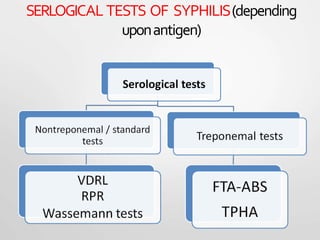
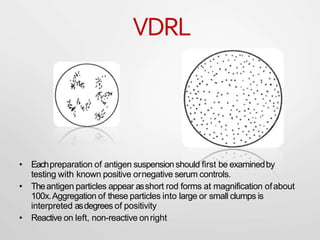
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is transmitted through direct contact with syphilis sores during sex, from mother to fetus, or rarely through blood transfusion. Syphilis has four stages - primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. The primary stage involves a painless sore called a chancre, while the secondary stage has diffuse symptoms like rash and fever. Without treatment, later stages can involve serious complications in multiple organ systems. Syphilis is diagnosed through clinical examination, dark-field microscopy of sores, and serological blood tests. Treatment involves antibiotics like penicillin or doxycycline.