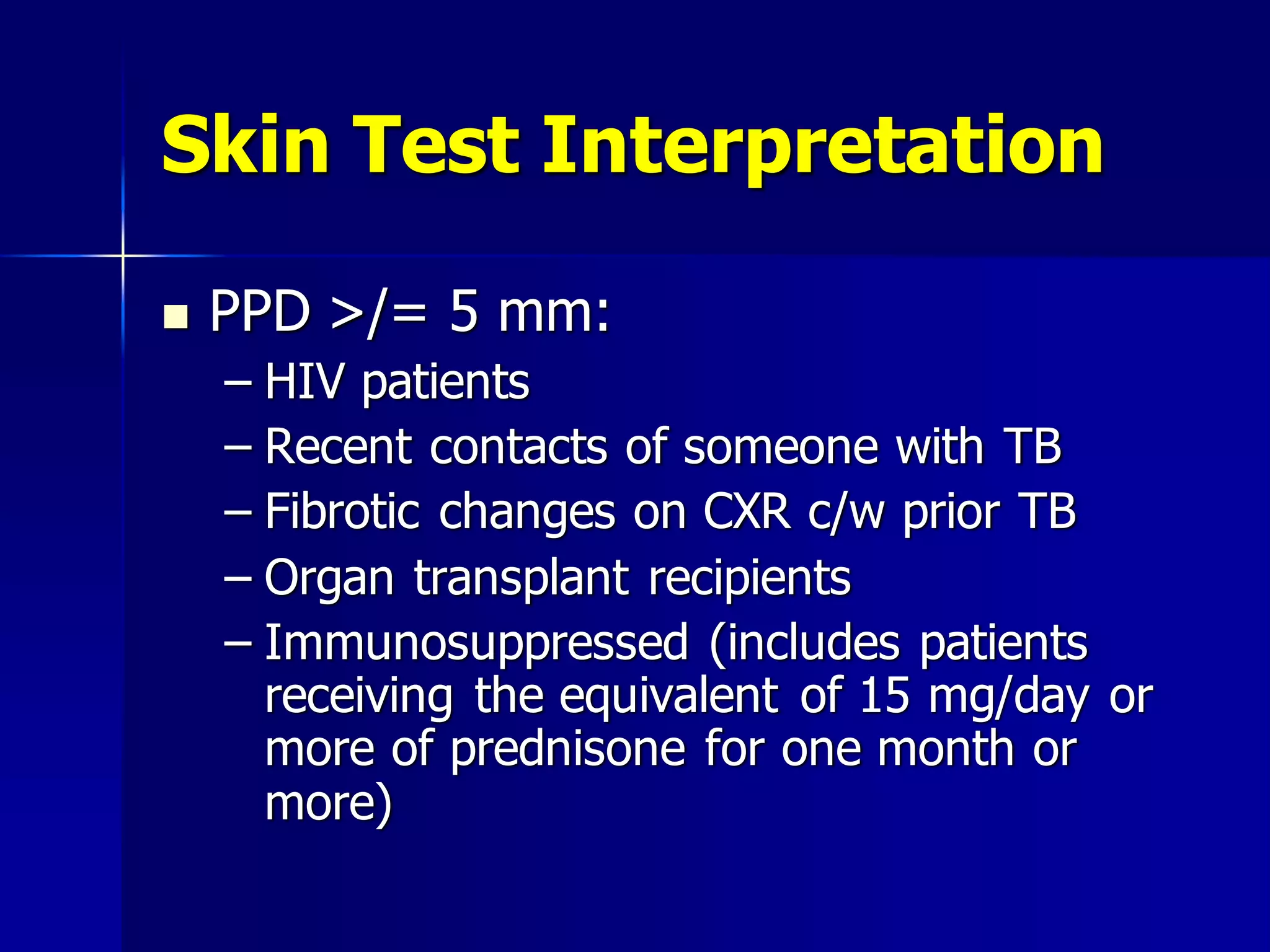
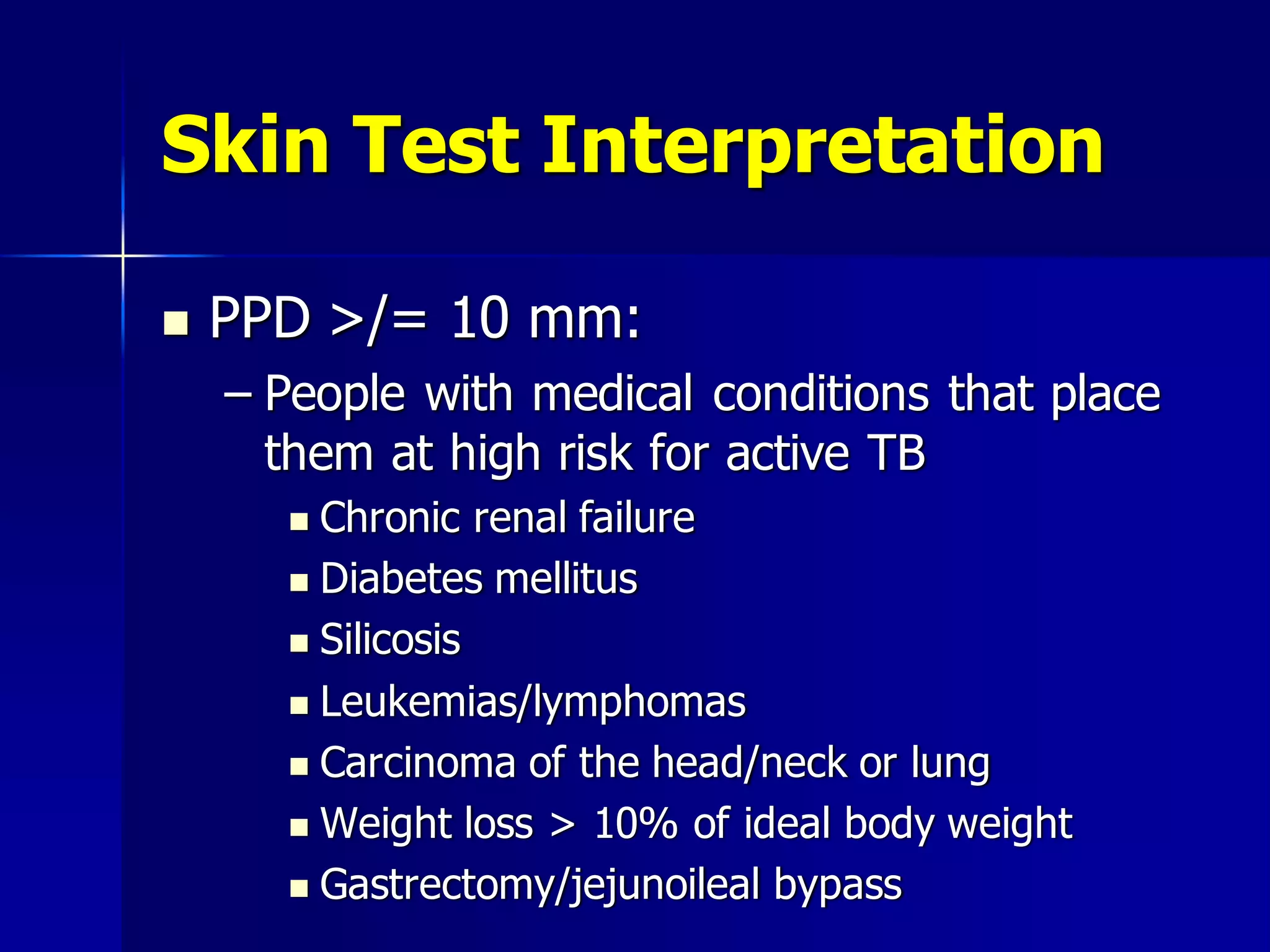
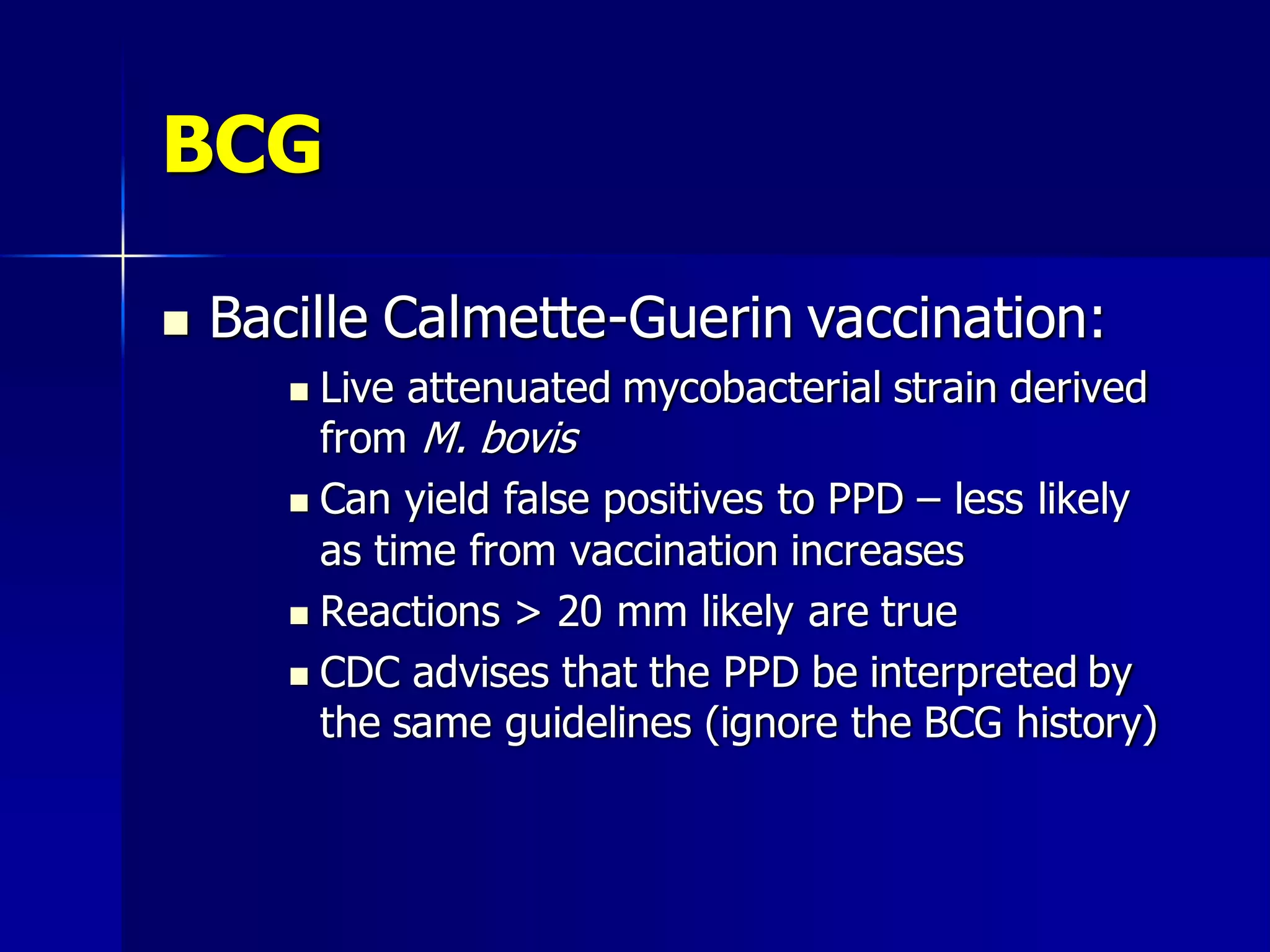
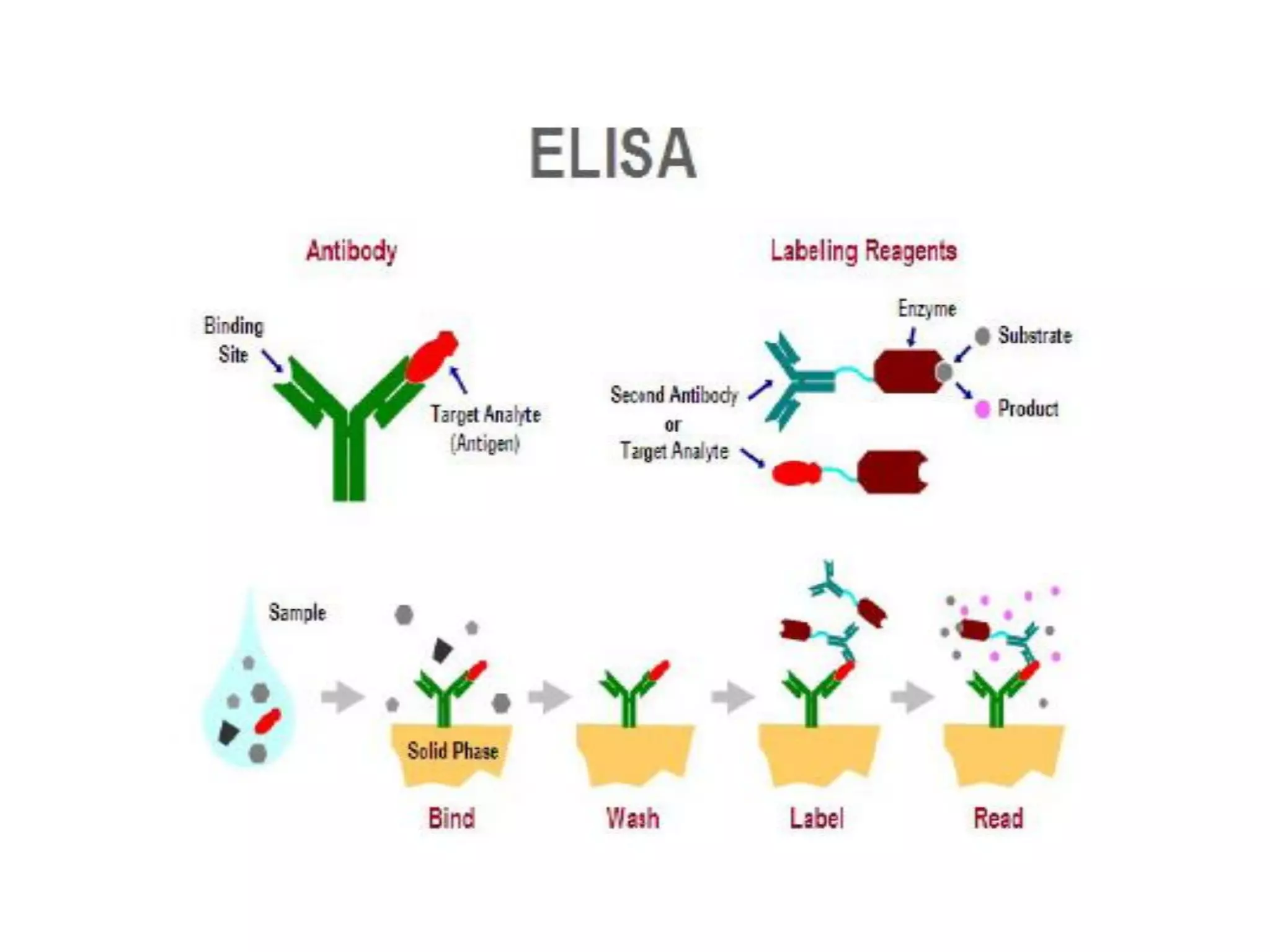
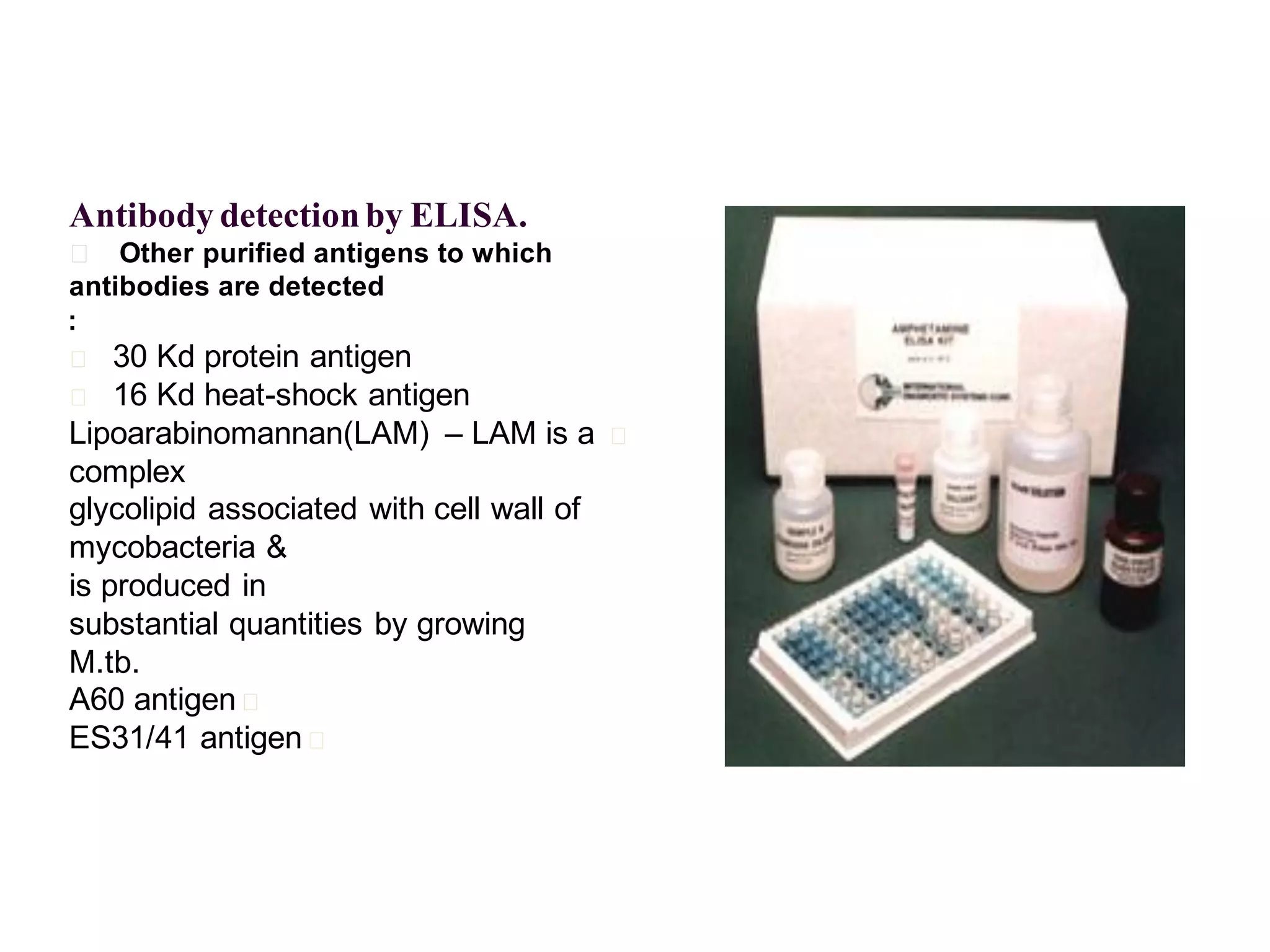
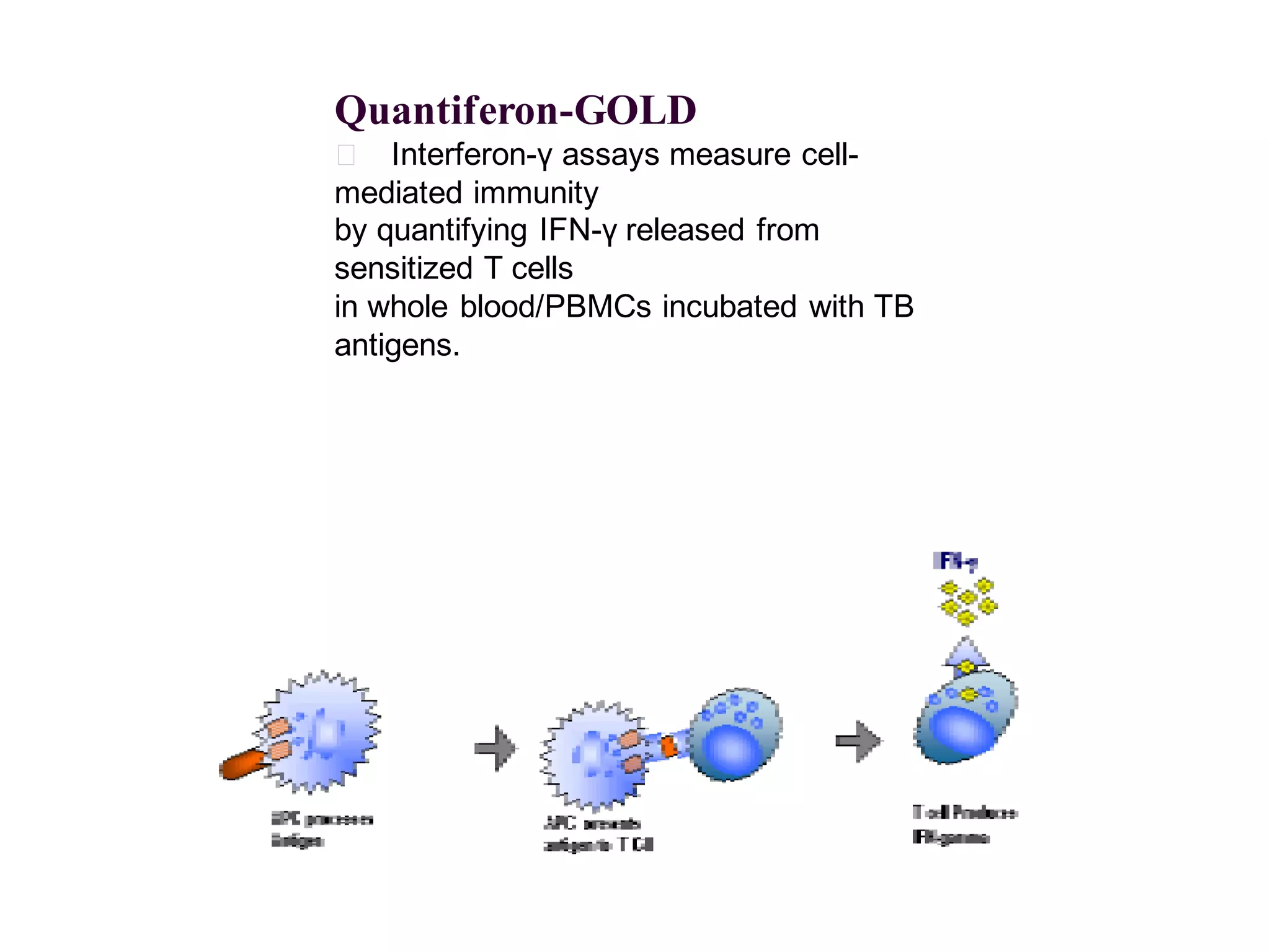
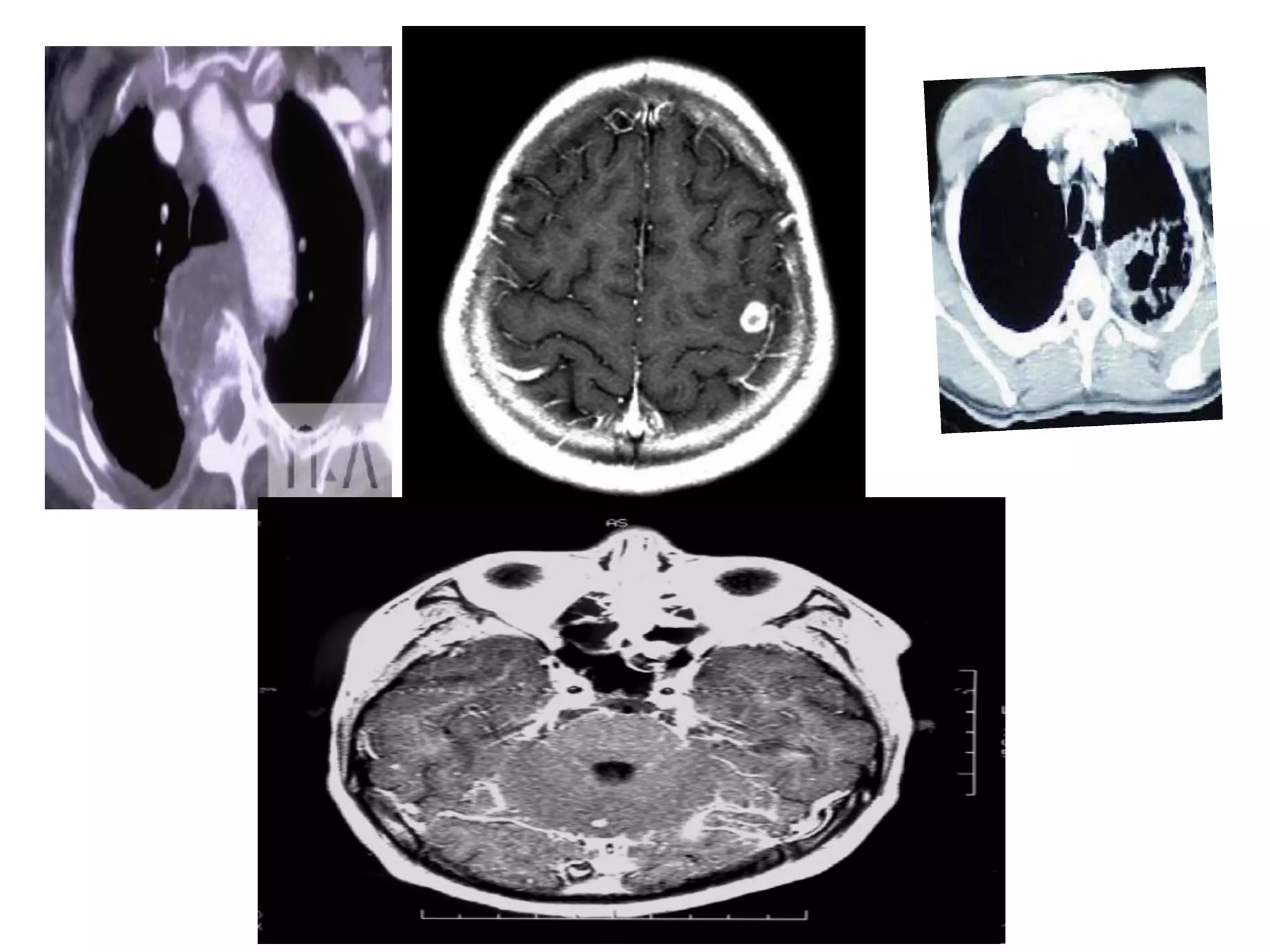
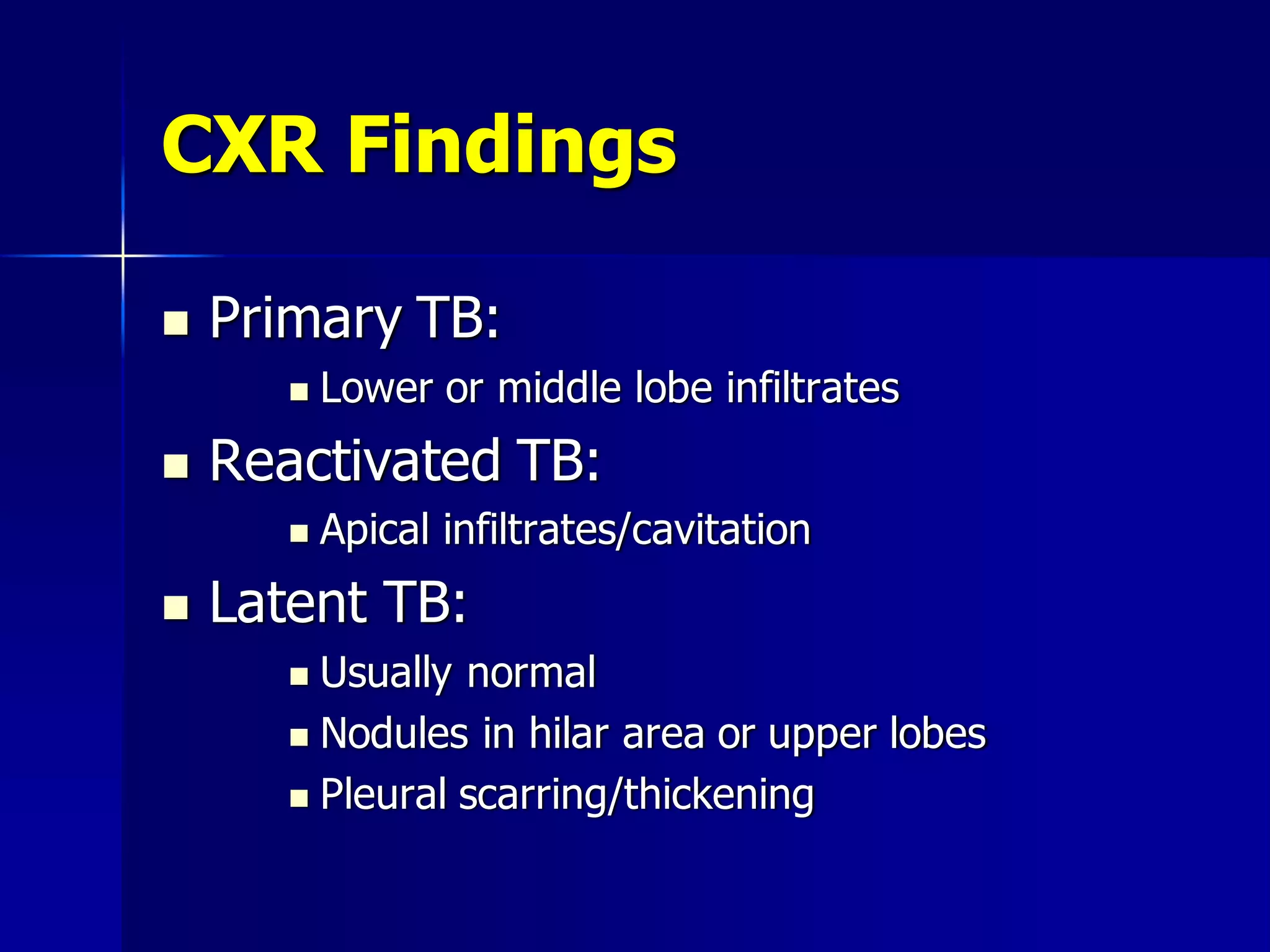
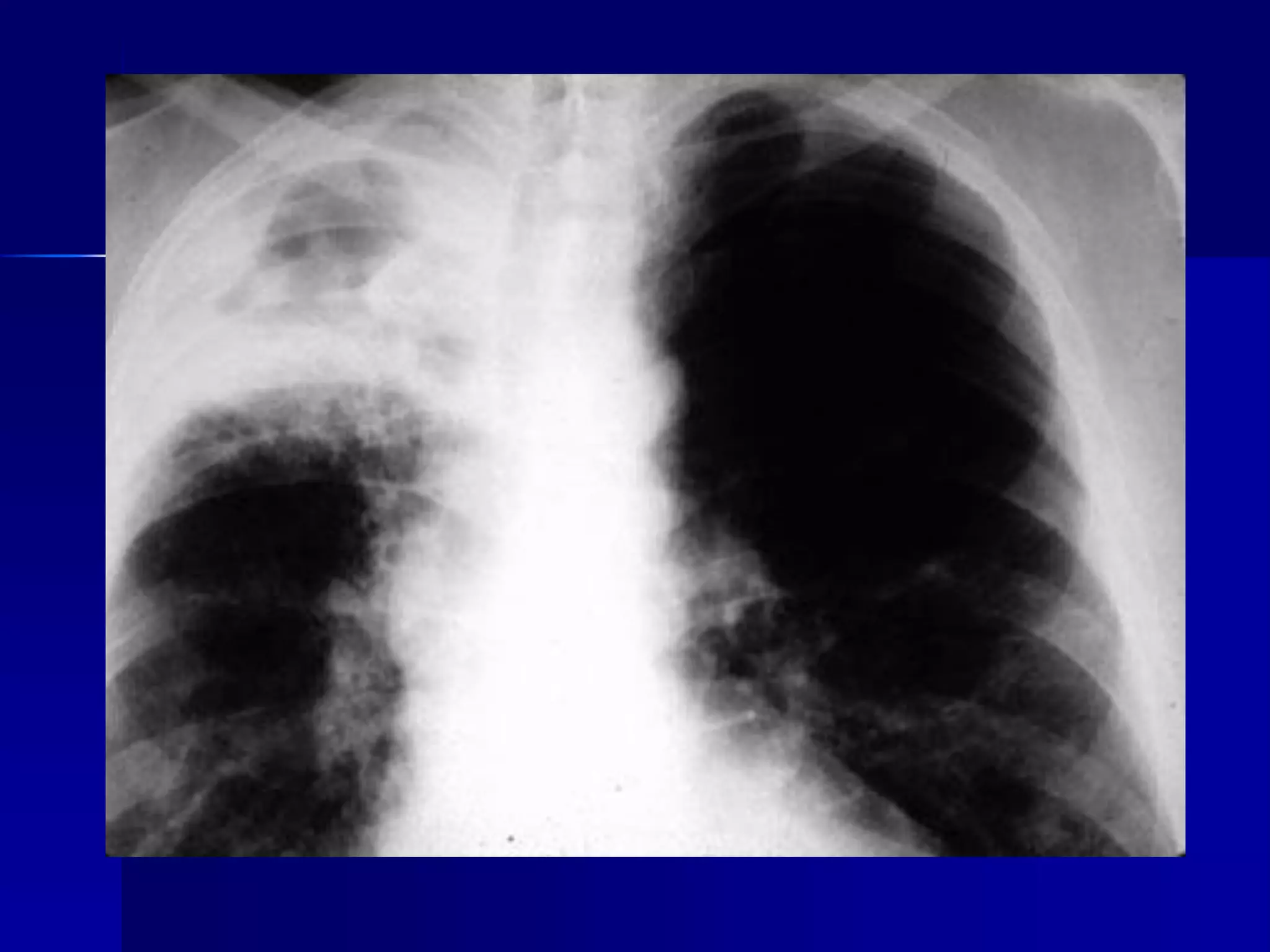
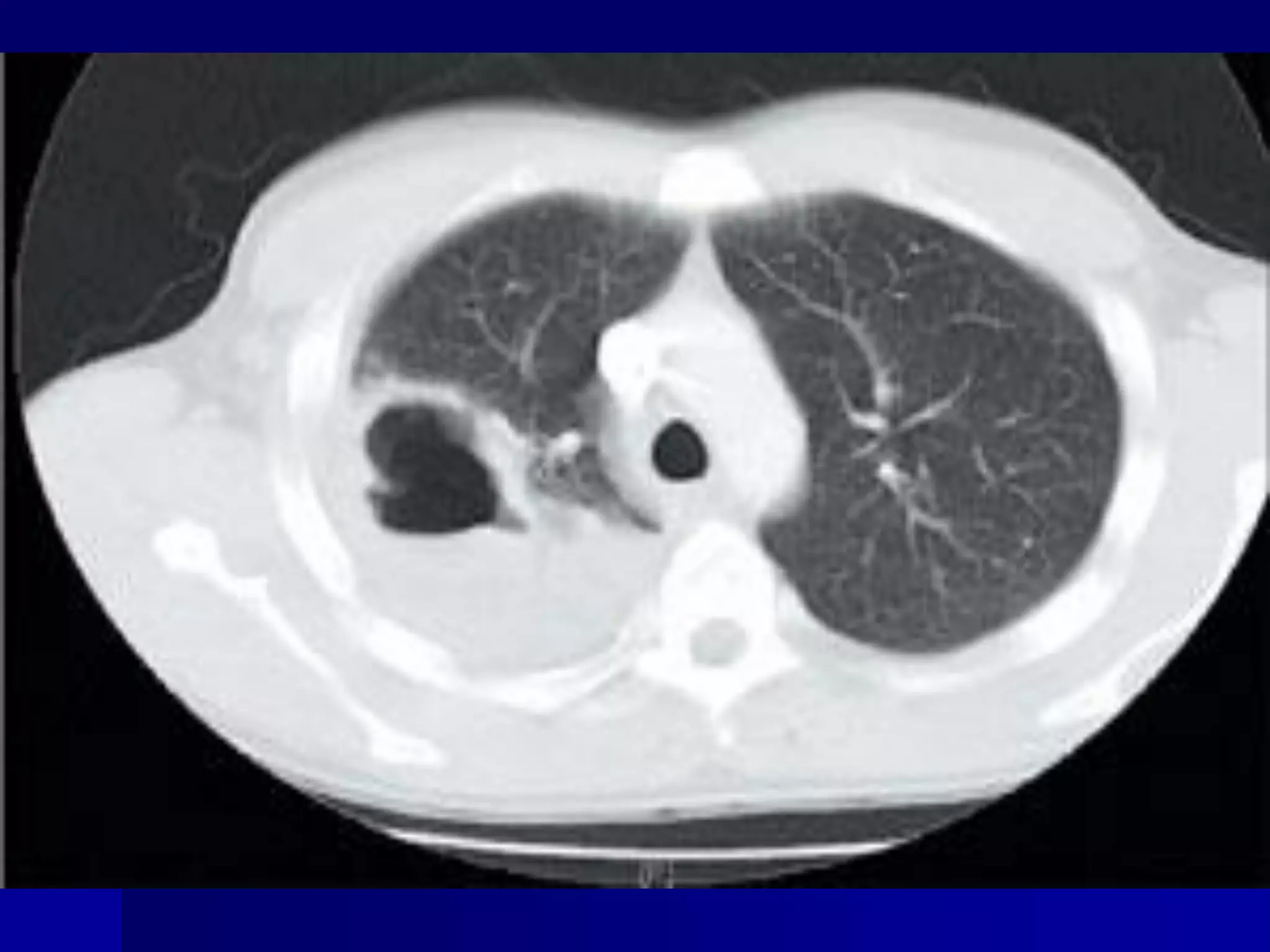
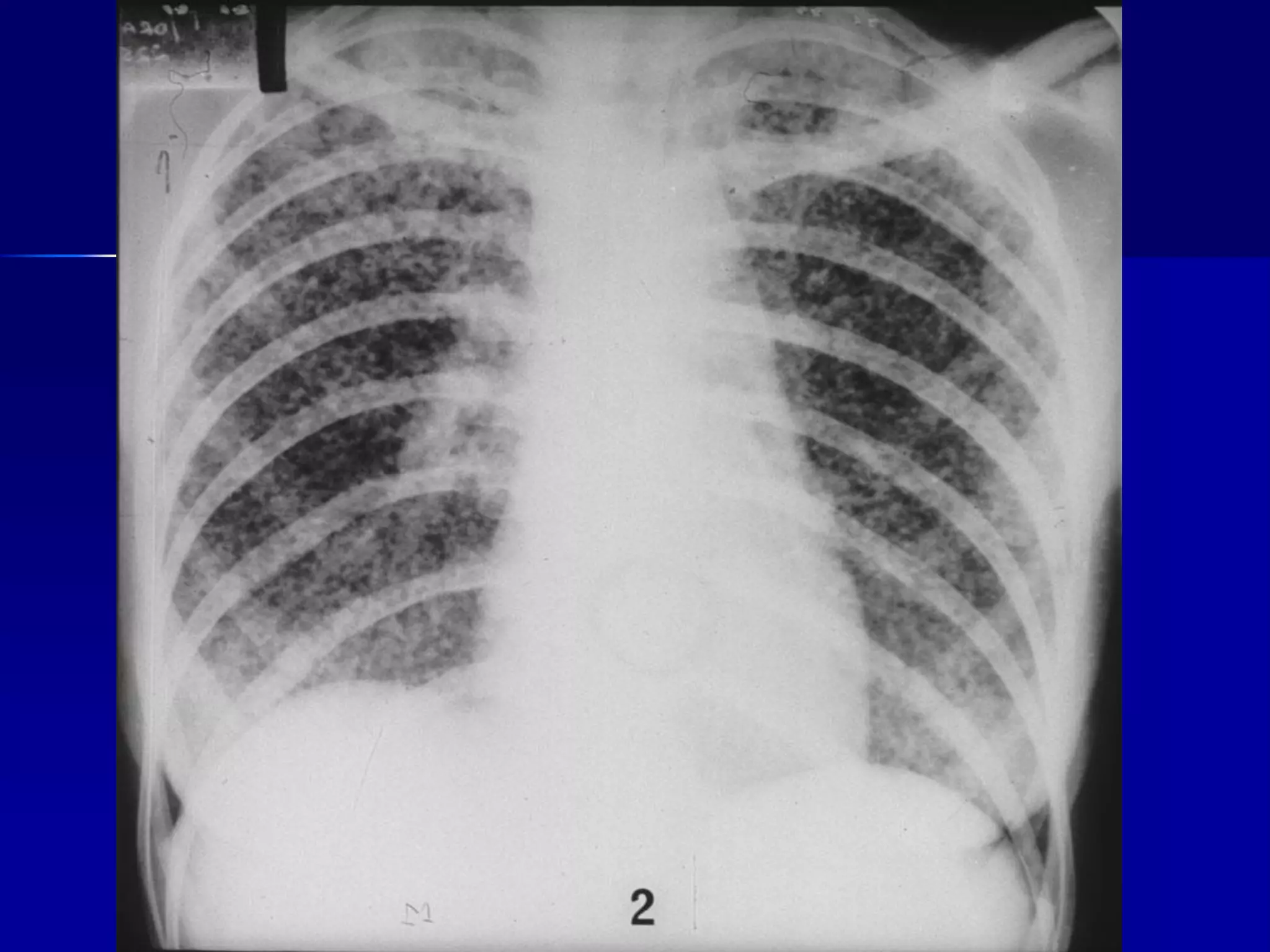
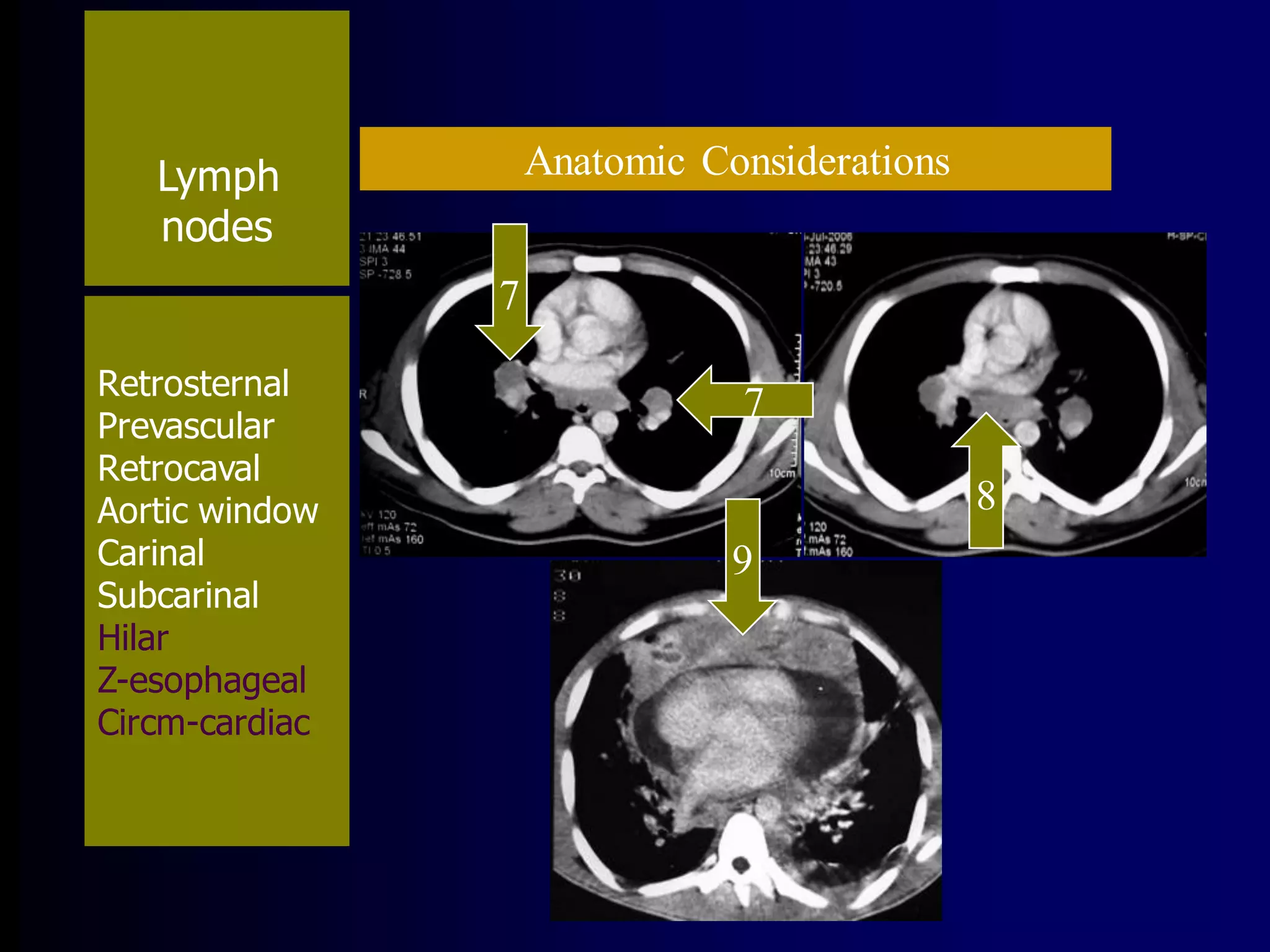
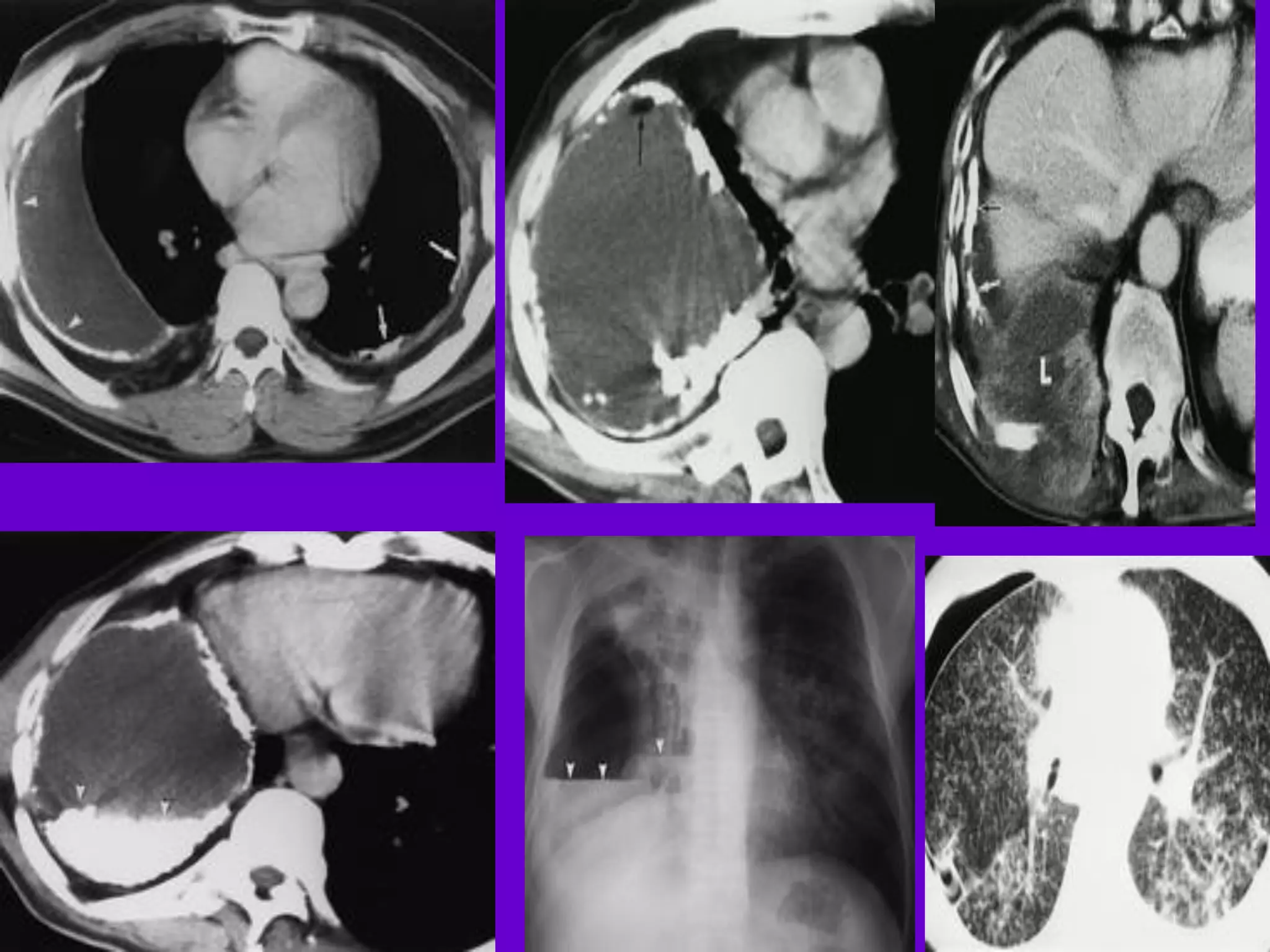
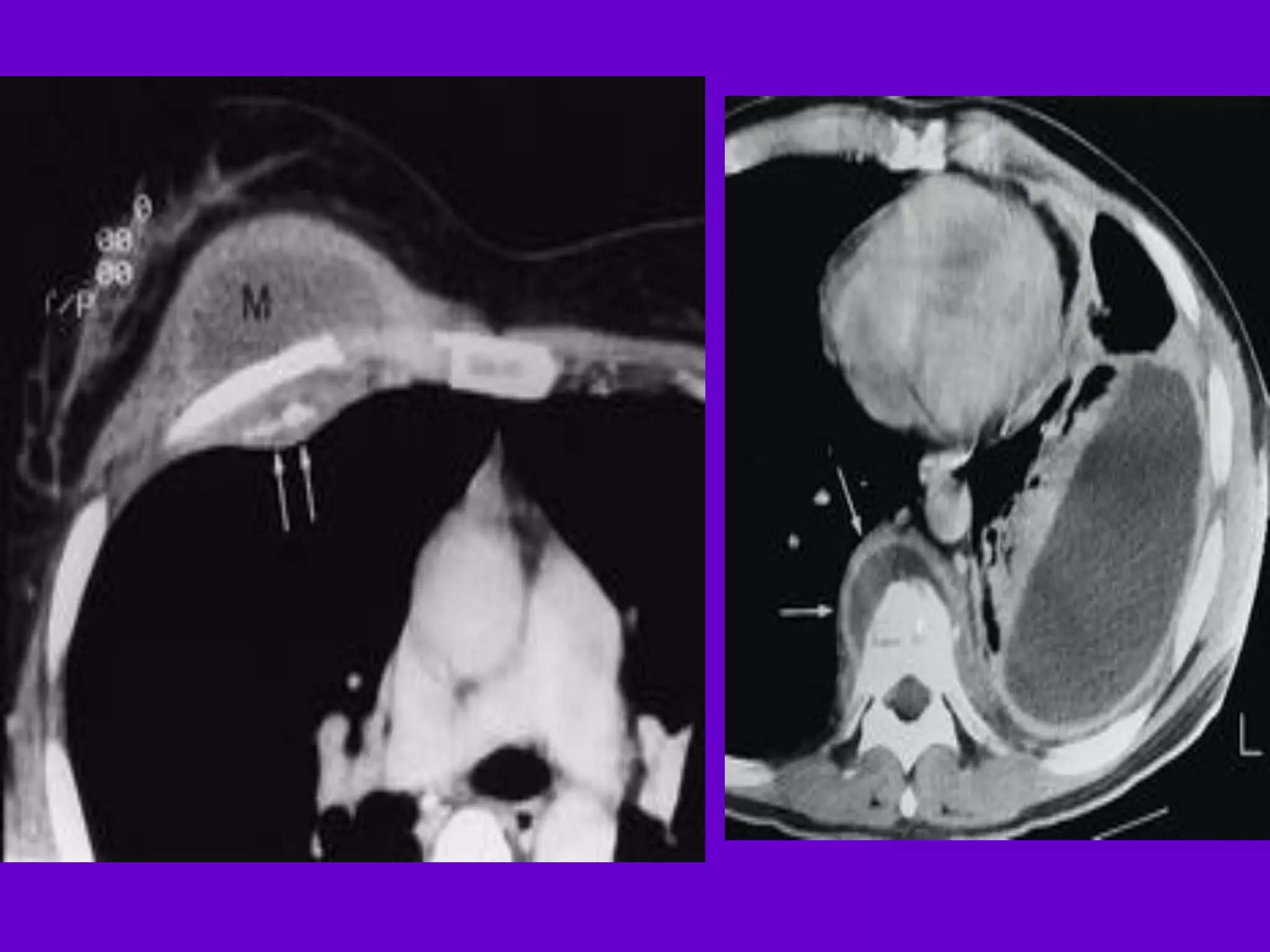
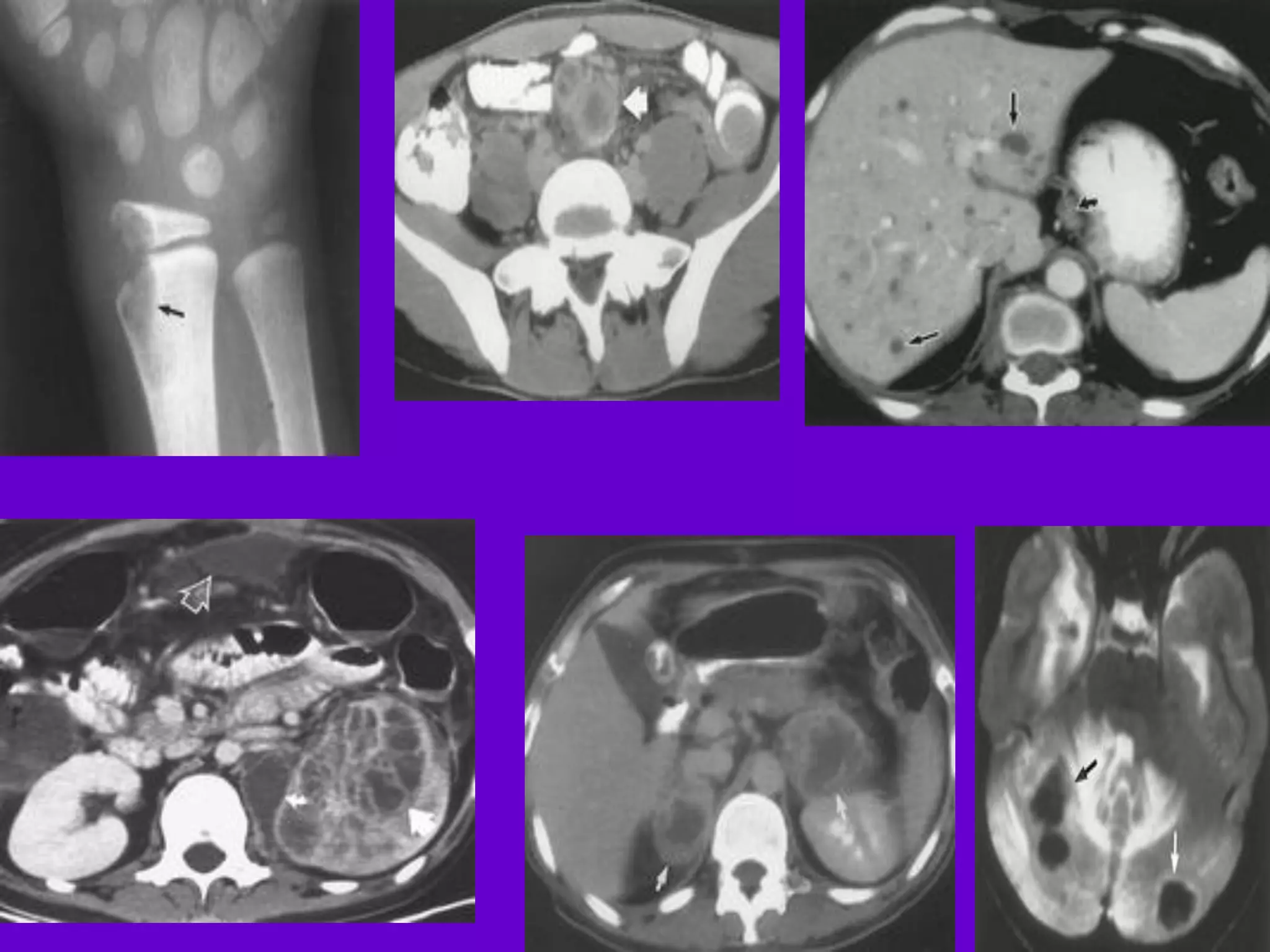
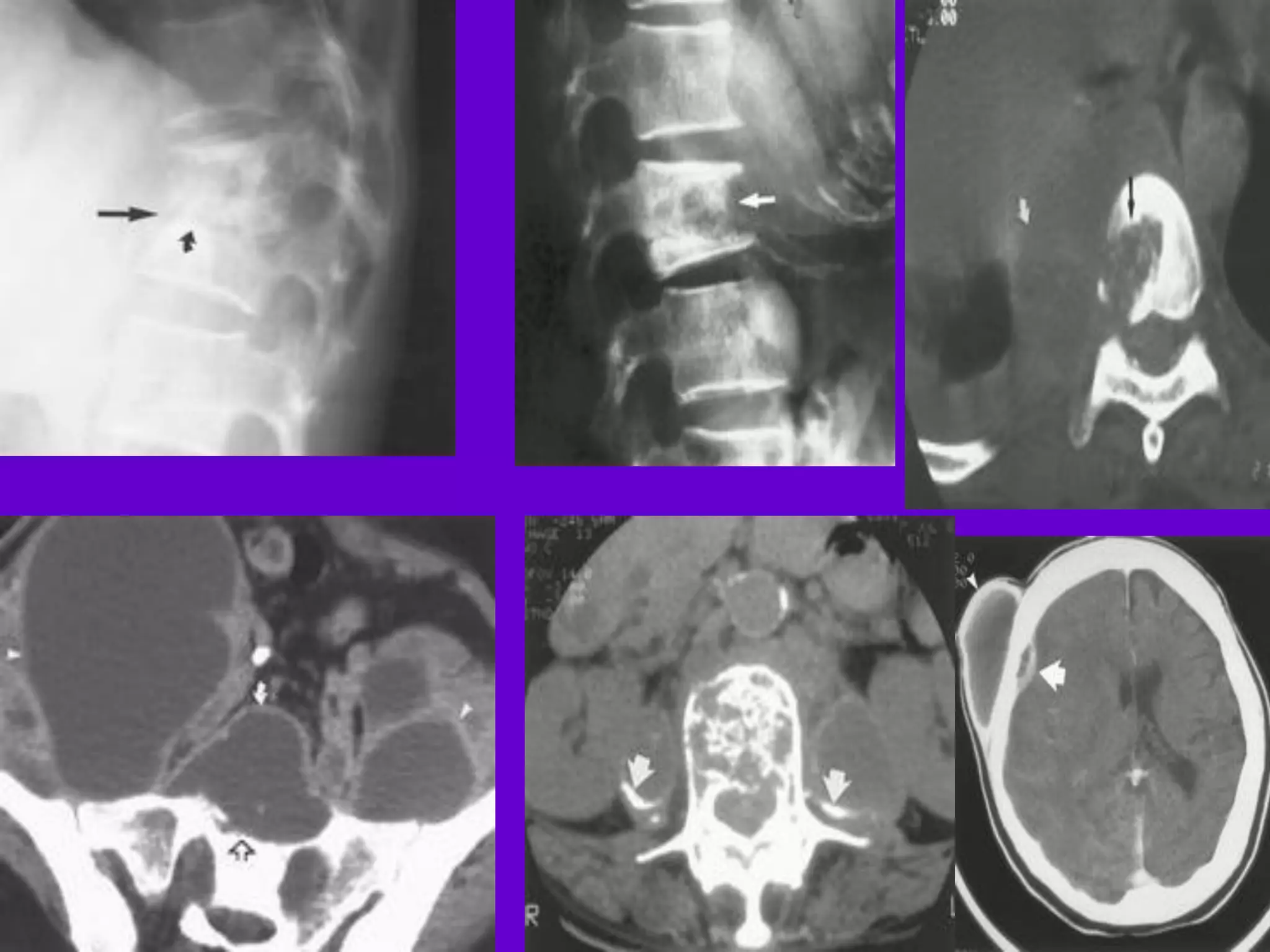
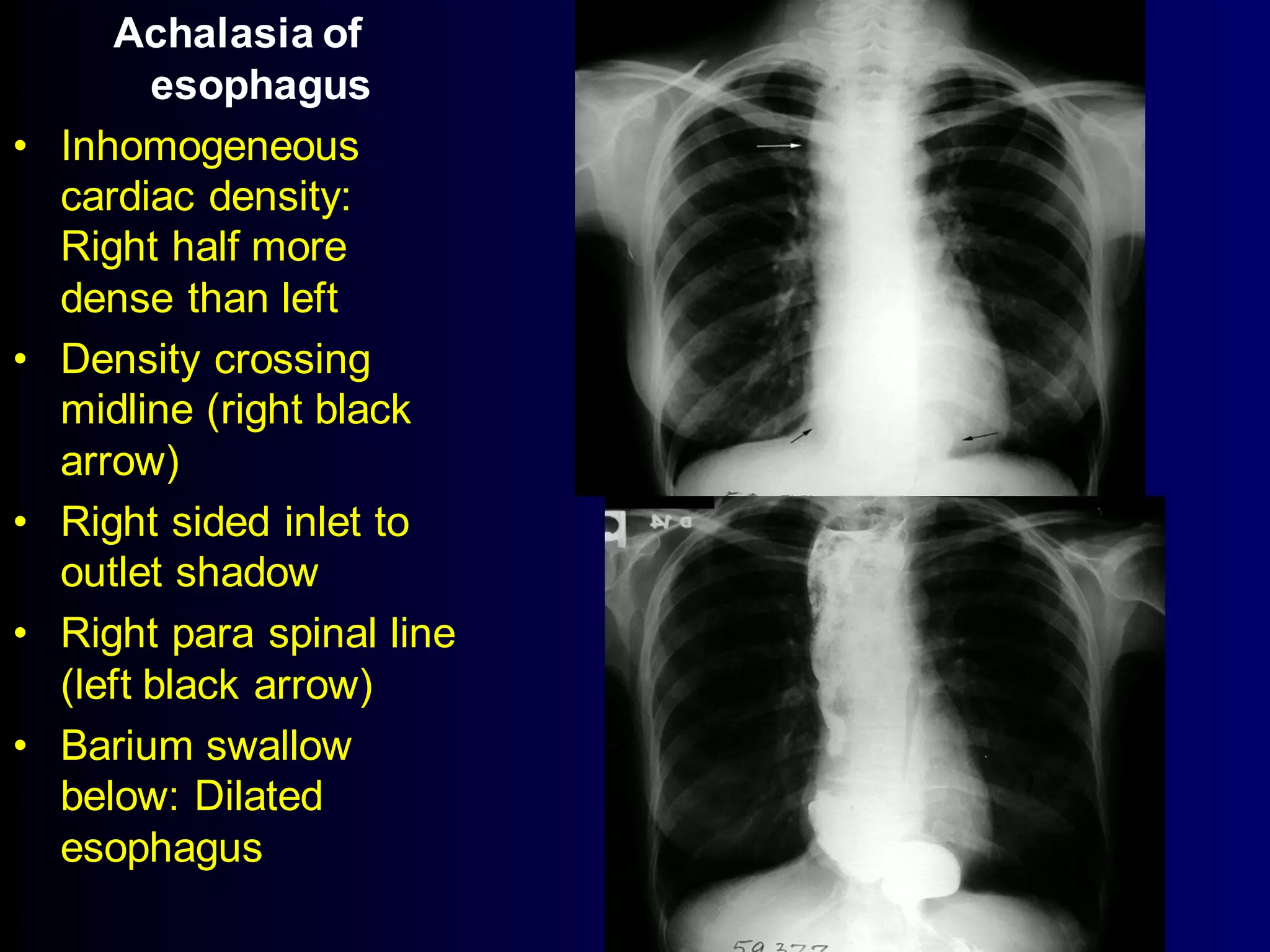
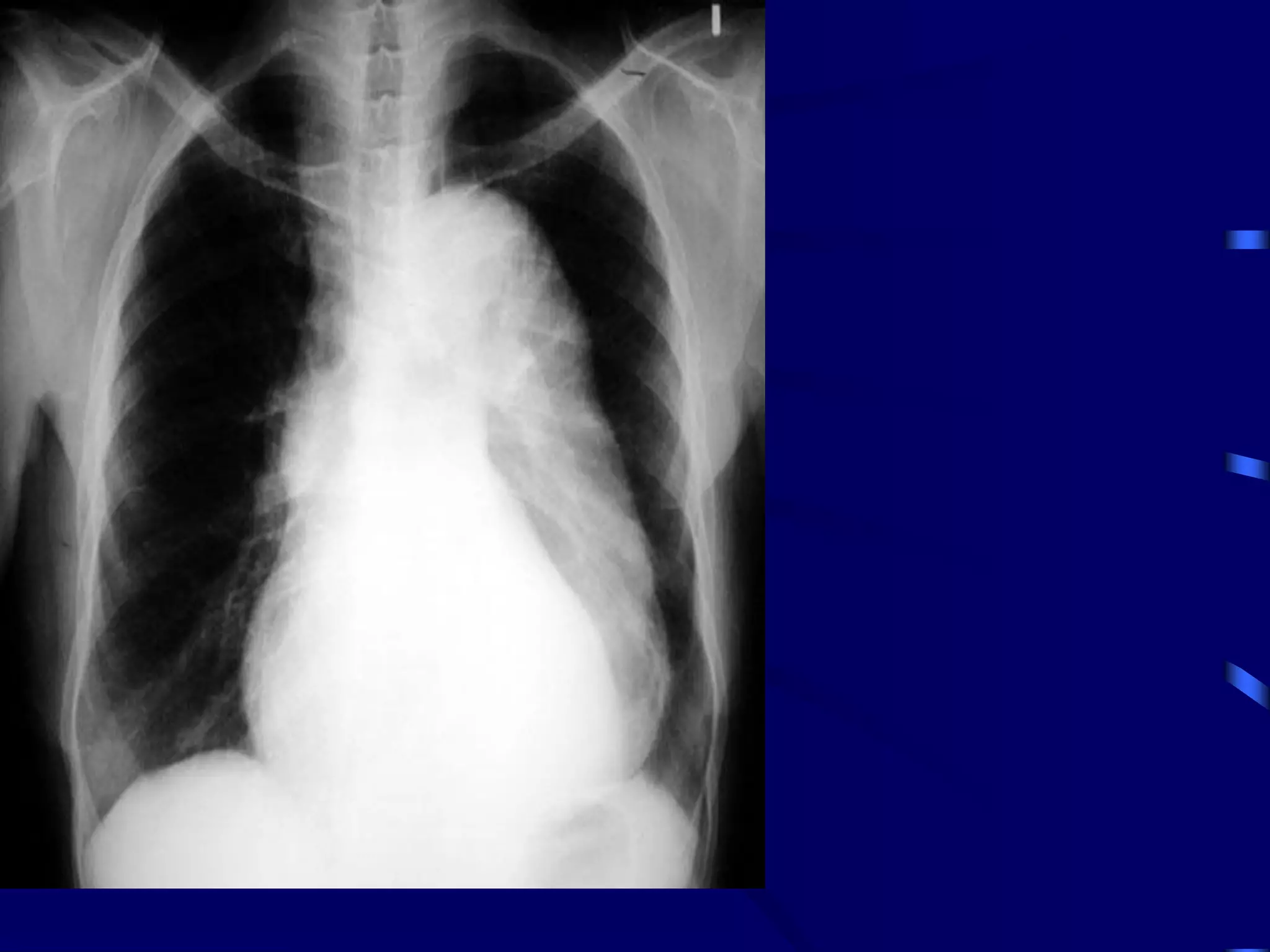
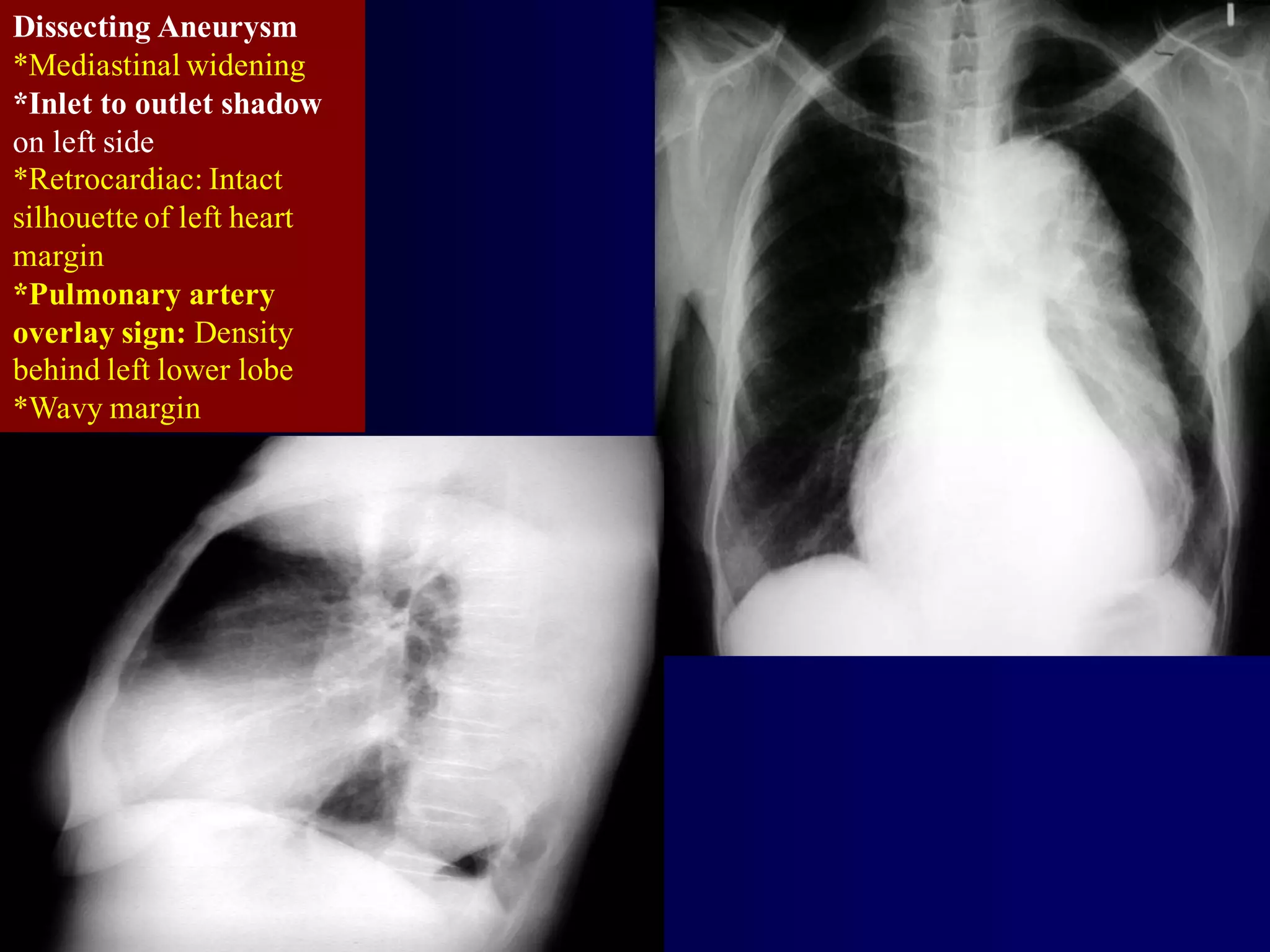
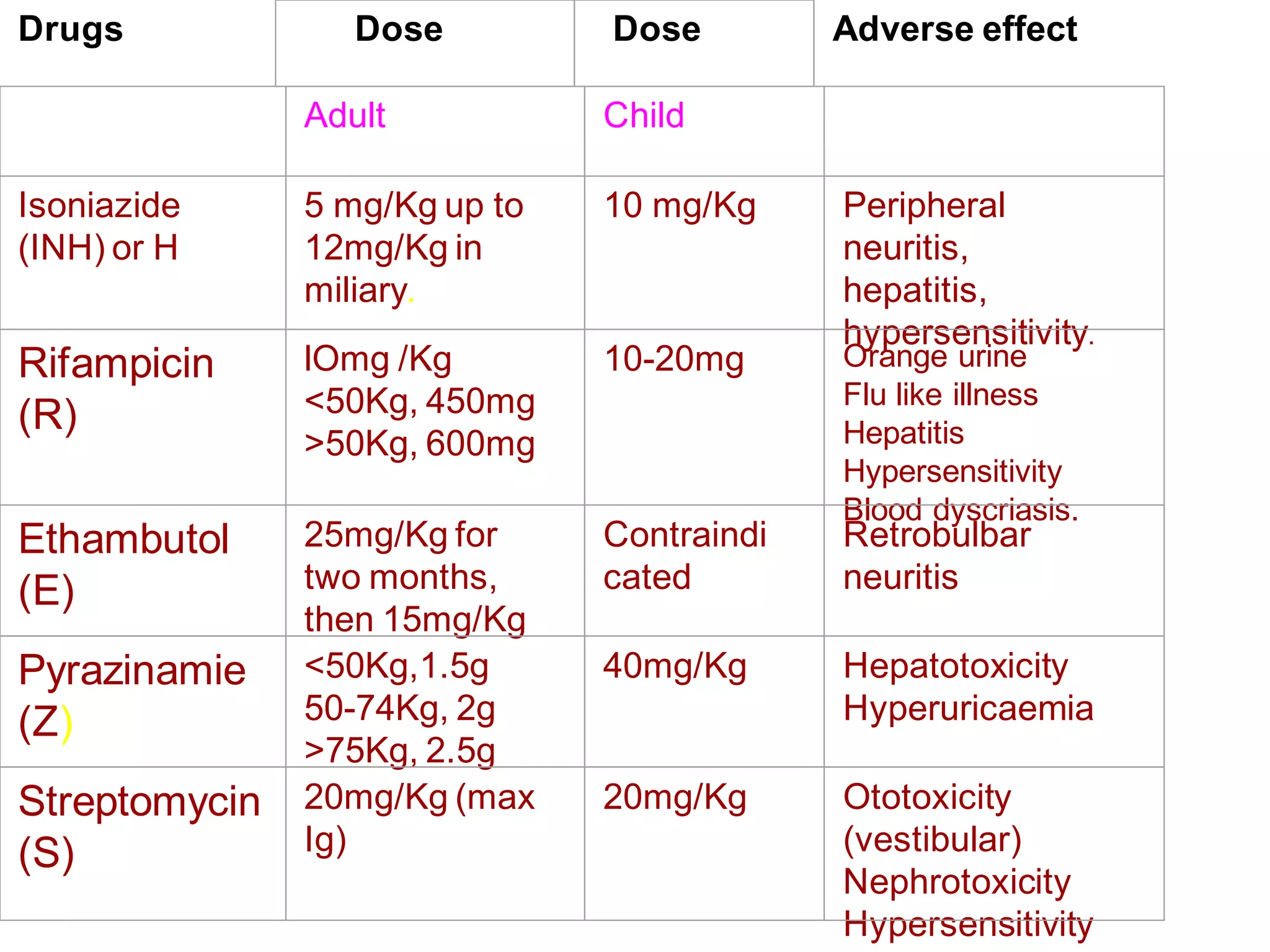
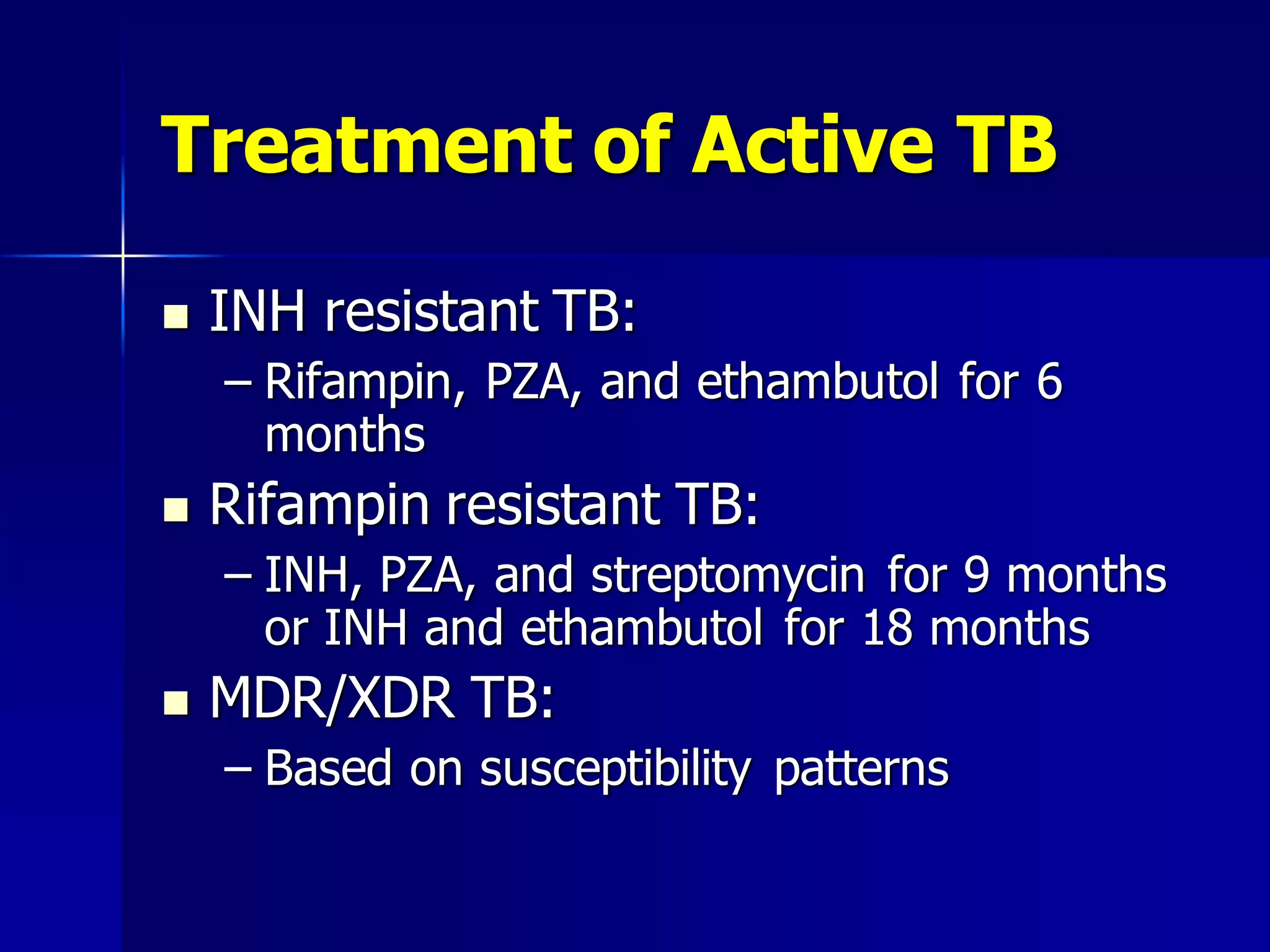
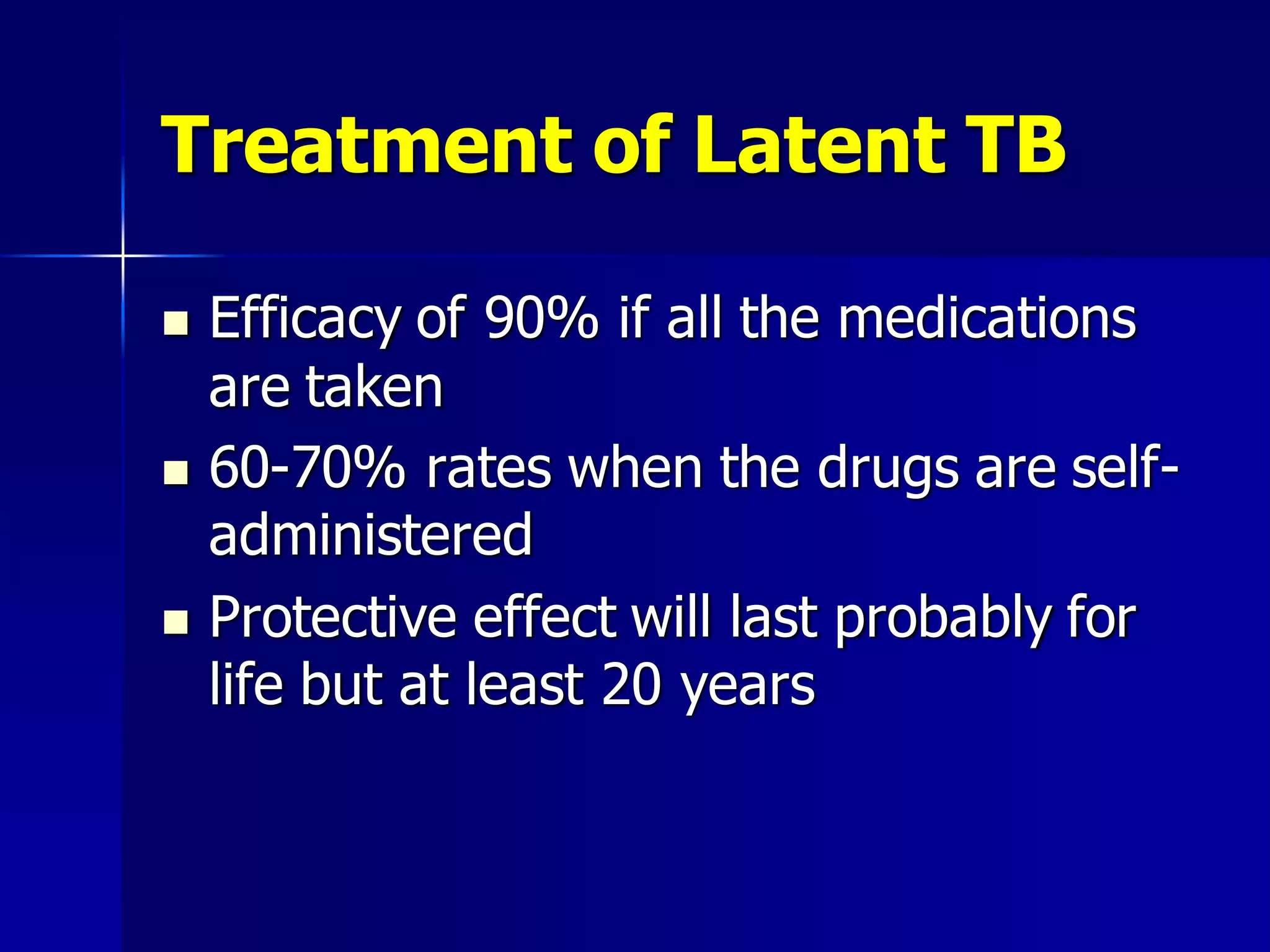
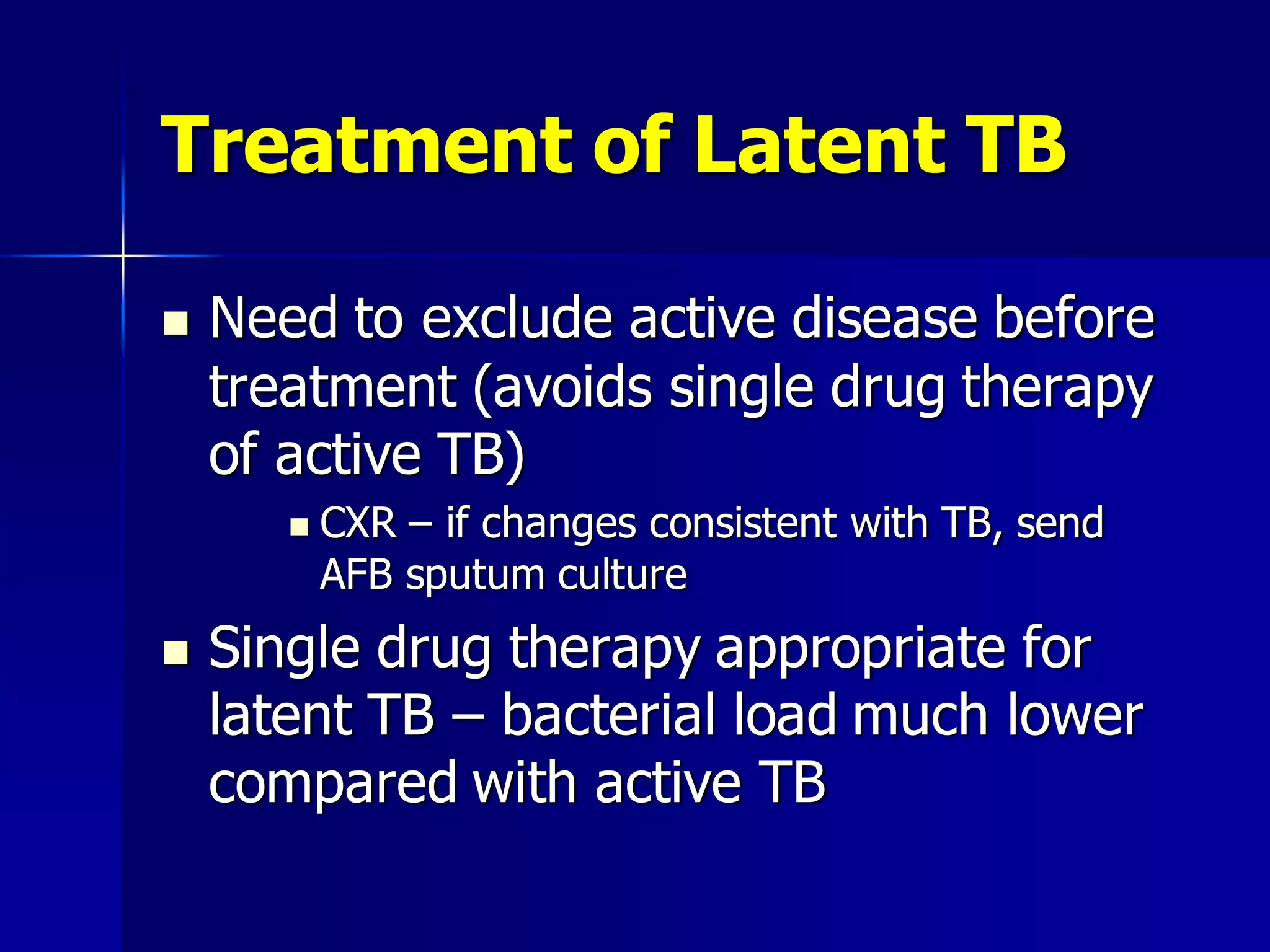
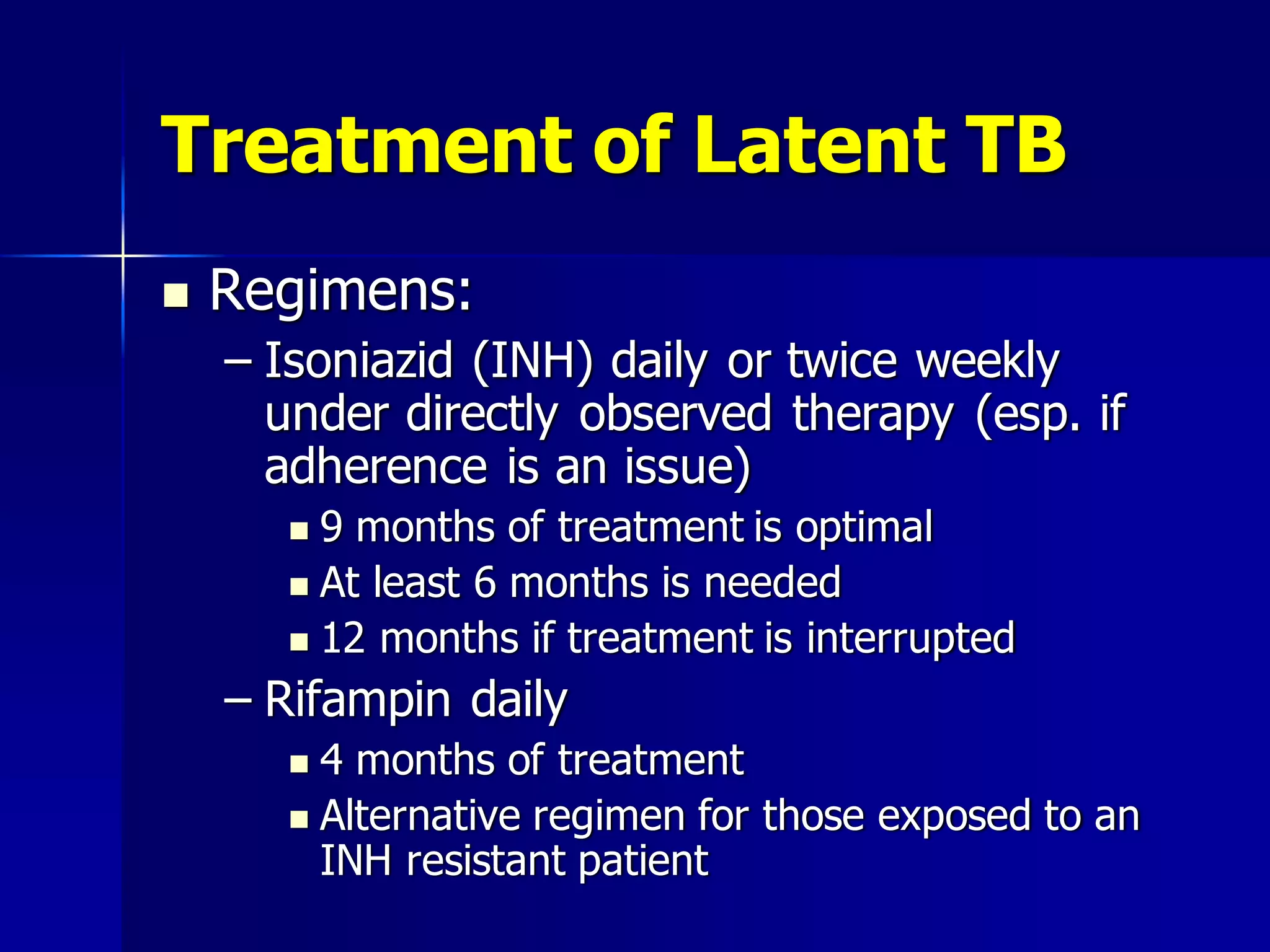
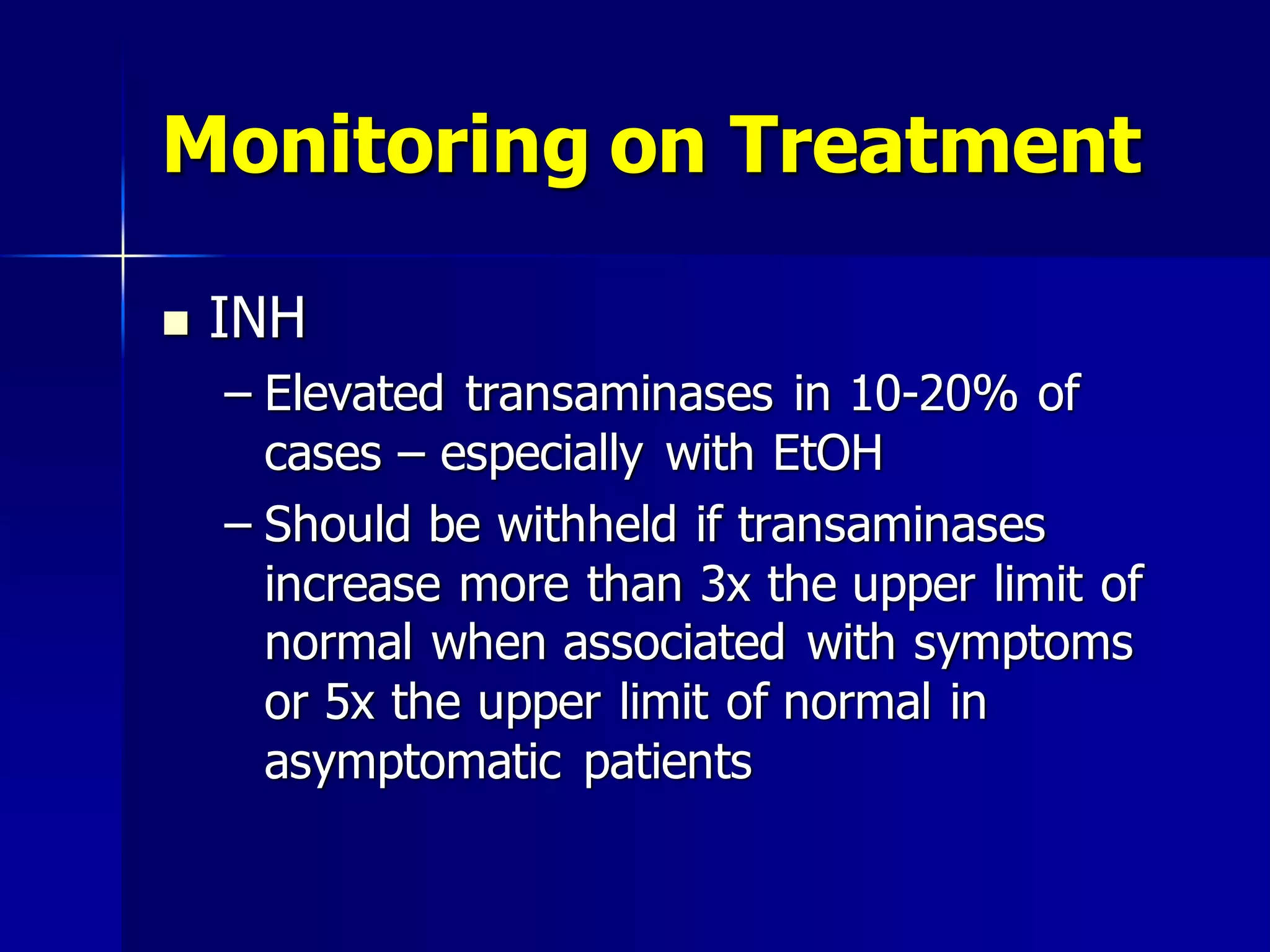
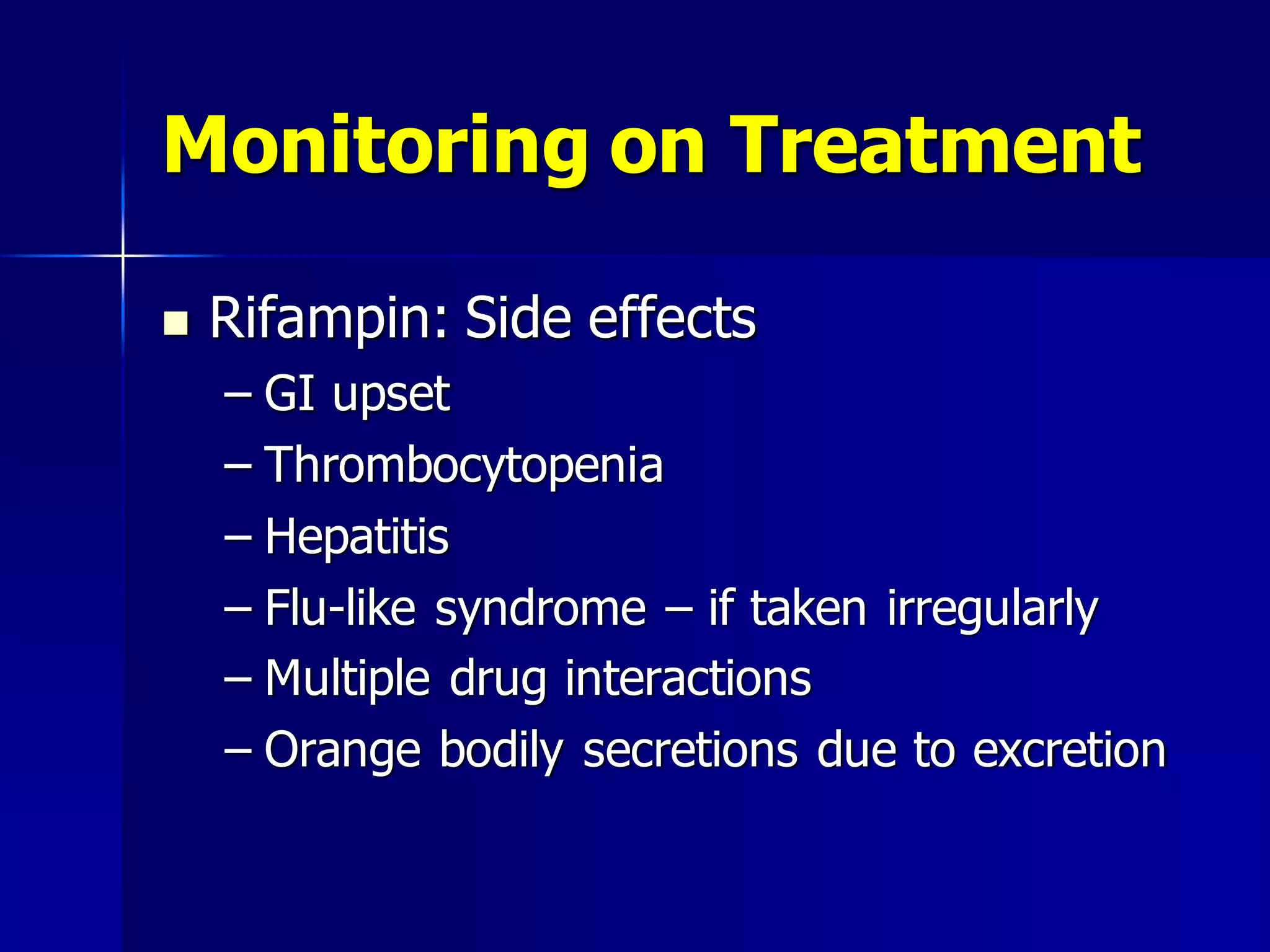
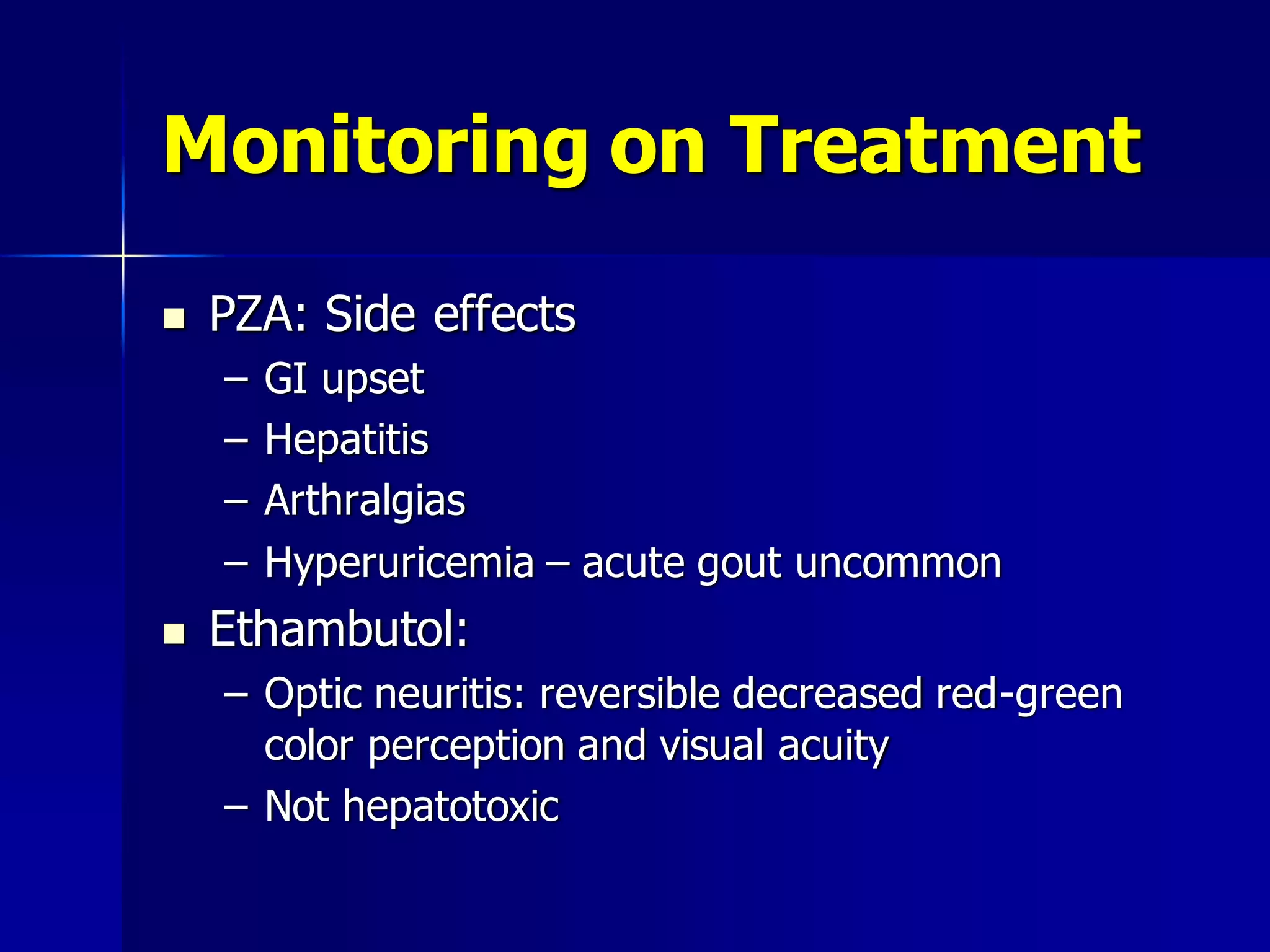
The document provides an overview of tuberculosis (TB), including its epidemiology, microbiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Some key points:
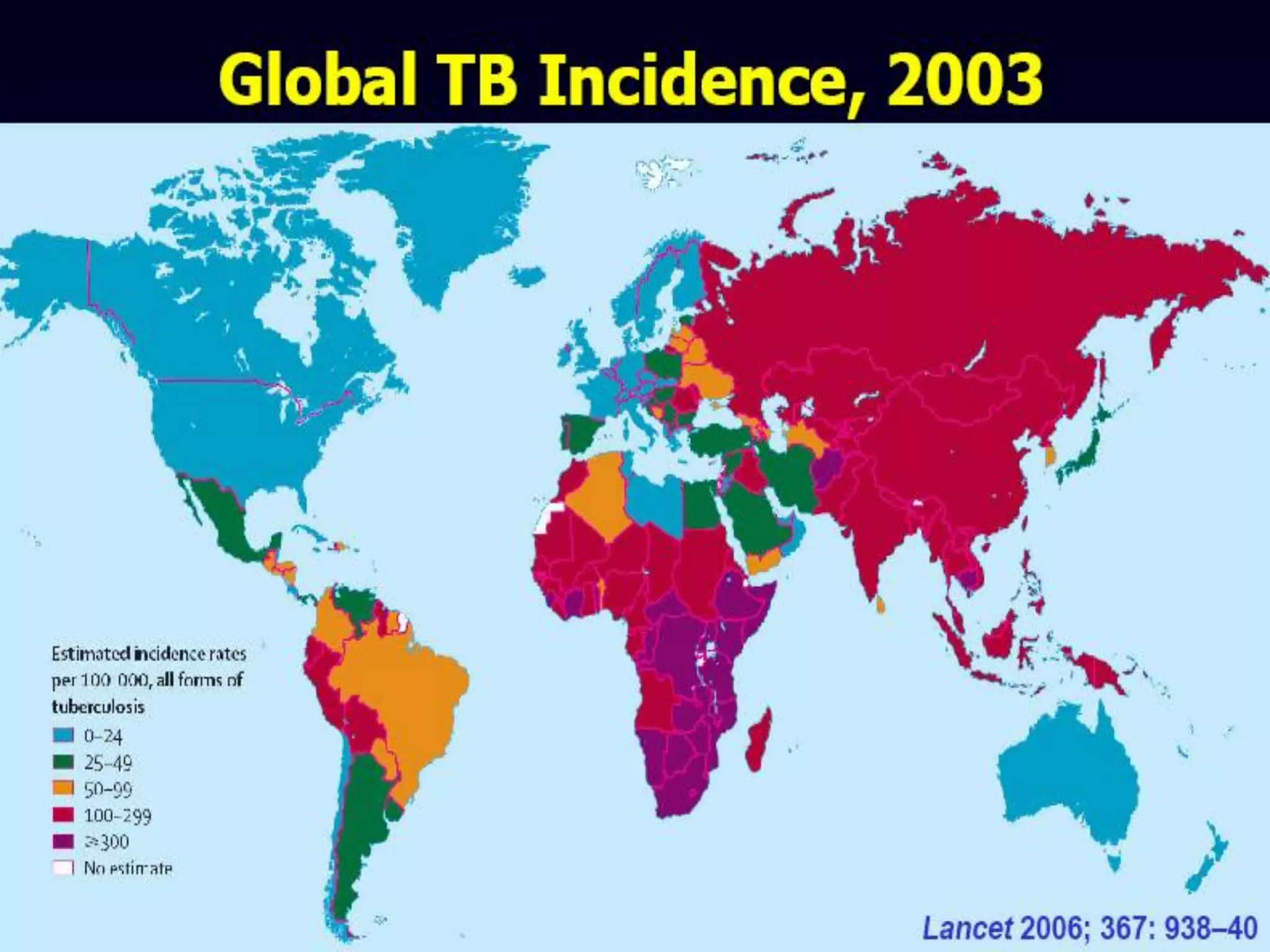
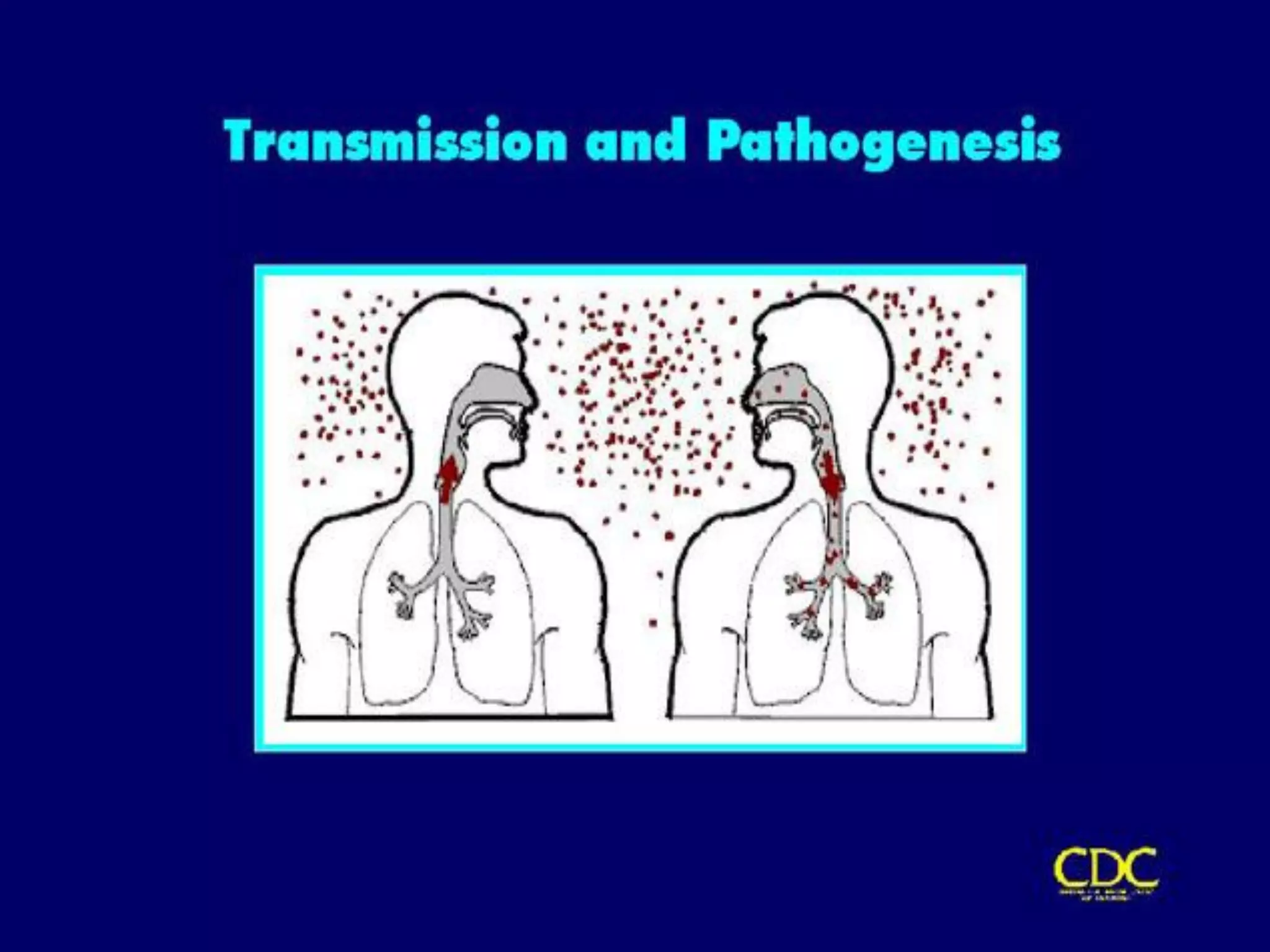
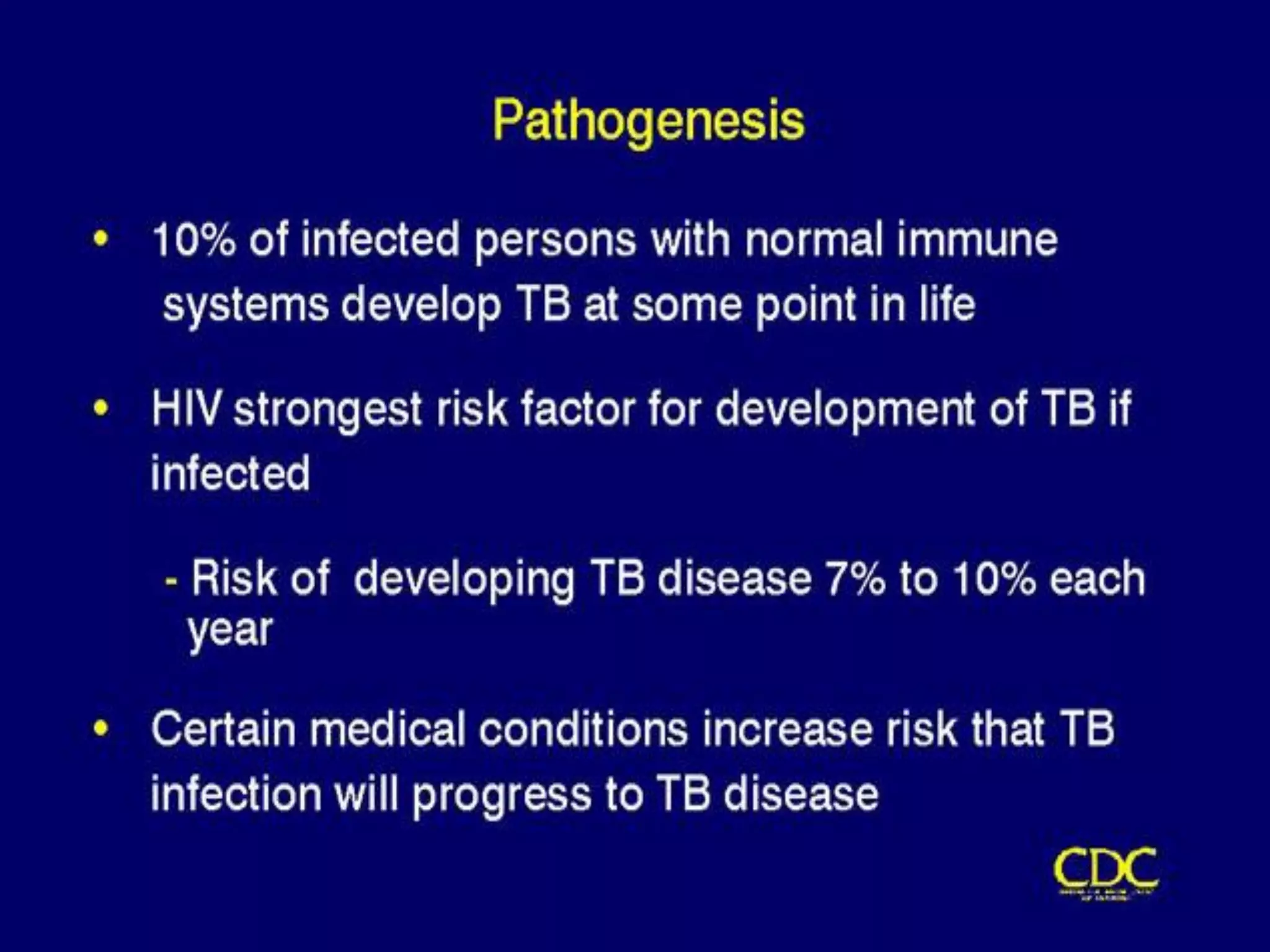
- TB infects millions worldwide each year and is a leading cause of death. 95% of cases occur in developing countries.
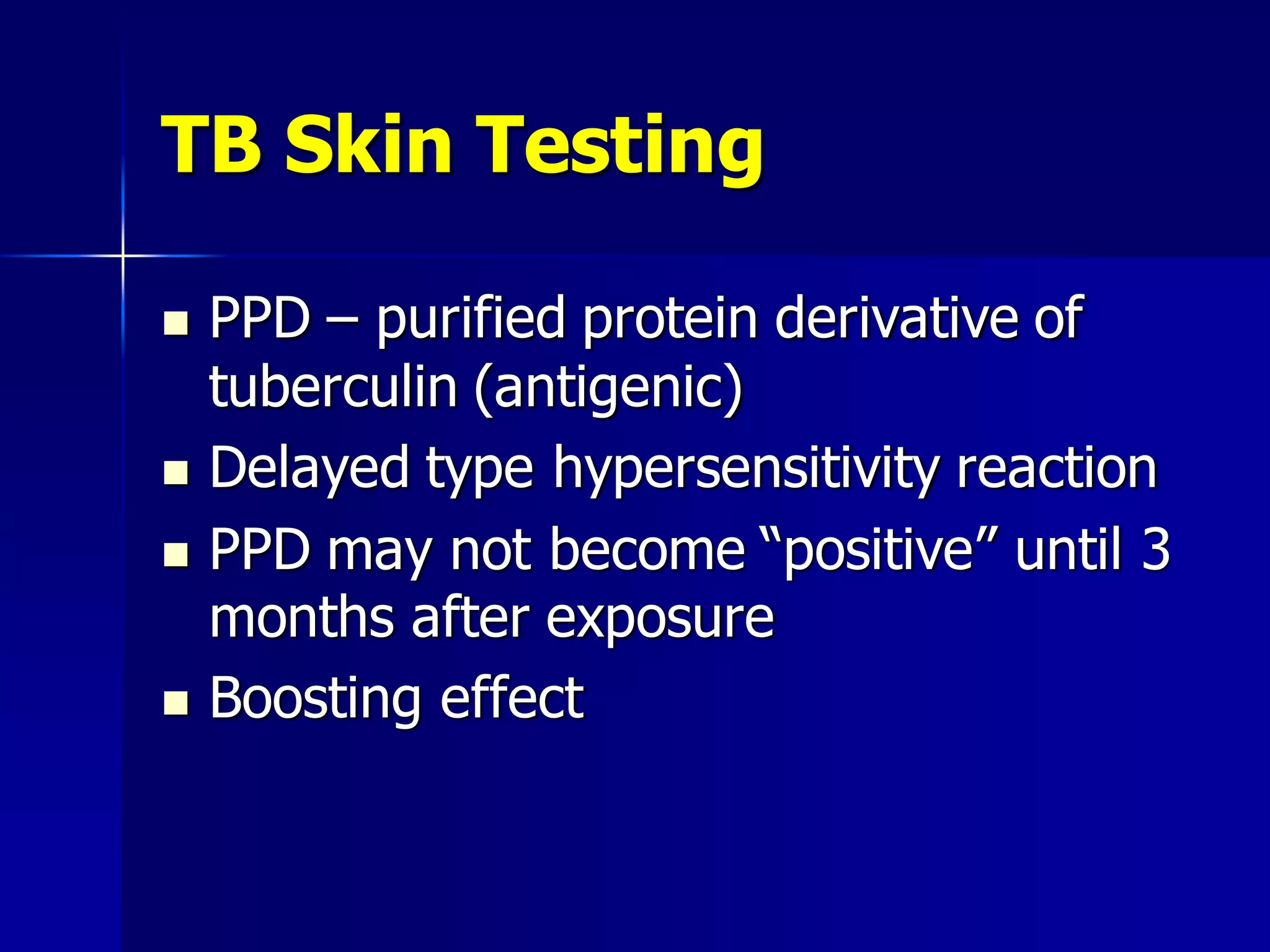
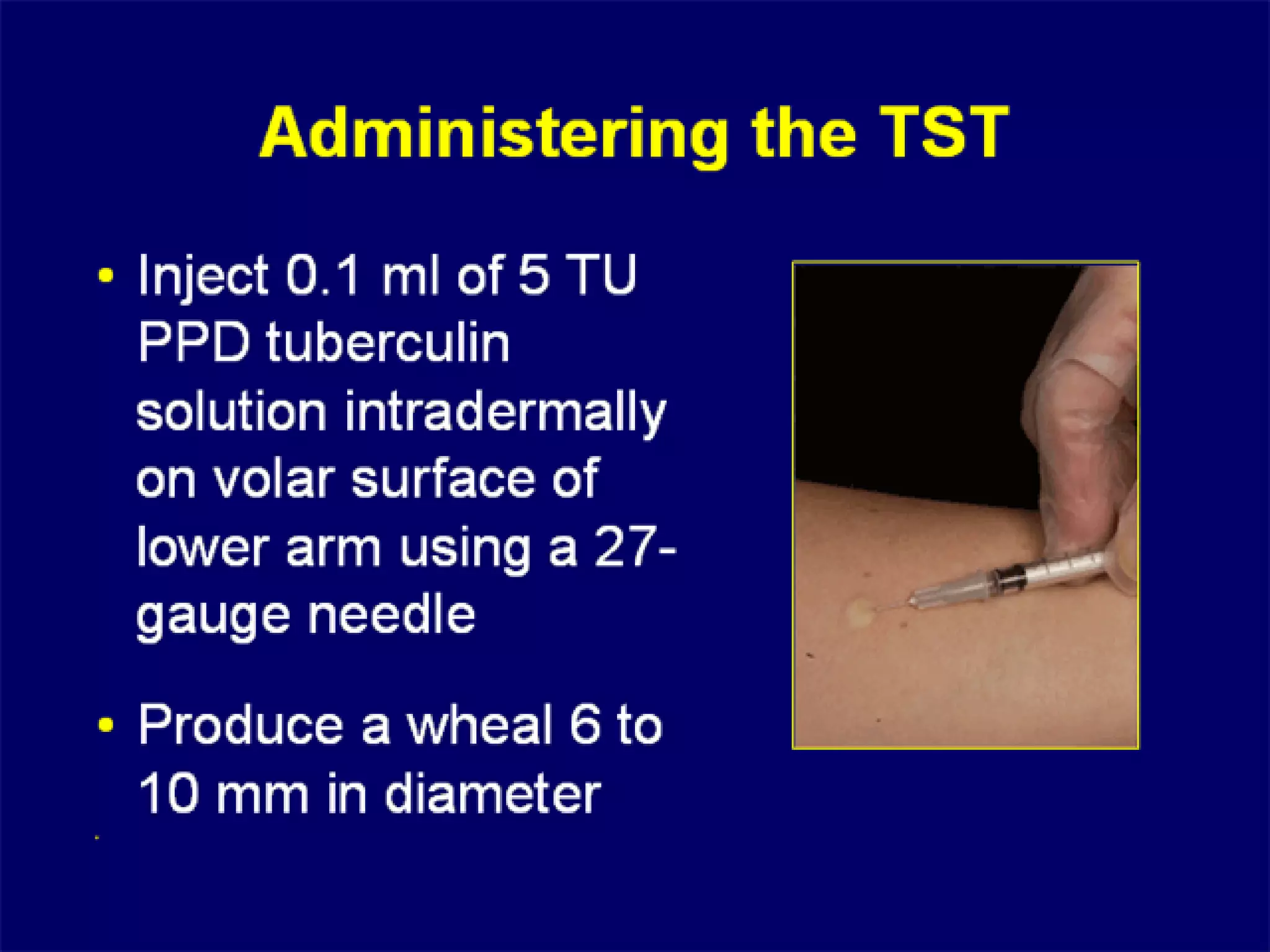
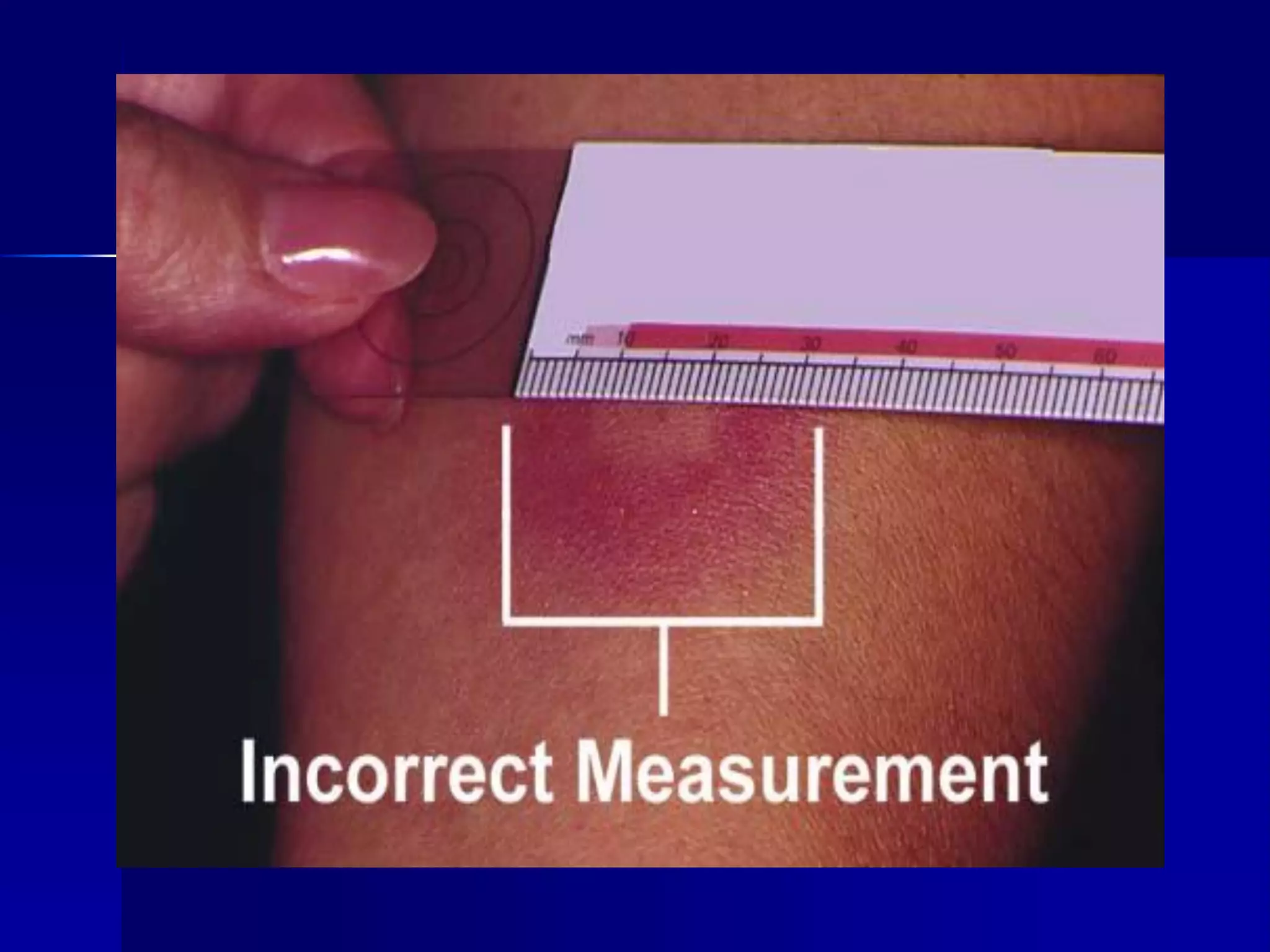
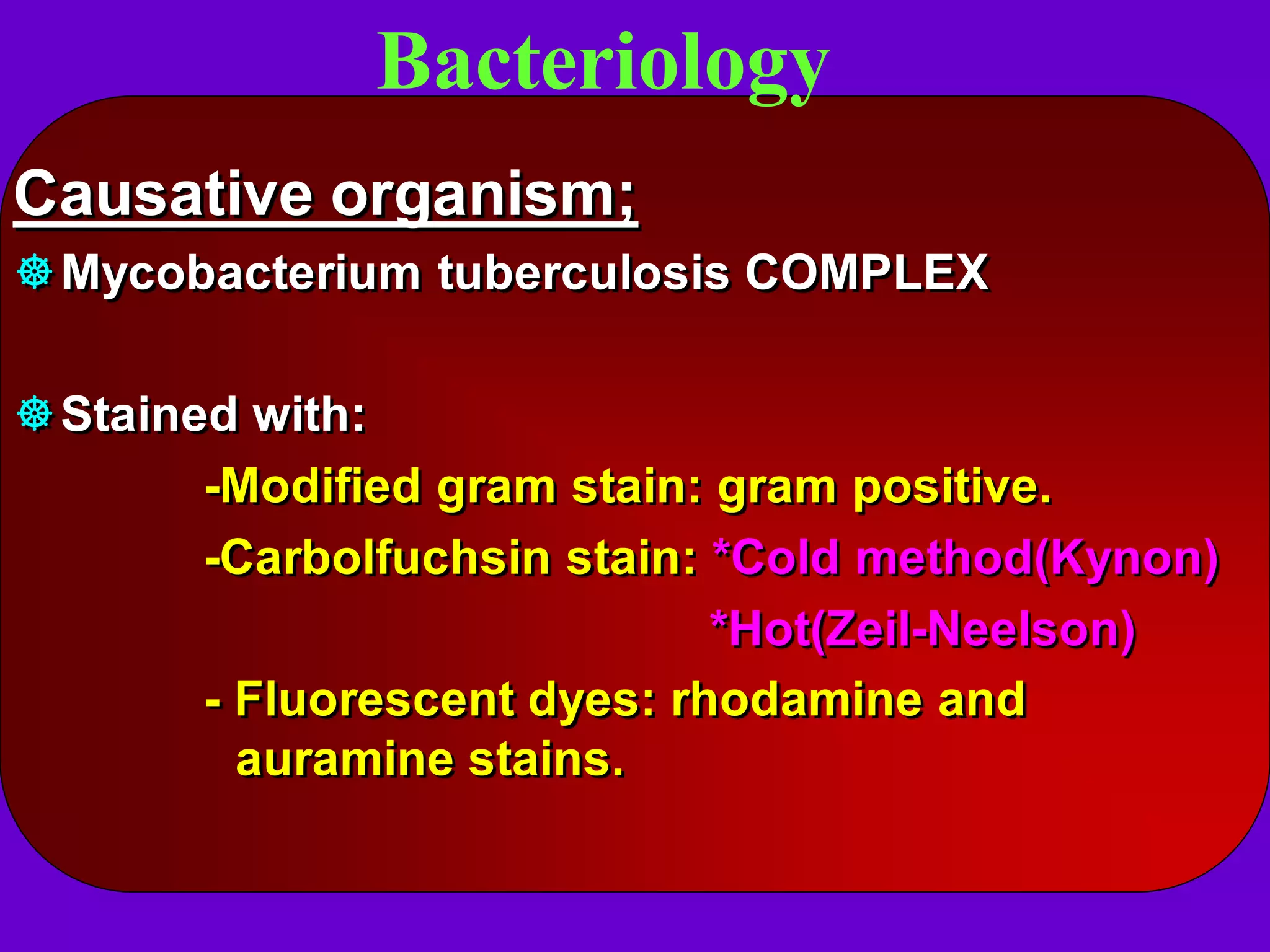
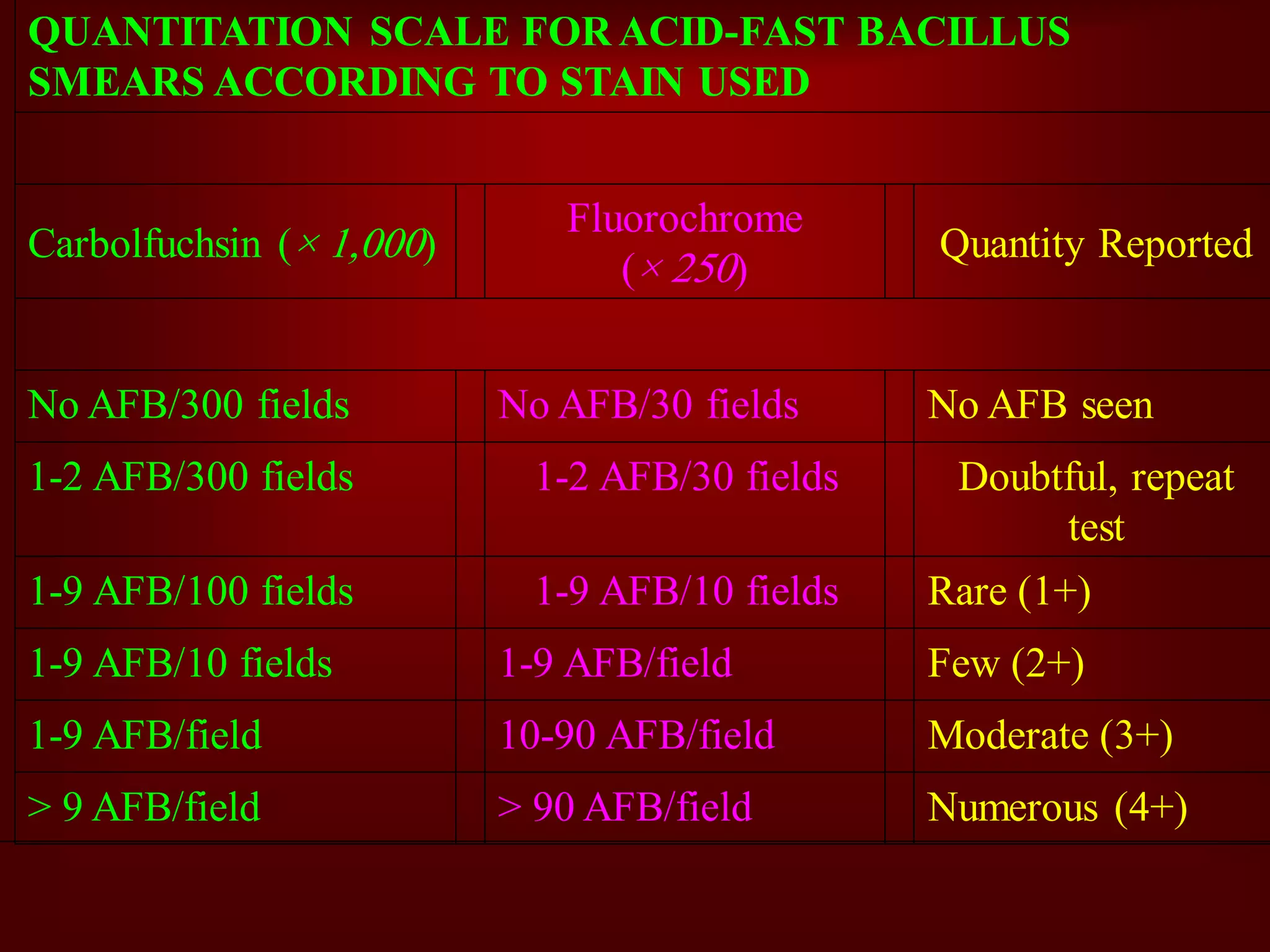
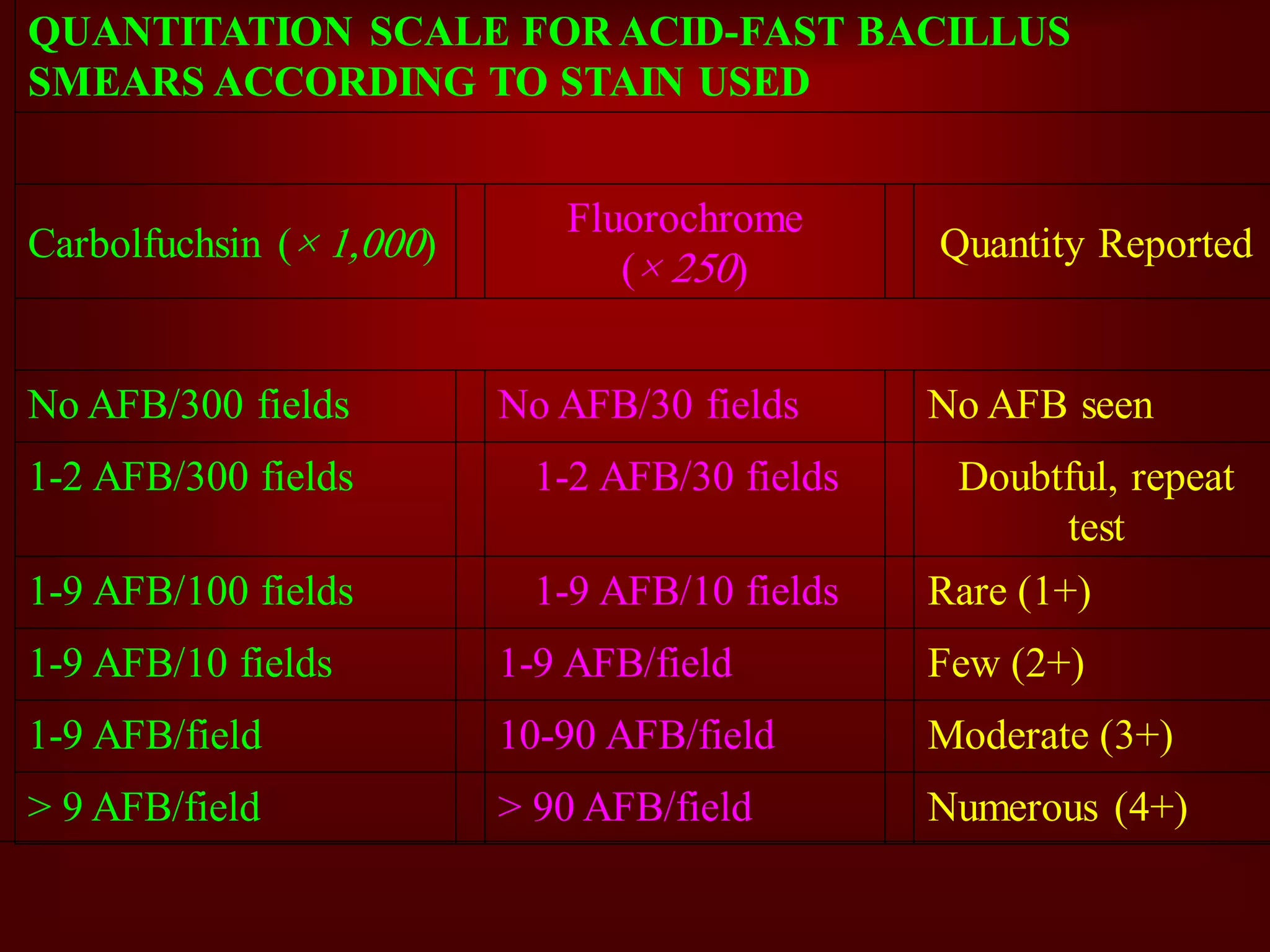
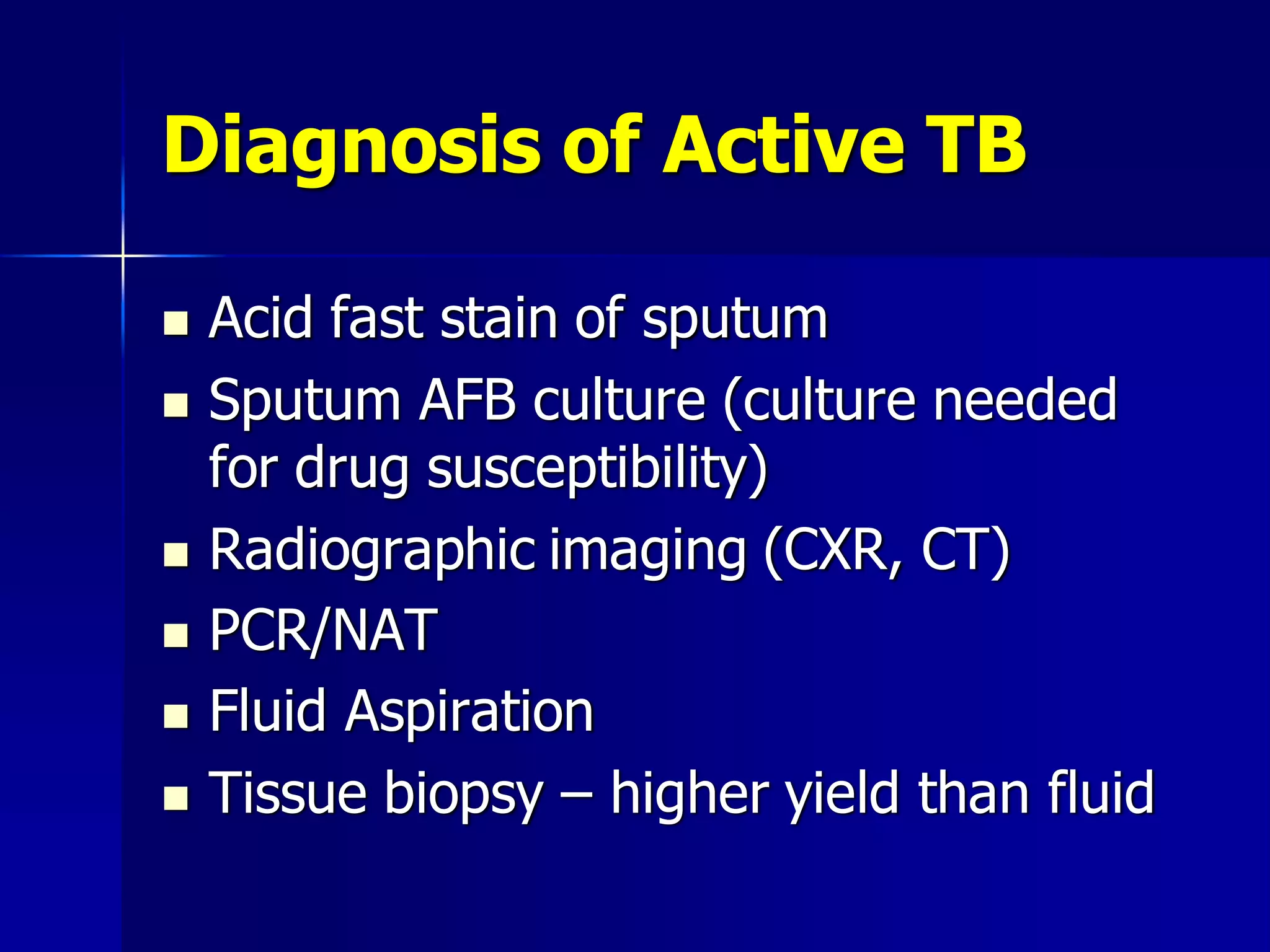
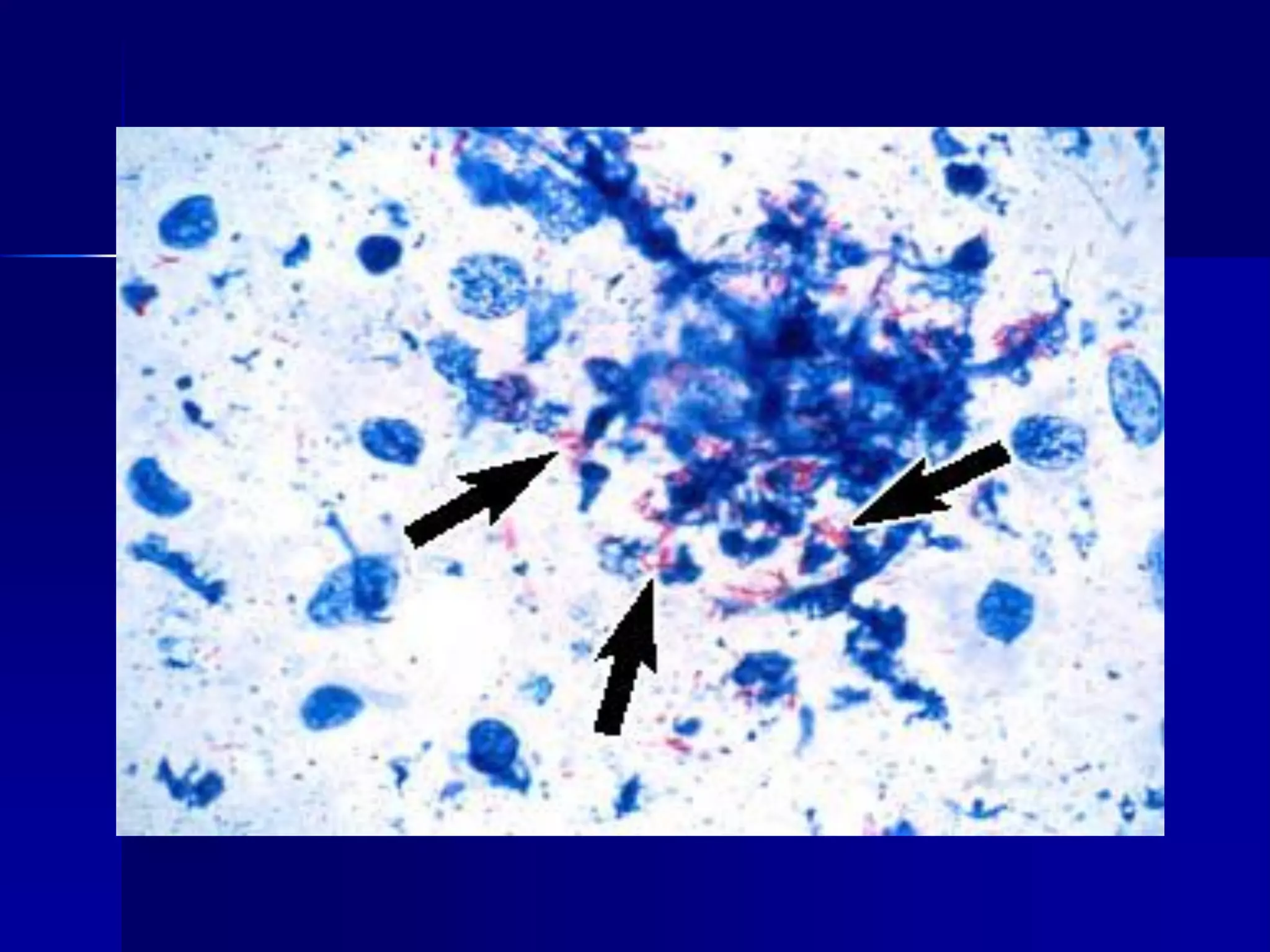
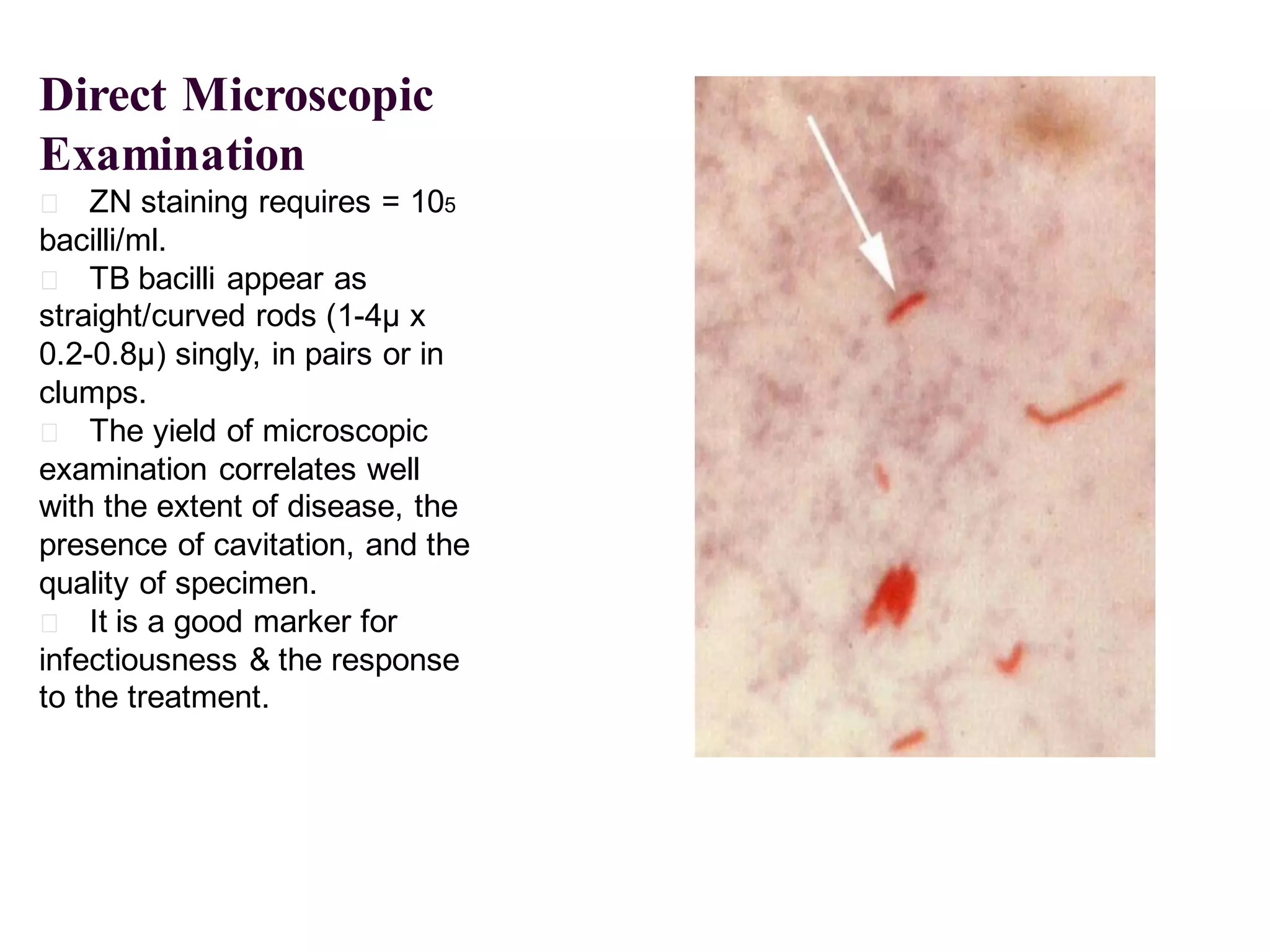
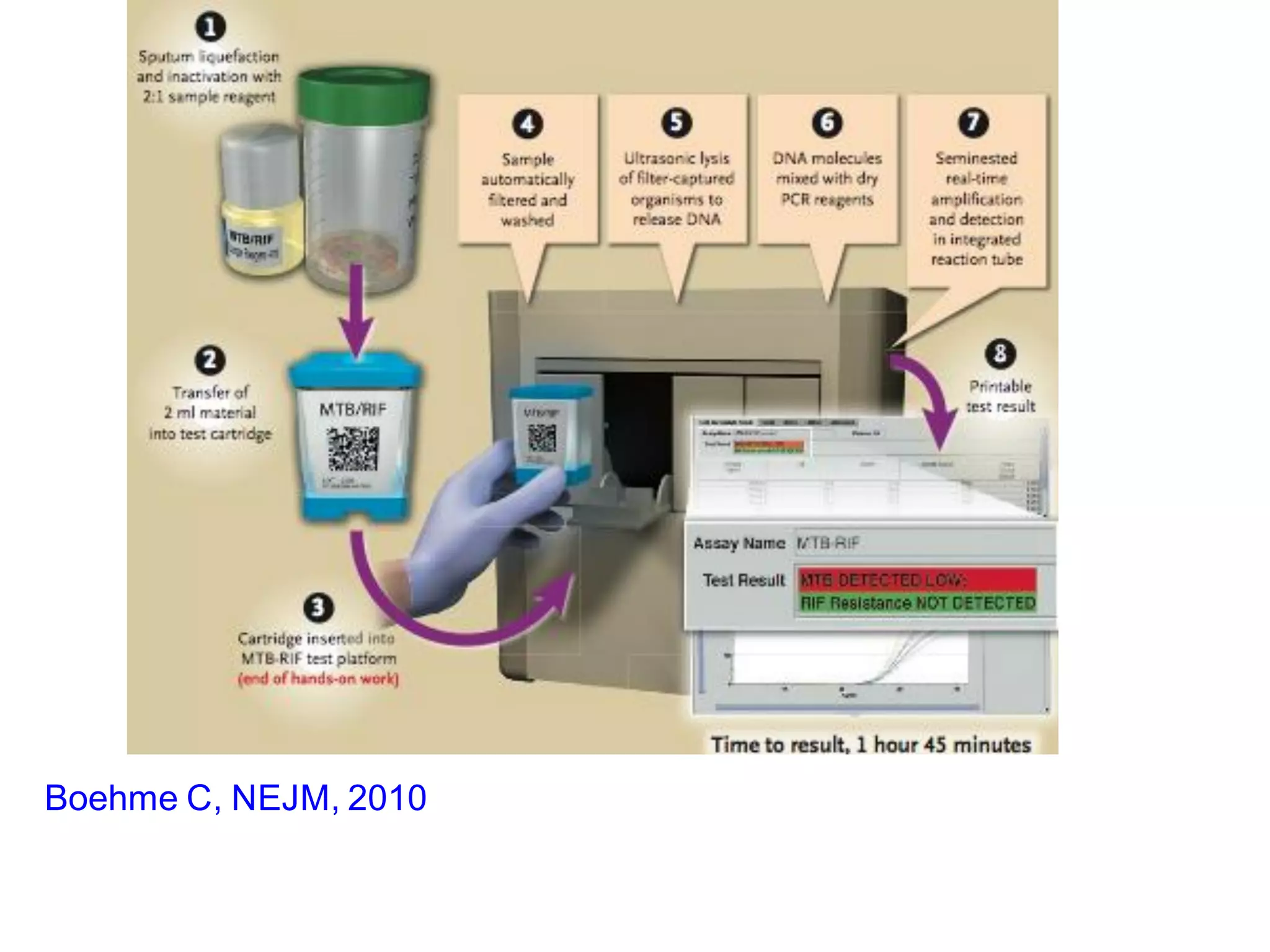
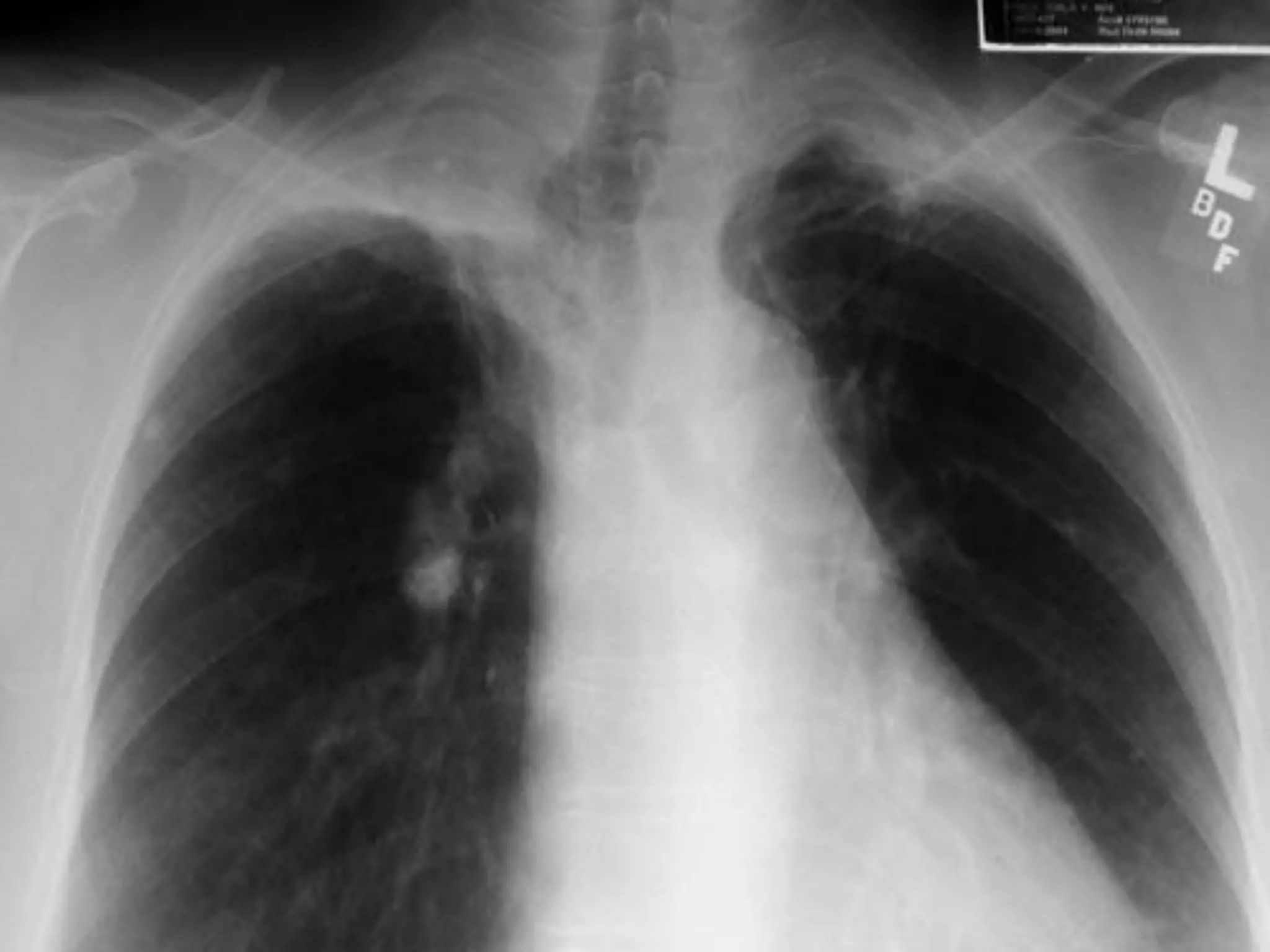
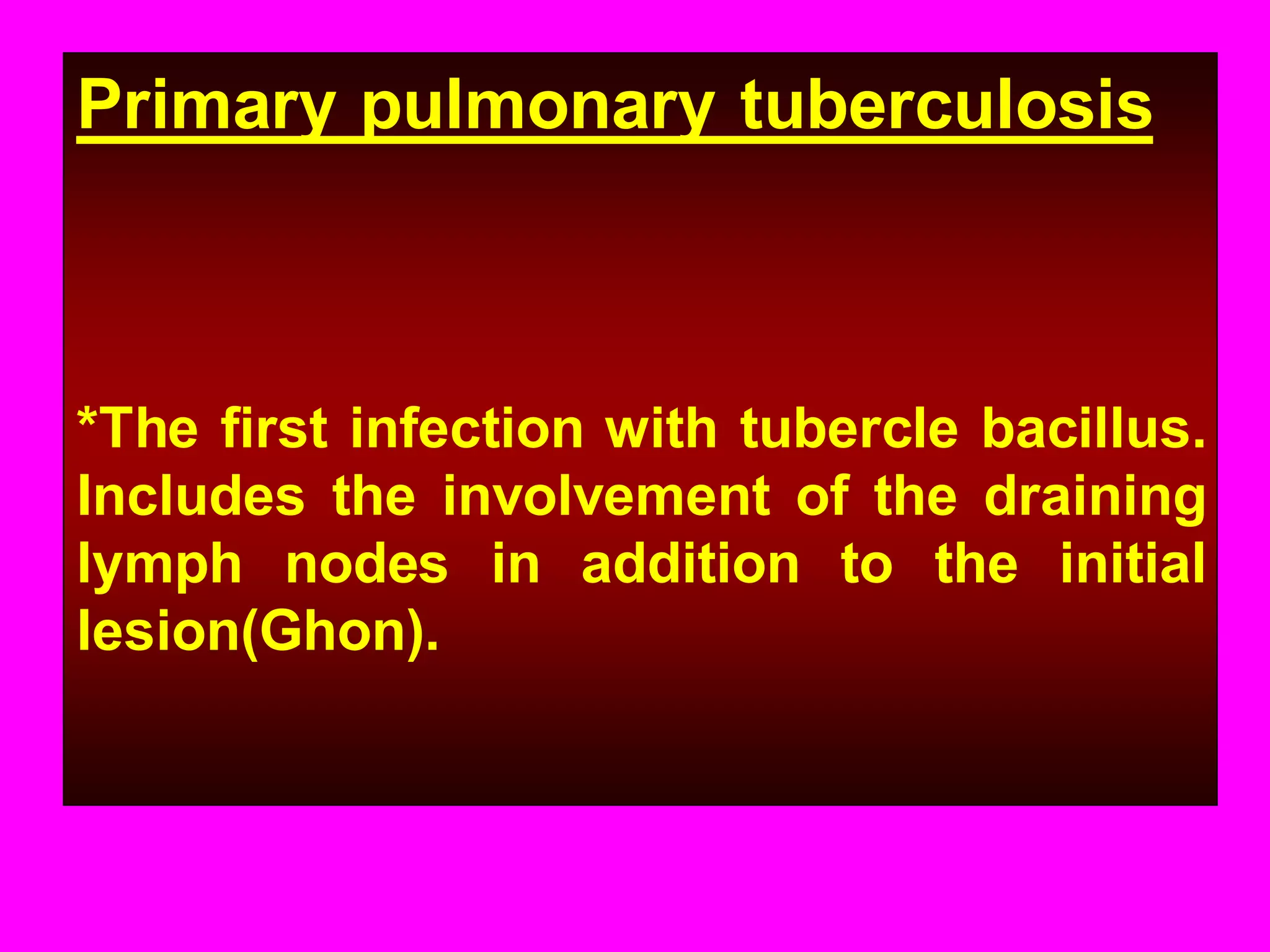
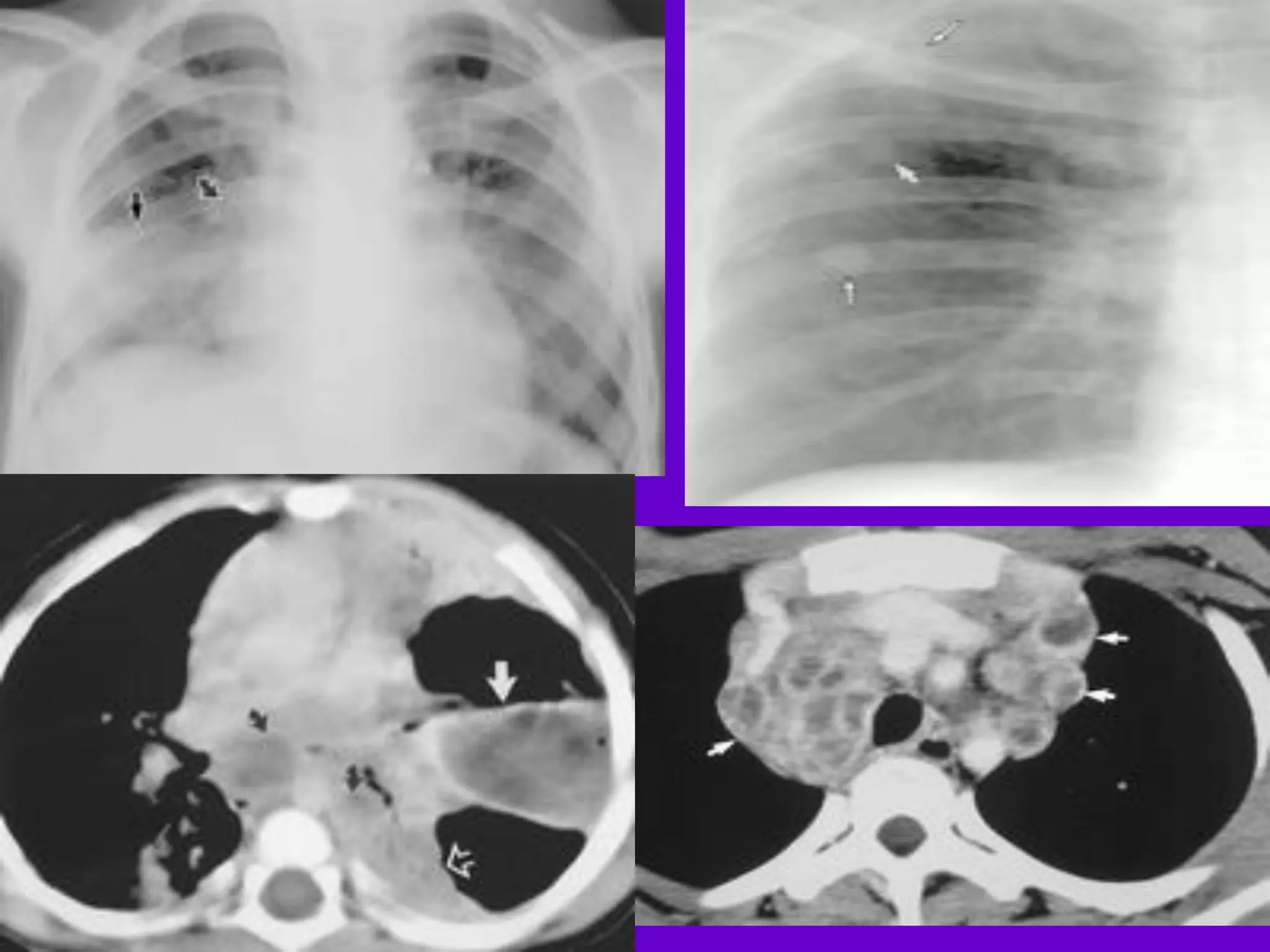
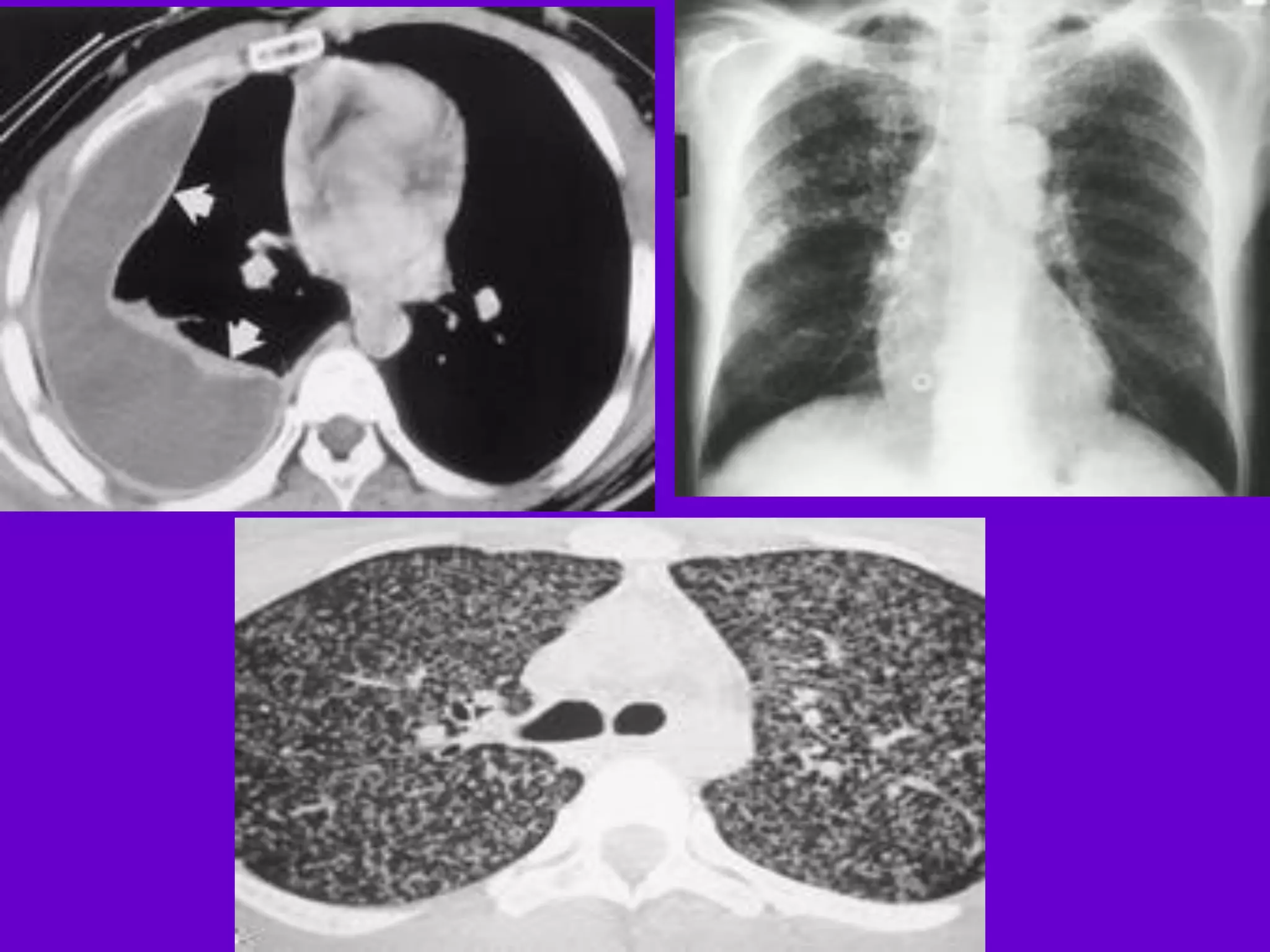
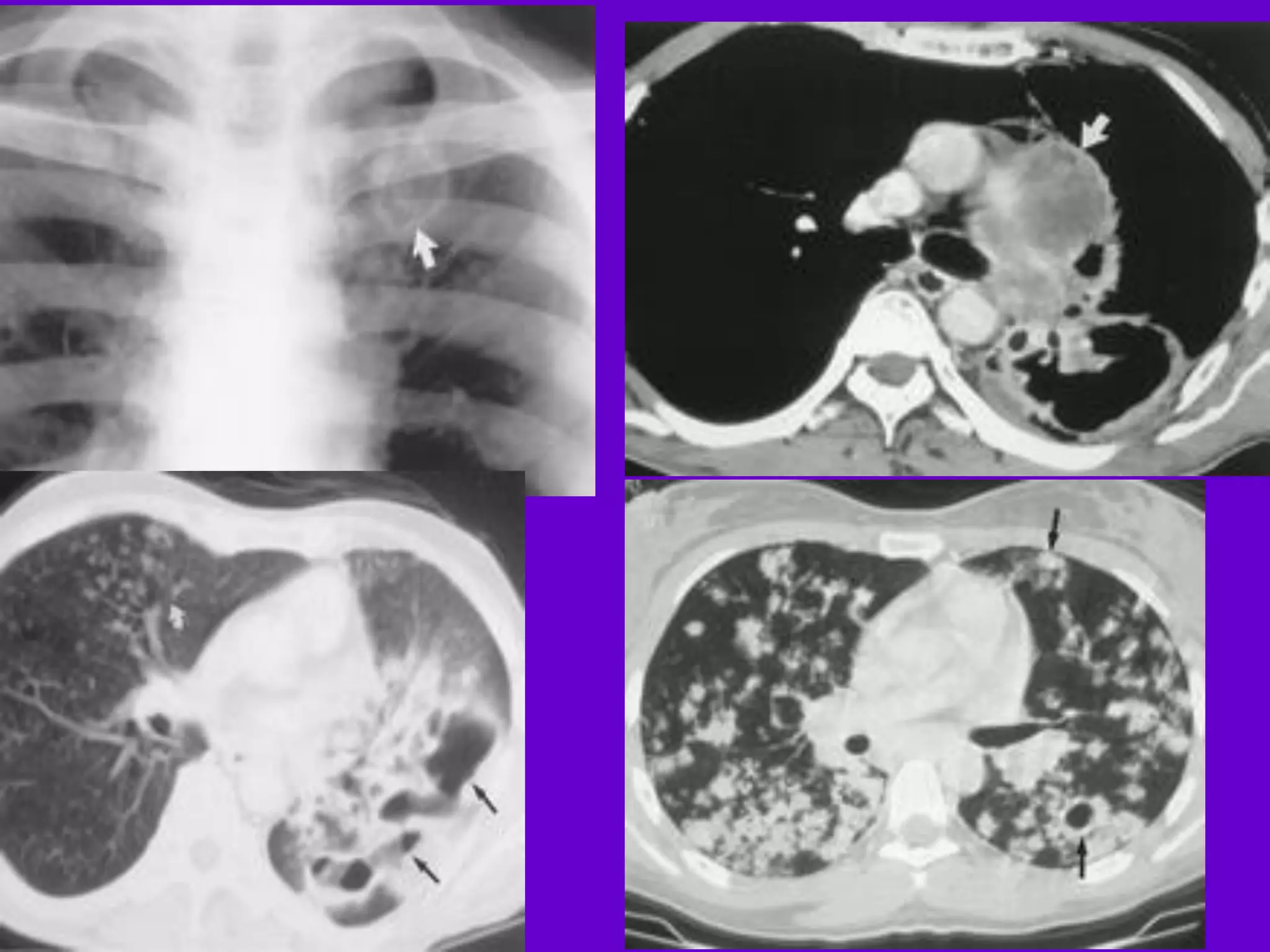
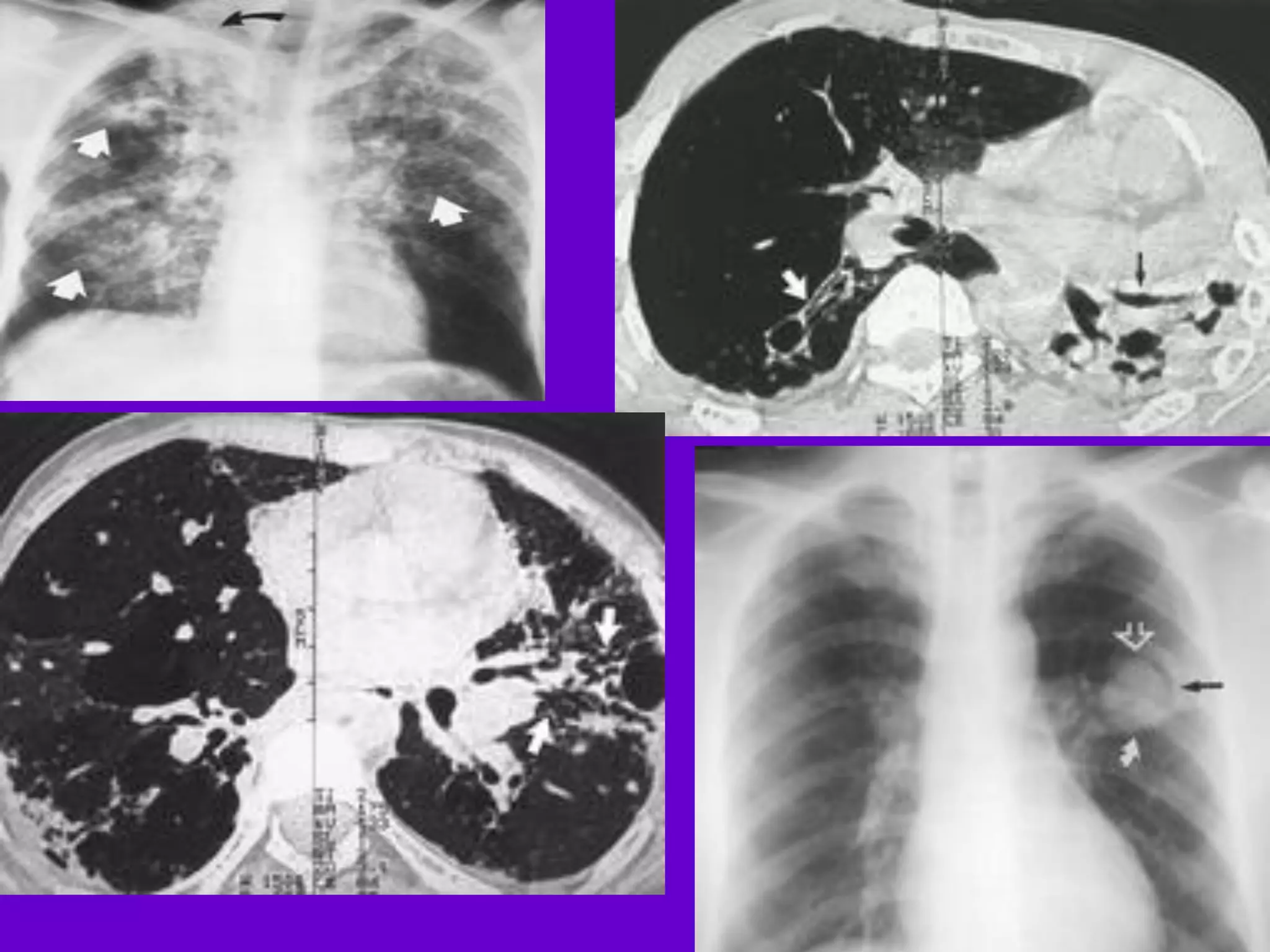
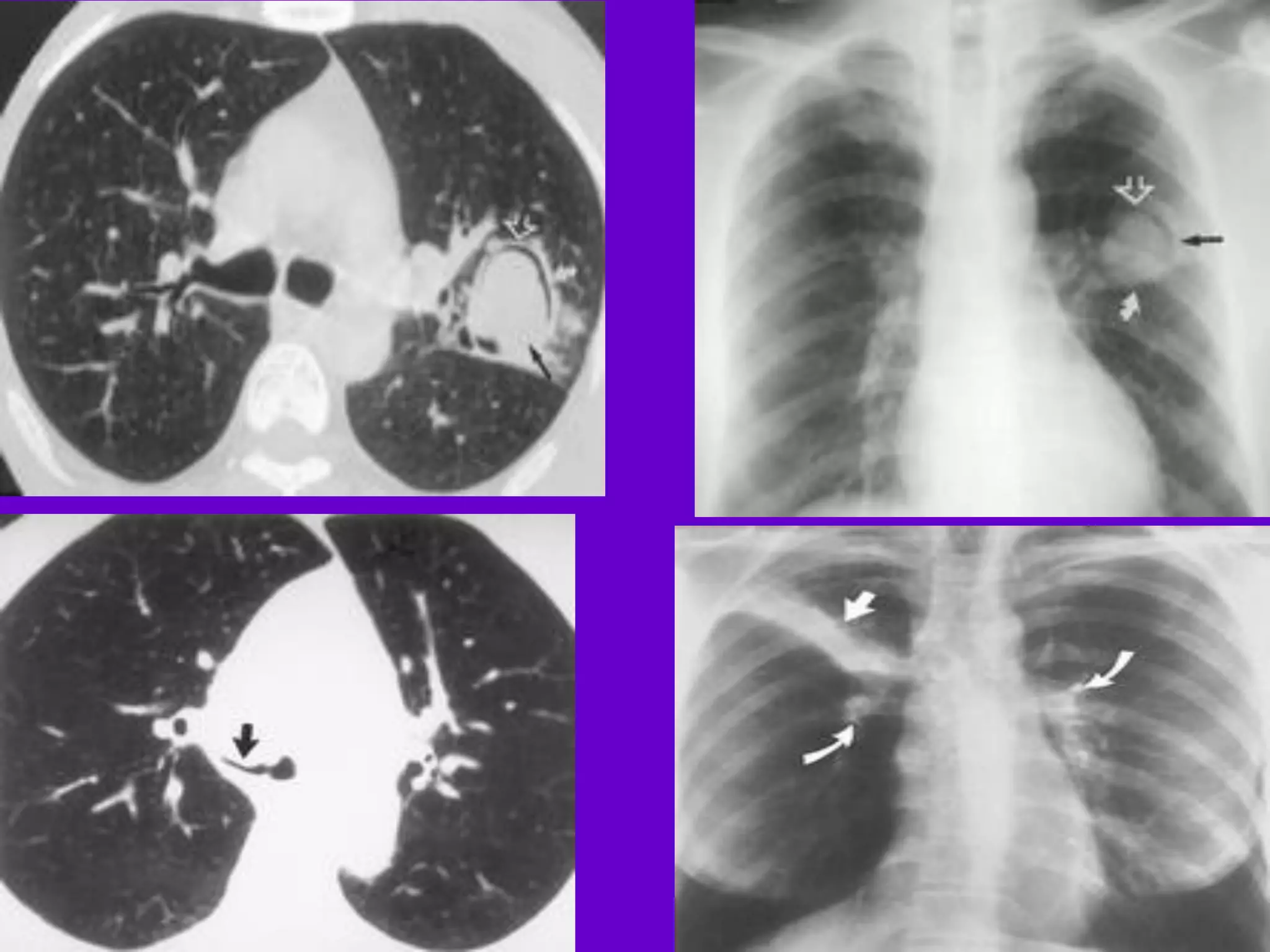
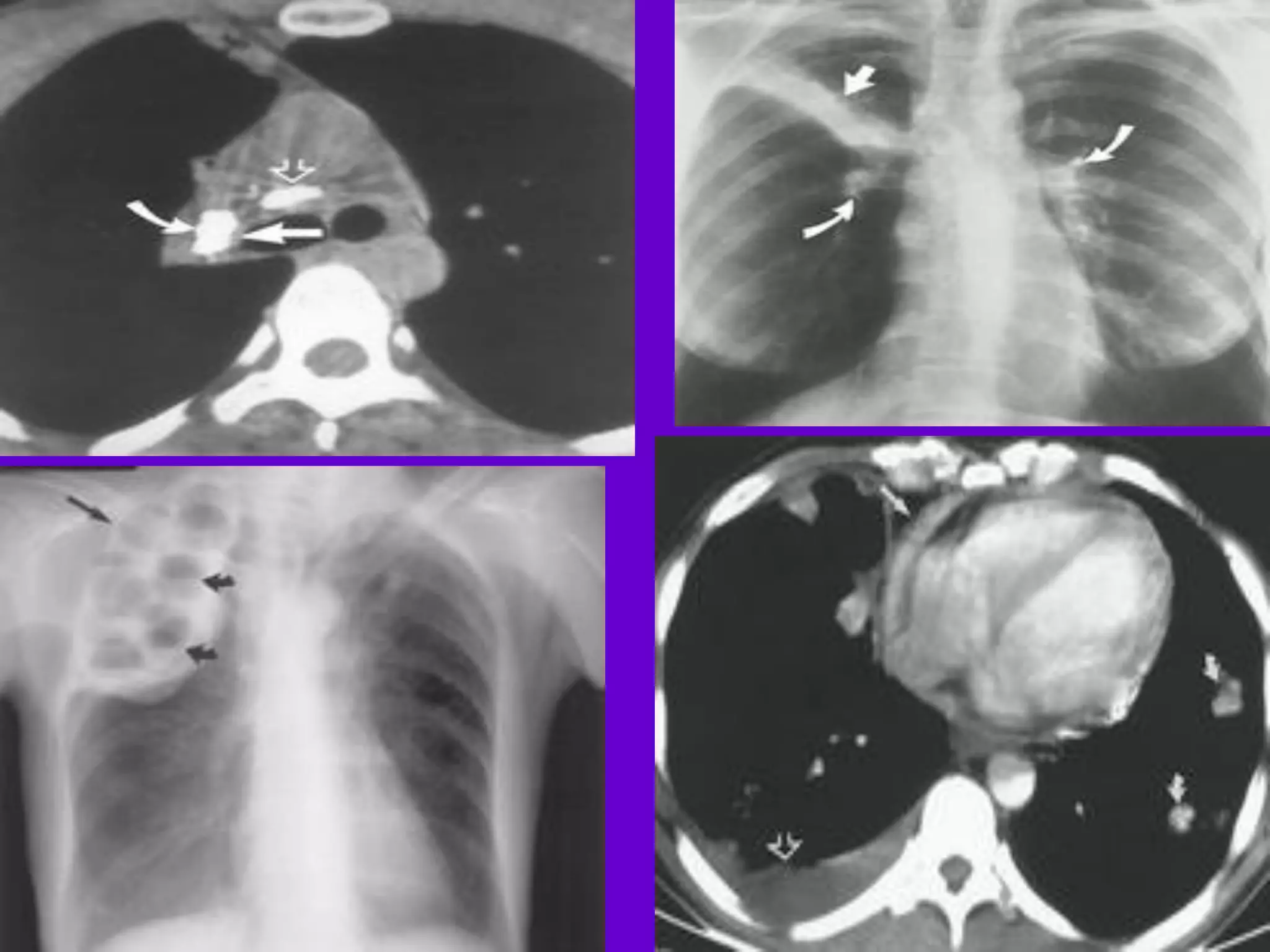
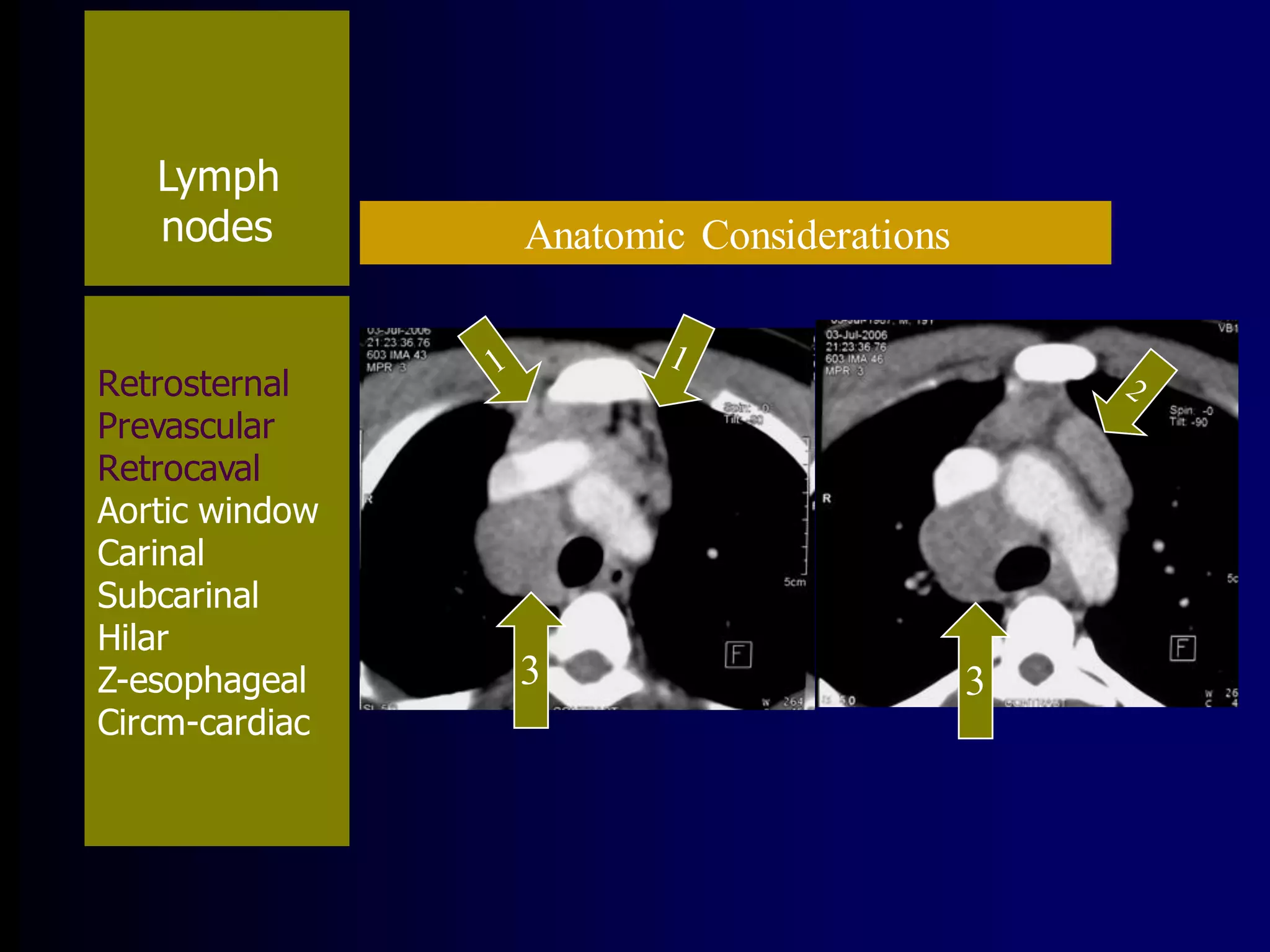
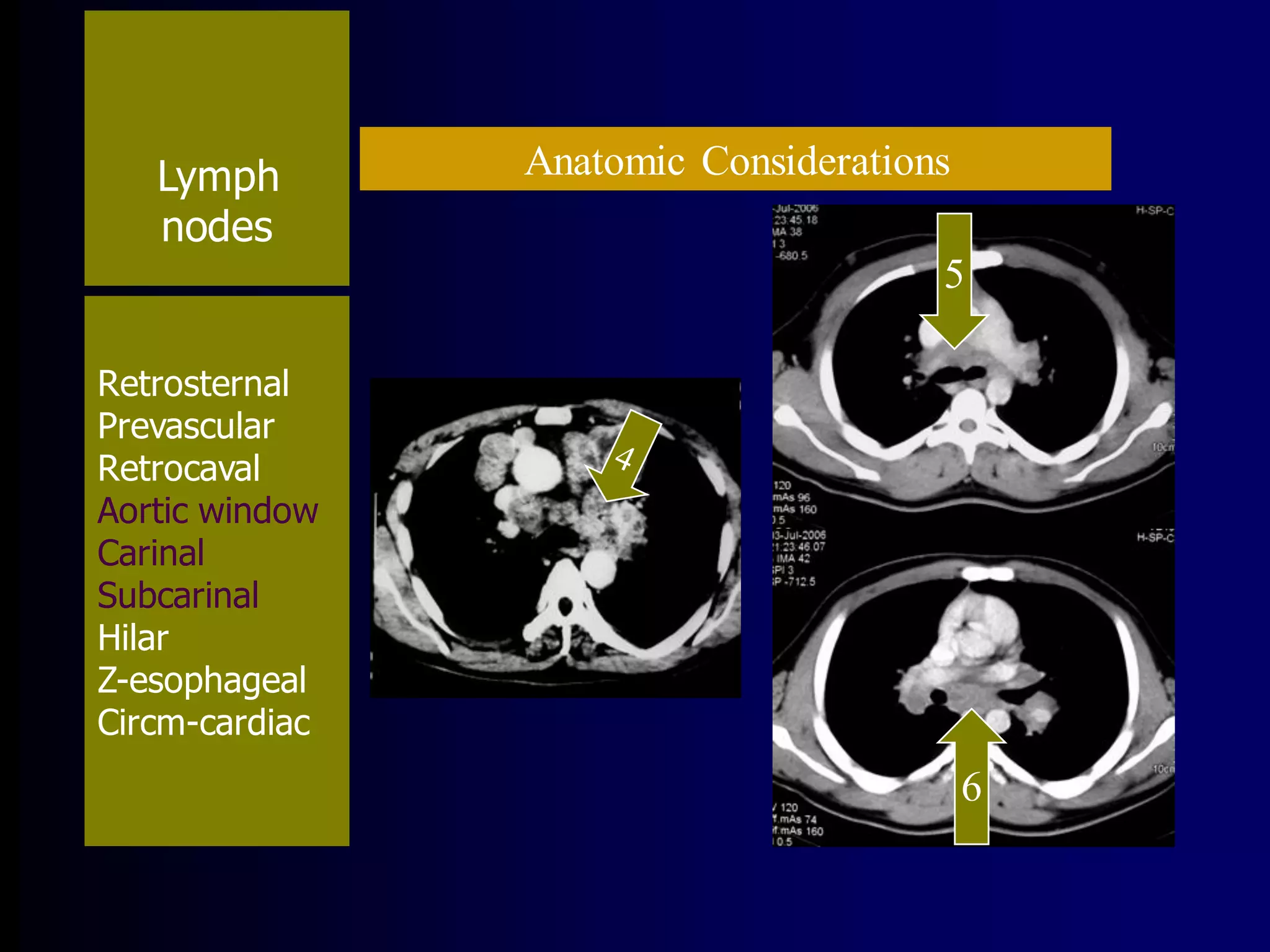
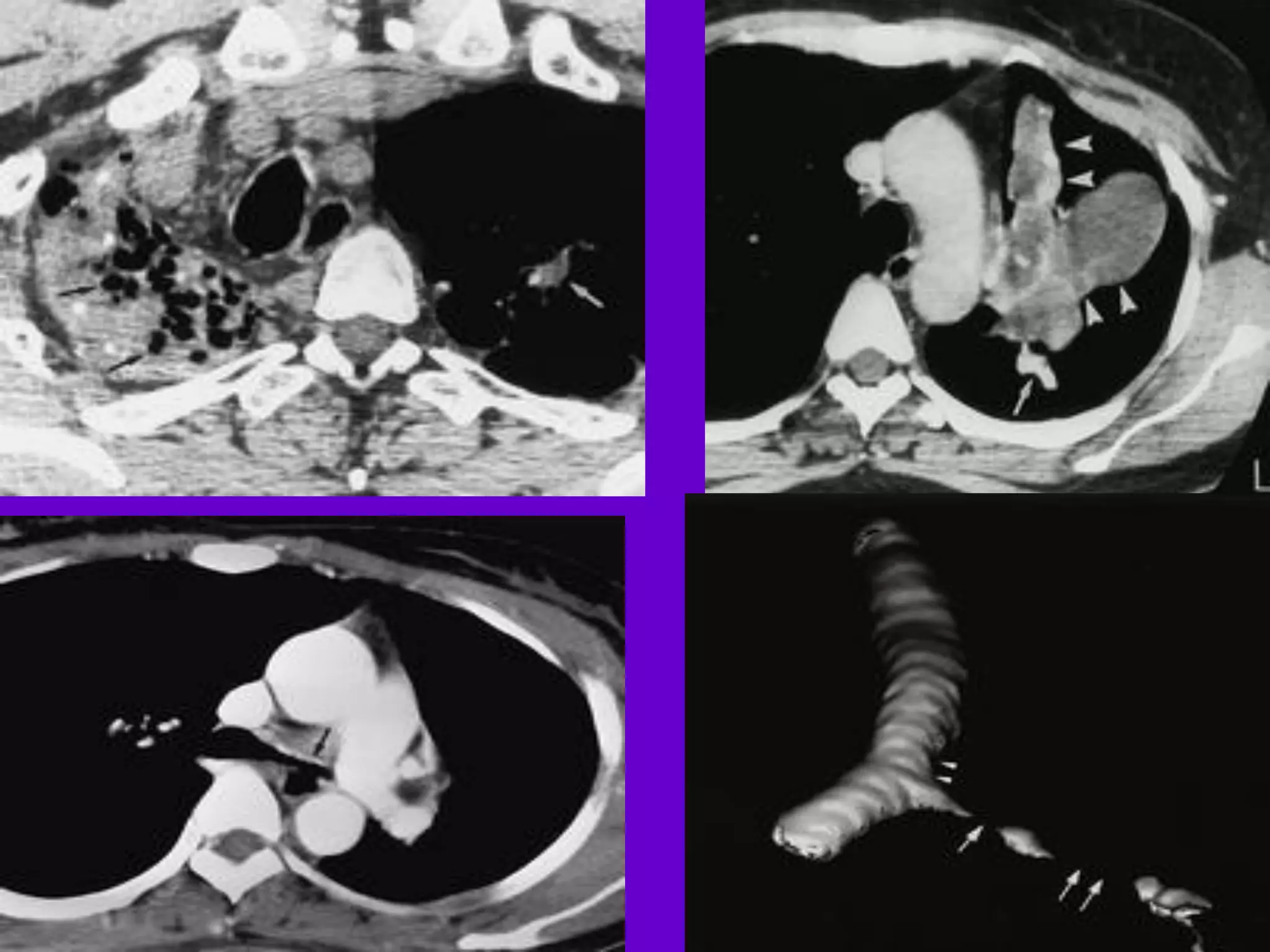
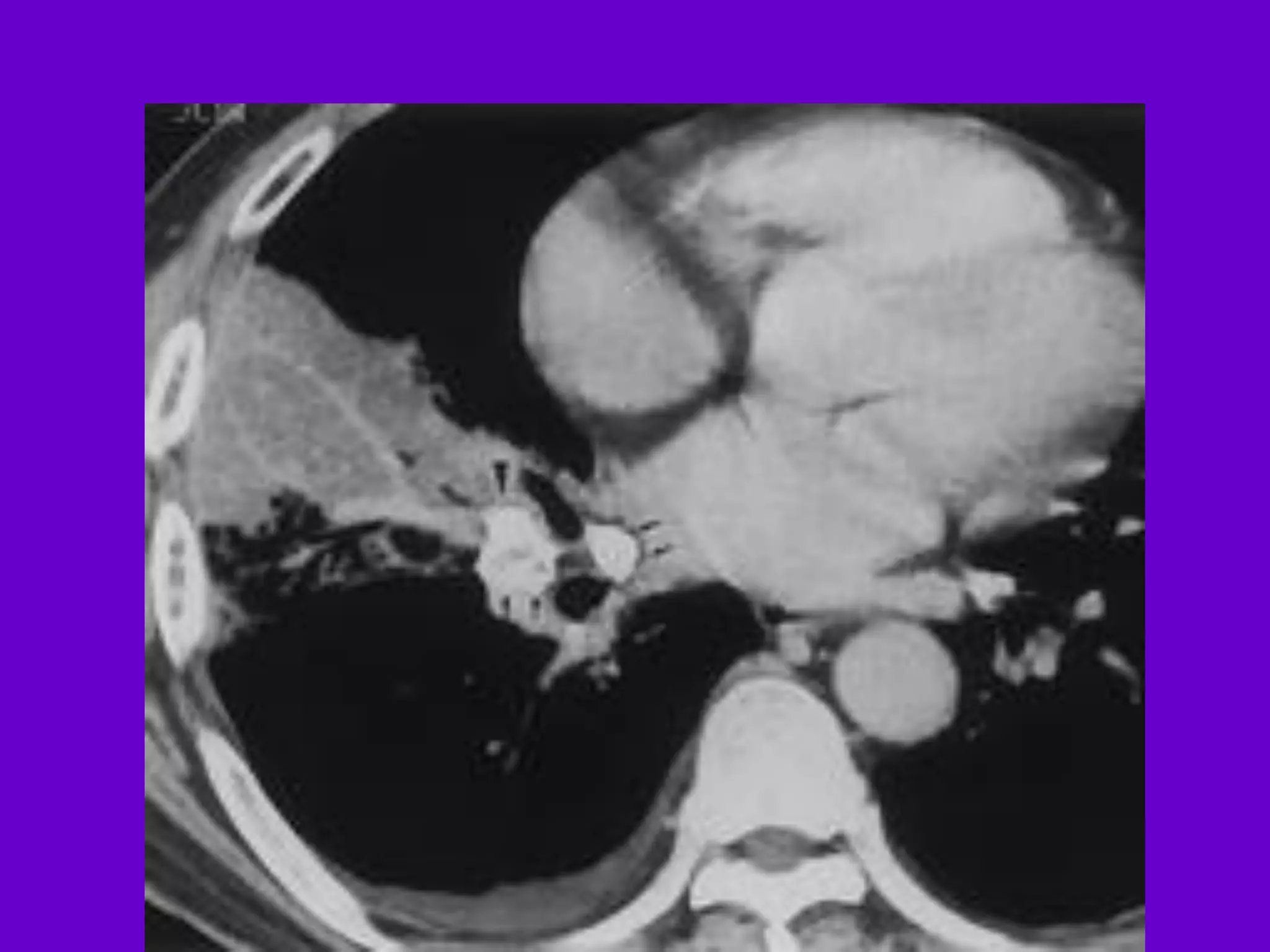
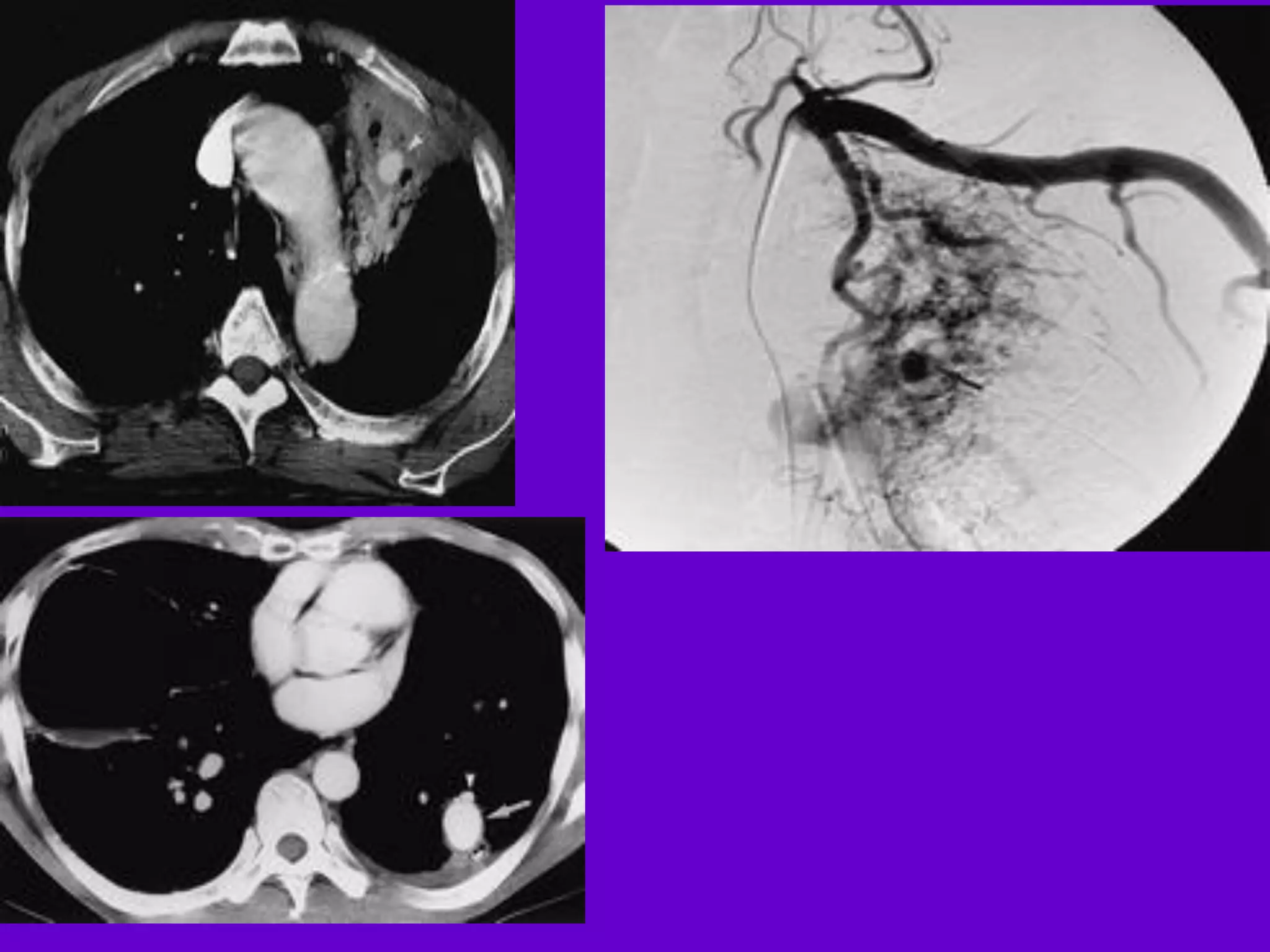
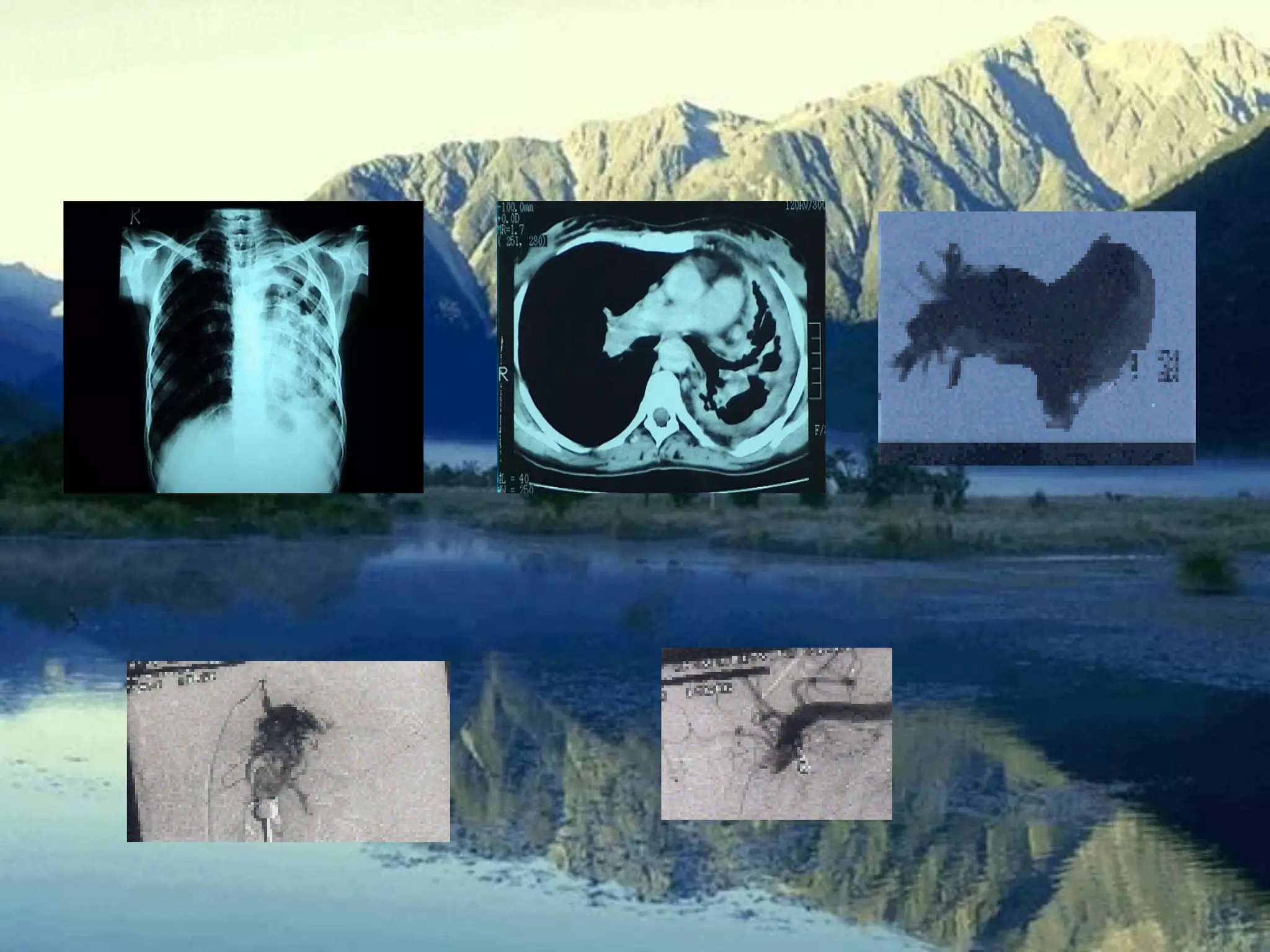
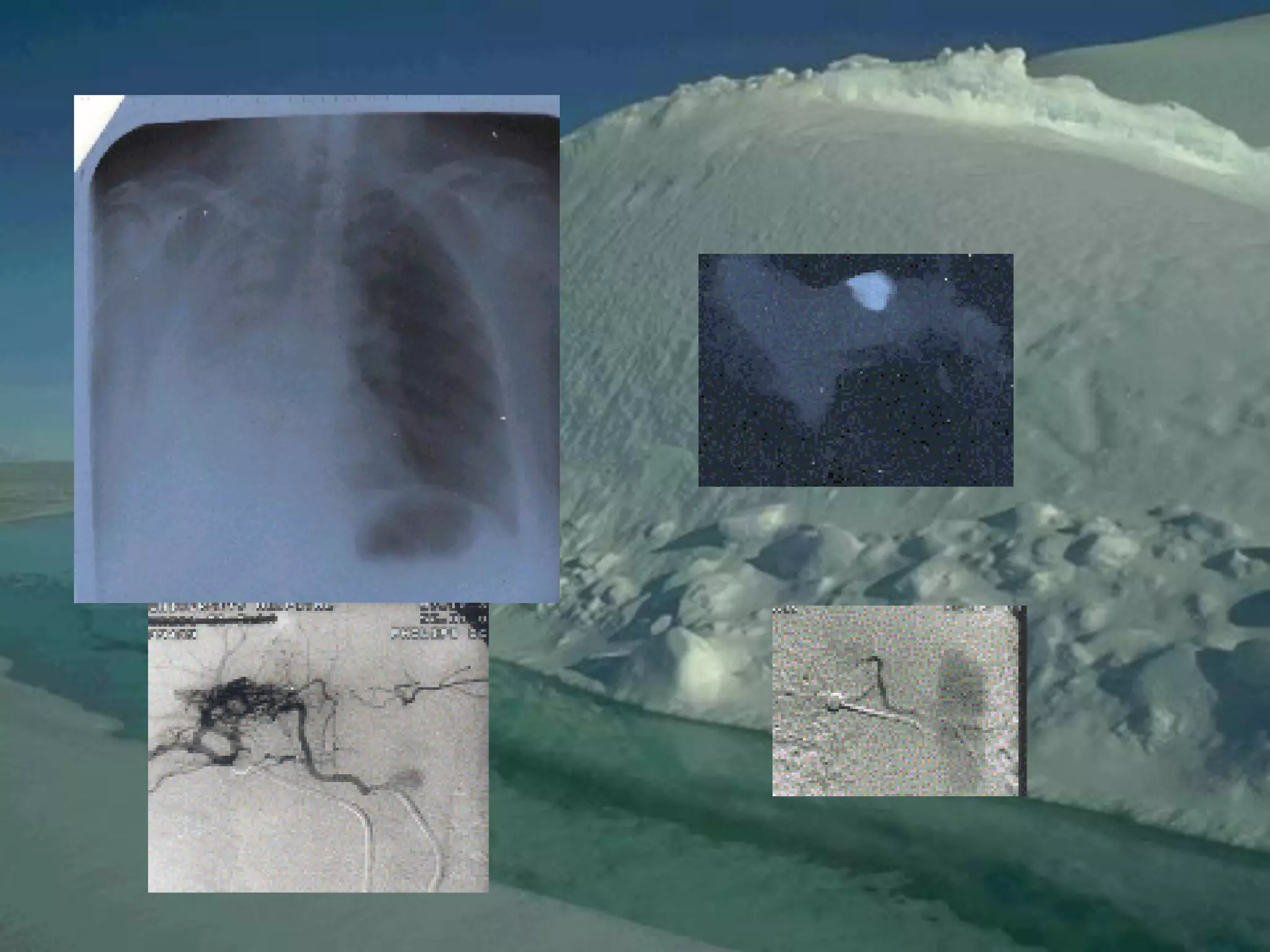
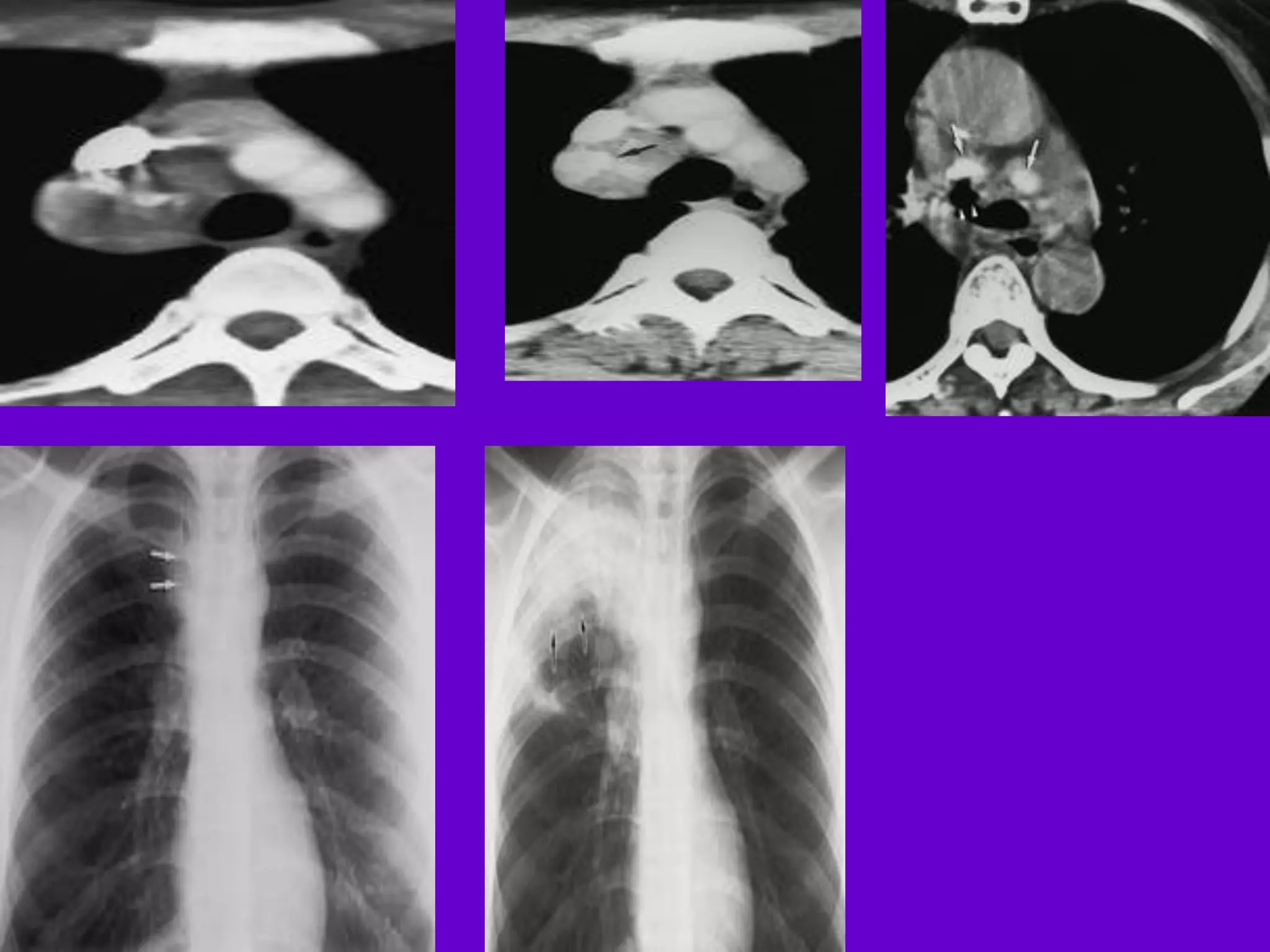
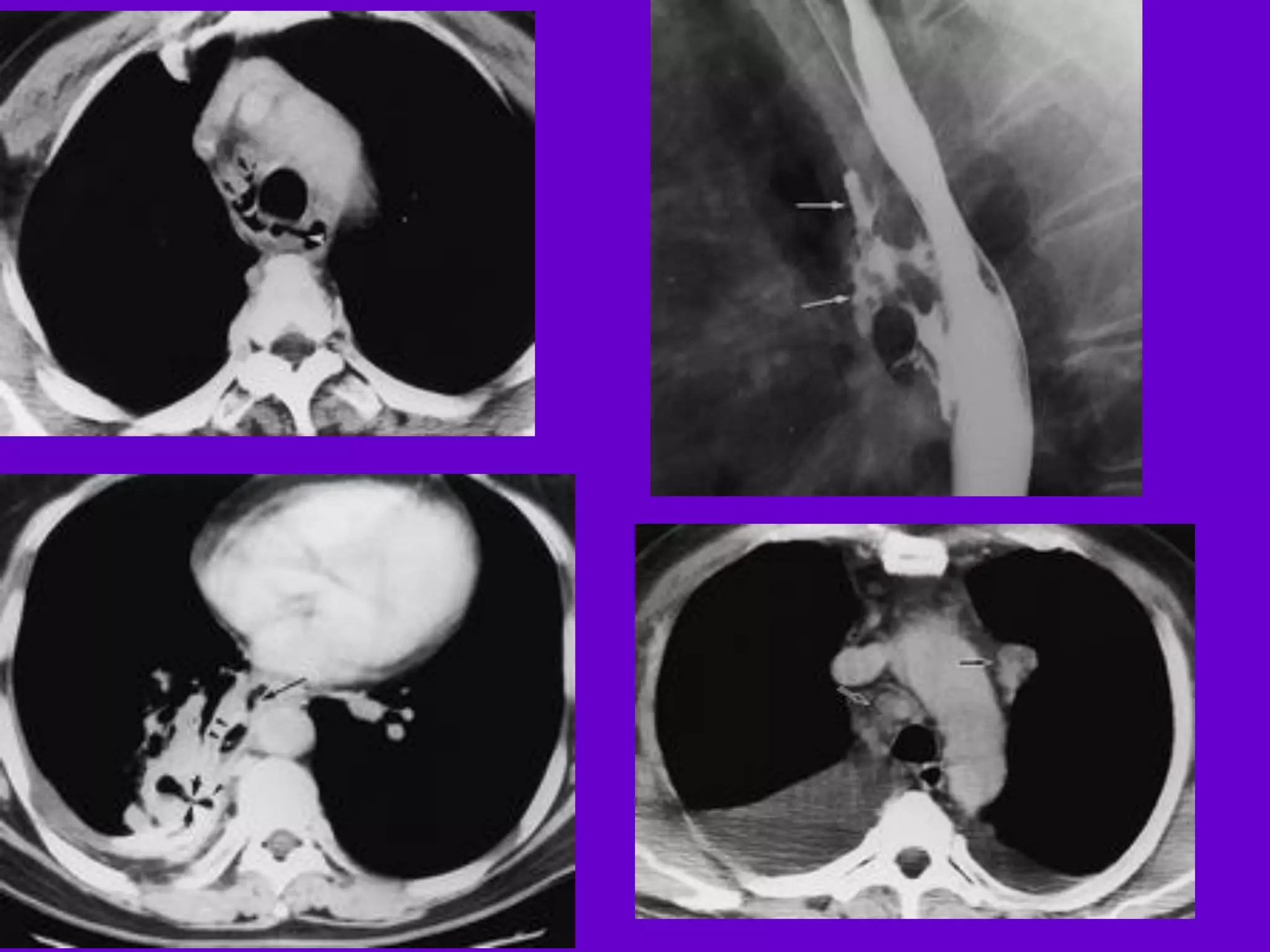
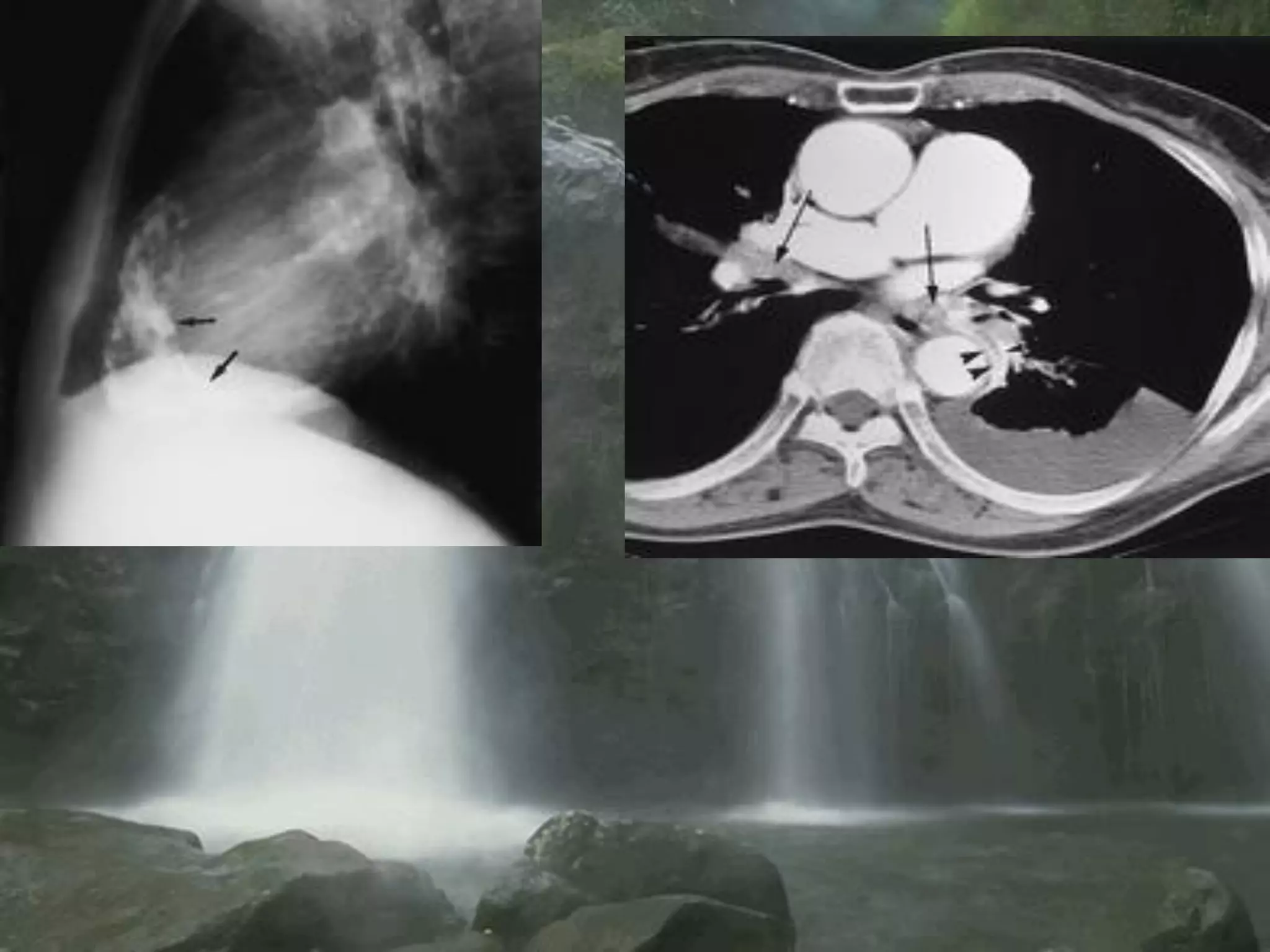
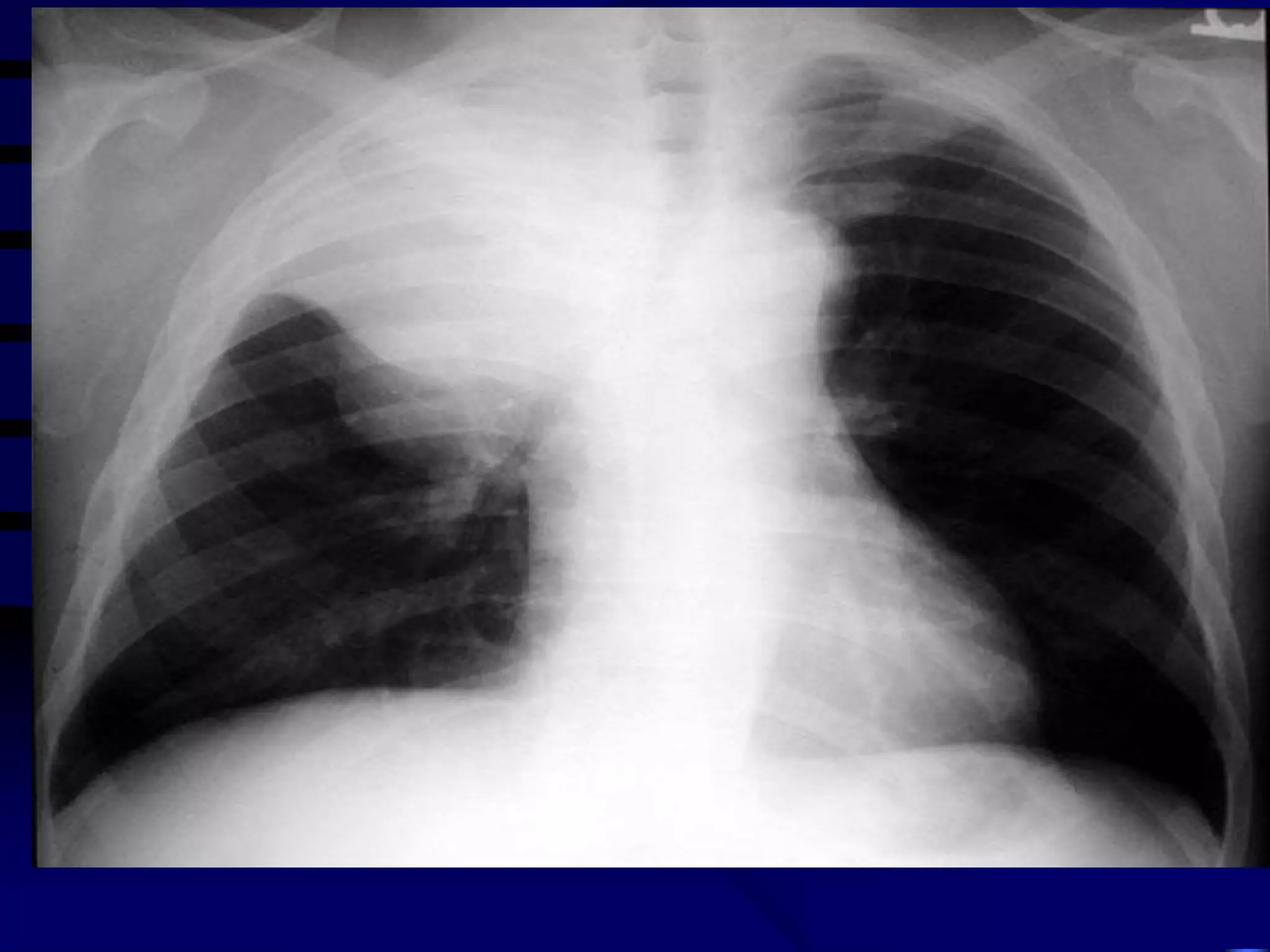
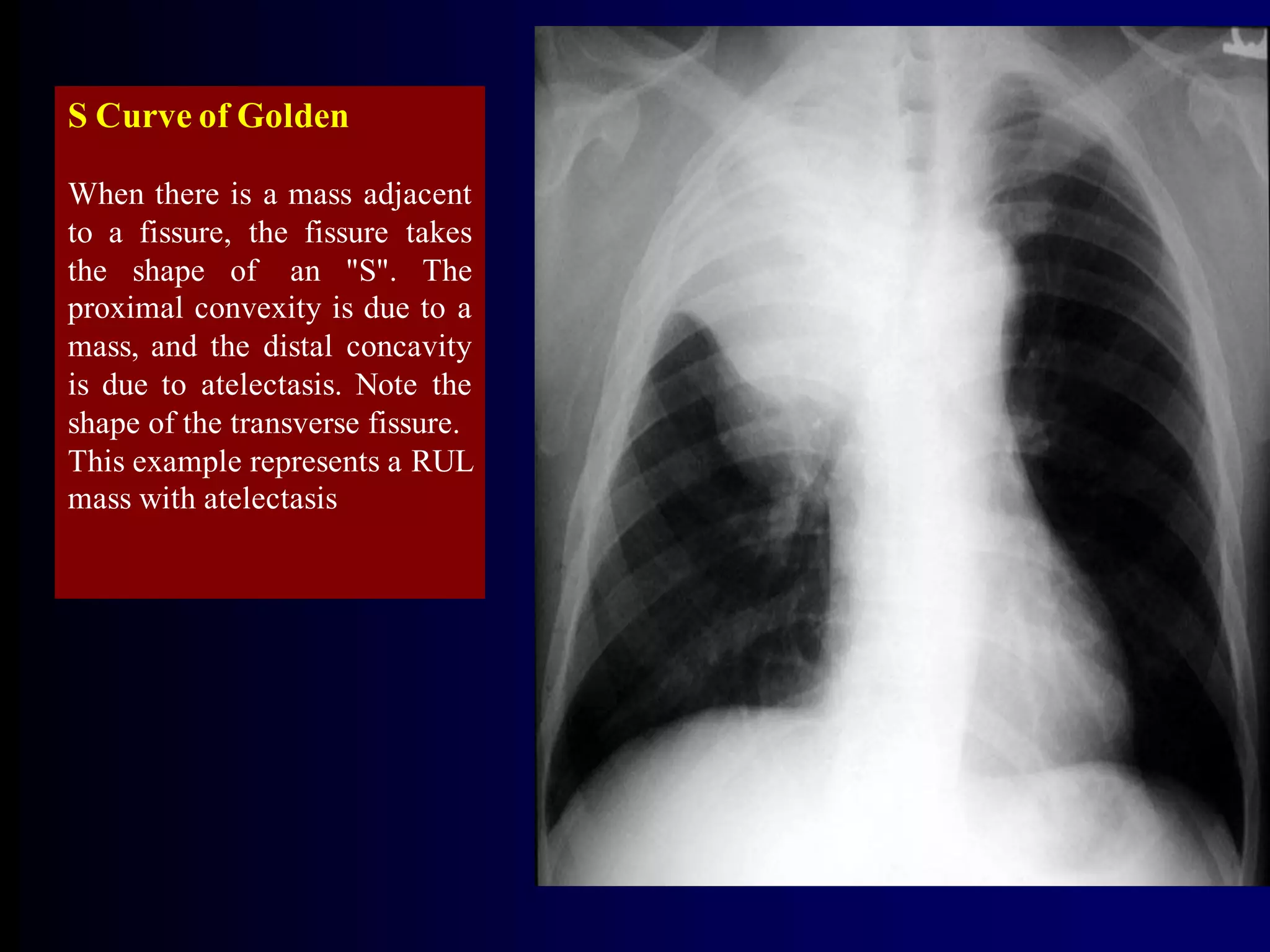
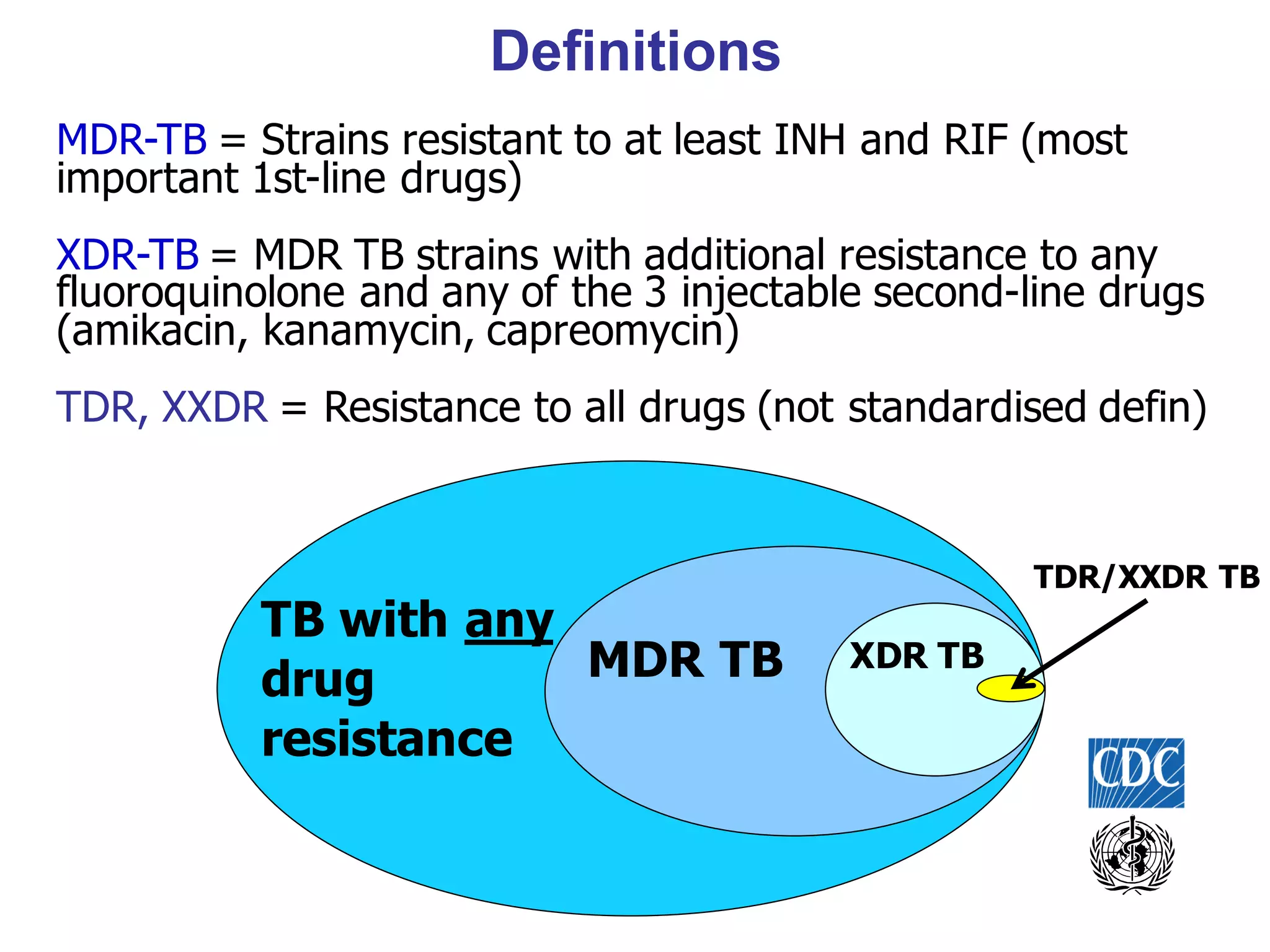
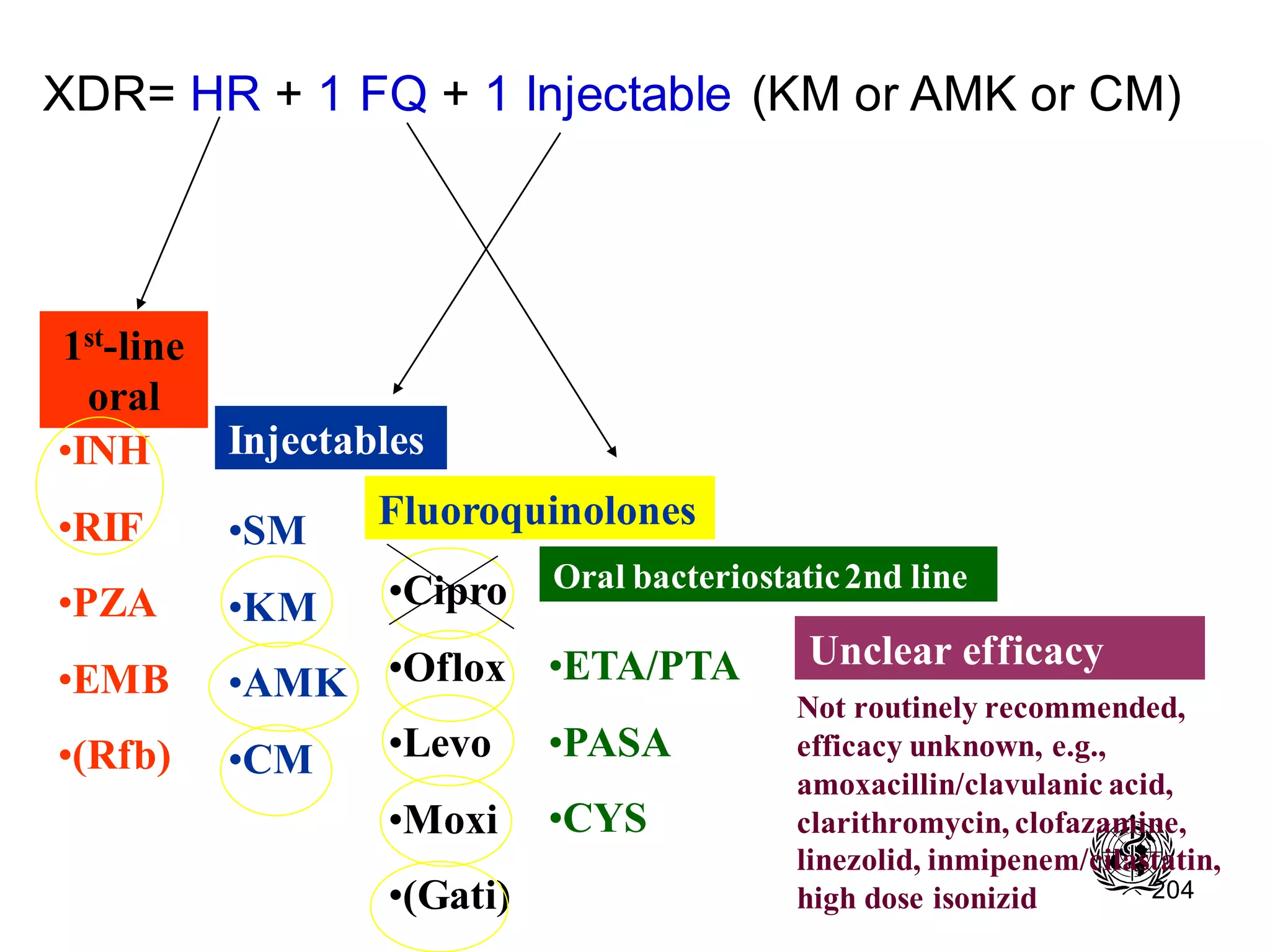
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that causes TB. Diagnosis involves acid-fast staining of sputum samples, sputum culture, imaging like chest x-rays, and PCR/NAT tests.
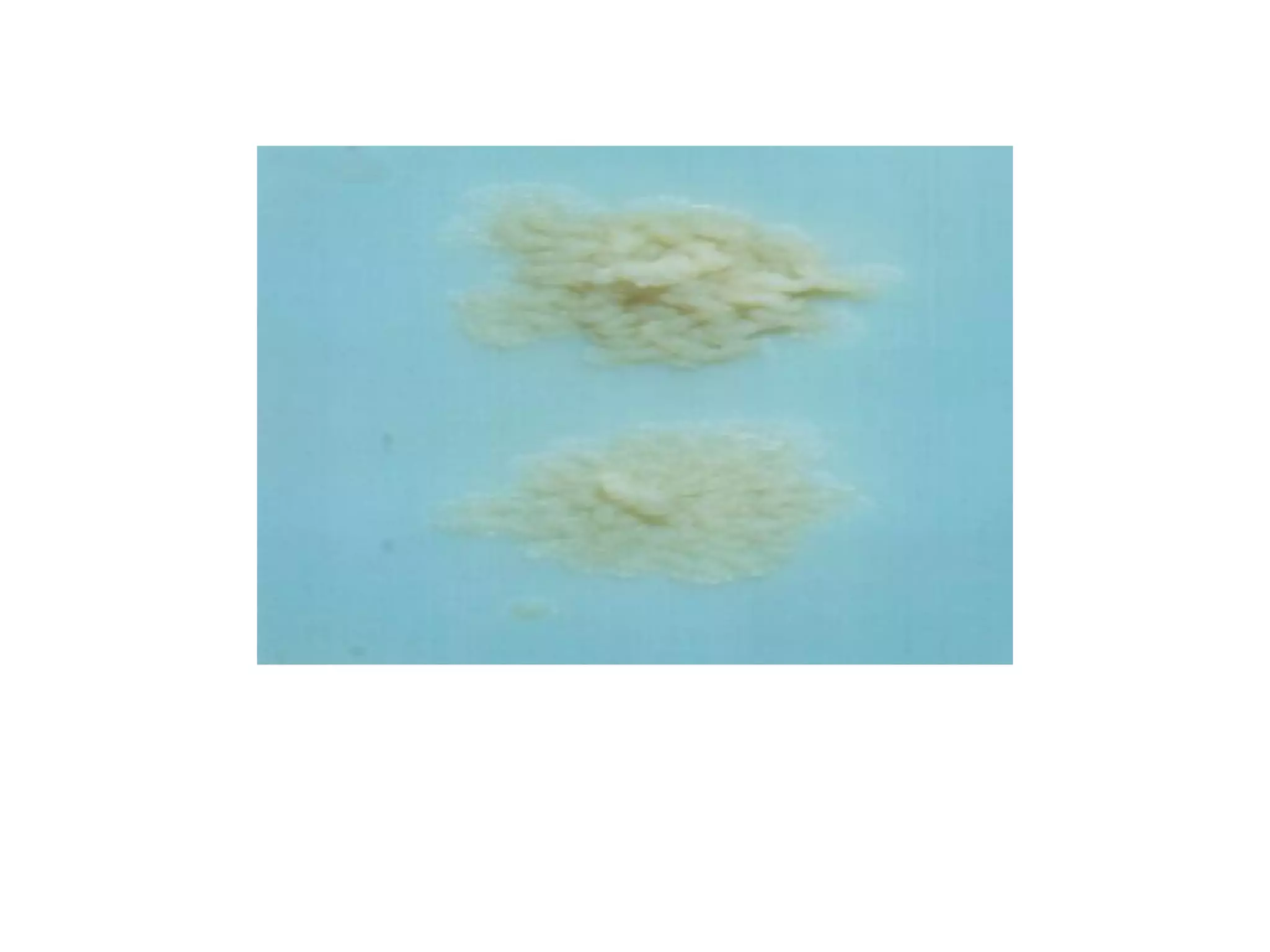
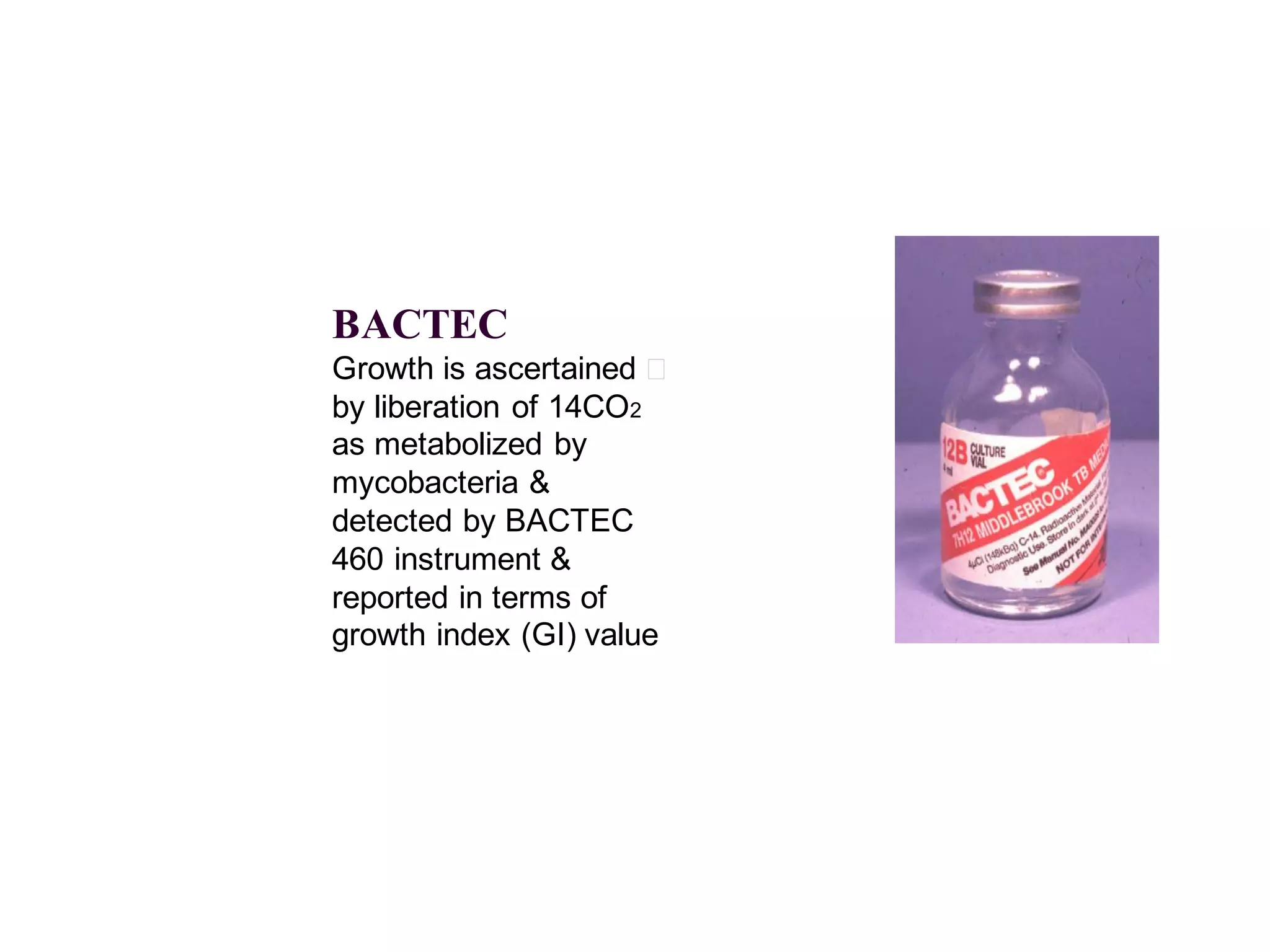
- Culture remains the gold standard for diagnosis and for determining drug susceptibility. Broth-based rapid culture methods like MGIT can detect M. tuberculosis in 10-12 days compared to 6-8 weeks for traditional methods.